Теорія комбінаторних ігор | Встановити 4 (Sprague - Grundy Theorem)
Передумови: Grundy Numbers/Numbers та MEX
Ми вже бачили в Set 2 (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/combinatorial-game-theory-set-2-game-nim/), що ми можемо знайти, хто виграє в грі в NIM, не граючи в гру.
Припустимо, ми трохи змінюємо класичну гру NIM. Цього разу кожен гравець може видалити лише 1 2 або 3 камені (і не будь -яка кількість каменів, як у класичній грі NIM). Чи можемо ми передбачити, хто переможе?
Так, ми можемо передбачити переможця за допомогою теореми Спраге-Грунд.
Що таке теорема Sprague-Grundy?
Припустимо, існує складна гра (більше однієї підгру), що складається з N підгемів, і два гравці A і B. Тоді теорема Спраге-Грунді каже, що якщо і і B грати оптимально (тобто вони не роблять помилок), то гравець, що починає спочатку, гарантується, якщо XOR xor grundy income ”у кожній підгоранню на початку гри не є азеро. В іншому випадку, якщо XOR оцінюється до нуля, то гравець A втратить, безумовно, незважаючи ні на що.
Як нанести теорему Sprague Grundy?
Ми можемо застосувати теорему Sprague-Grundy в будь-яку неупереджена гра і вирішити це. Основні кроки перераховані наступним чином:
- Розбийте складену гру на піджання.
- Потім для кожної підгру обчисліть Grundy Wum в цьому положенні.
- Потім обчисліть XOR всіх обчислених грандіозних чисел.
- Якщо значення XOR є ненульовим, то гравець, який збирається зробити поворот (перший гравець), виграє ще в іншому випадку, йому судилося втратити незалежно від того.
Приклад гра: Гра починається з 3 палі, що мають 3 4 та 5 каменів, а гравець для переміщення може зайняти будь -яку додаткову кількість каменів до 3 лише від будь -якого з палі [за умови, що в купі є велика кількість каменів]. Останній гравець, який рухається, перемагає. Який гравець виграє гру, припускаючи, що обидва гравці грають оптимально?
Як сказати, хто виграє, застосувавши теорему Спраге-Грундій?
Як ми бачимо, що ця гра сама складається з декількох підгоранів.
Перший крок: Підгри можна розглядати як кожен палі.
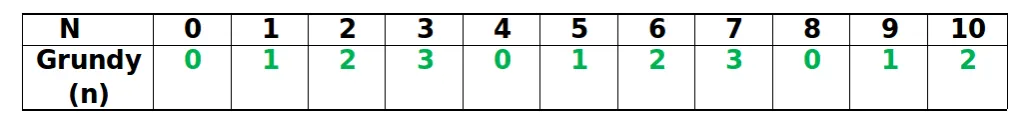
Другий крок: Ми бачимо з таблиці нижче
Grundy(3) = 3 Grundy(4) = 0 Grundy(5) = 1

Ми вже бачили, як обчислити грандіозні числа цієї гри в попередній стаття.
Третій крок: XOR 3 0 1 = 2
Четвертий крок: Оскільки XOR є ненульовим числом, то ми можемо сказати, що перший гравець переможе.
Нижче програма, яка реалізує вище 4 кроків.
C++ /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ #include using namespace std ; /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ #define PLAYER1 1 #define PLAYER2 2 // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set int calculateMex ( unordered_set < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . find ( Mex ) != Set . end ()) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy []) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != -1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); unordered_set < int > Set ; // A Hash Table for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . insert ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); } return ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main () { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = sizeof ( piles ) / sizeof ( piles [ 0 ]); // Find the maximum element int maximum = * max_element ( piles piles + n ); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [ maximum + 1 ]; memset ( Grundy -1 sizeof ( Grundy )); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ return ( 0 ); }
Java import java.util.* ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; static int PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < Integer > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy [] ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ] ); // A Hash Table HashSet < Integer > Set = new HashSet < Integer > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ] ); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]] ; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]] ; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = Arrays . stream ( piles ). max (). getAsInt (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [] = new int [ maximum + 1 ] ; Arrays . fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3 ''' Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing''' PLAYER1 = 1 PLAYER2 = 2 # A Function to calculate Mex of all # the values in that set def calculateMex ( Set ): Mex = 0 ; while ( Mex in Set ): Mex += 1 return ( Mex ) # A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' def calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ): Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ): return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A Hash Table Set = set () for i in range ( 1 4 ): Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )) # Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ) return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A function to declare the winner of the game def declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ): xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for i in range ( 1 n ): xorValue = ( xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]) if ( xorValue != 0 ): if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : # Test Case 1 piles = [ 3 4 5 ] n = len ( piles ) # Find the maximum element maximum = max ( piles ) # An array to cache the sub-problems so that # re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided Grundy = [ - 1 for i in range ( maximum + 1 )]; # Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for i in range ( n ): calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); ''' Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); ''' # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# using System ; using System.Linq ; using System.Collections.Generic ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; //static int PLAYER2 = 2; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . Contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int [] Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table HashSet < int > Set = new HashSet < int > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . Add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int [] piles int [] Grundy int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code static void Main () { // Test Case 1 int [] piles = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . Length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = piles . Max (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int [] Grundy = new int [ maximum + 1 ]; Array . Fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by mits
JavaScript < script > /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ let PLAYER1 = 1 ; let PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set function calculateMex ( Set ) { let Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . has ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' function calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table let Set = new Set (); for ( let i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game function declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ) { let xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); } return ; } // Driver code // Test Case 1 let piles = [ 3 4 5 ]; let n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element let maximum = Math . max (... piles ) // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided let Grundy = new Array ( maximum + 1 ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < maximum + 1 ; i ++ ) Grundy [ i ] = 0 ; // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( let i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 < /script>
Вихід:
Player 1 will win
Складність часу: O (n^2), де n - максимальна кількість каменів у купі.
Складність космосу: O (n), оскільки Grundy Array використовується для зберігання результатів субпроблем, щоб уникнути зайвих обчислень, і він займає O (n) місця.
Список літератури:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/sprague%E2%80%93grundy_theorem
Вправа до читачів: Розглянемо нижче гру.
Гра грає два гравці з N цілими чиселами A1 A2 .. An. На його повороті гравець вибирає ціле число розділяє його на 2 3 або 6, а потім бере підлогу. Якщо ціле число стає 0, воно видаляється. Останній гравець, який рухається, перемагає. Який гравець виграє гру, якщо обидва гравці грають оптимально?
Підказка: див. Приклад 3 попередній стаття.