Python'da XML ayrıştırma
Bu makale, belirli bir XML dosyasının nasıl ayrıştırılabileceğine ve ondan bazı yararlı verilerin yapılandırılmış bir şekilde nasıl çıkarılabileceğine odaklanmaktadır. XML: XML, Genişletilebilir İşaretleme Dili anlamına gelir. Verileri depolamak ve taşımak için tasarlandı. Hem insan hem de makine tarafından okunabilecek şekilde tasarlandı. Bu nedenle XML'in tasarım hedefleri basitliği, genelliği ve İnternet genelinde kullanılabilirliği vurgular. Bu eğitimde ayrıştırılacak XML dosyası aslında bir RSS beslemesidir. RSS: RSS (Genellikle Gerçekten Basit Dağıtım olarak adlandırılan Zengin Site Özeti), blog girişleri, haber başlıkları, sesli video gibi sık sık güncellenen bilgileri yayınlamak için standart web besleme formatlarından oluşan bir aileyi kullanır. RSS, XML formatlı düz metindir.
- RSS formatının hem otomatik süreçler hem de insanlar tarafından okunması nispeten kolaydır.
- Bu eğitimde işlenen RSS, popüler bir haber web sitesinden en önemli haberlerin RSS beslemesidir. Kontrol edebilirsin Burada . Amacımız bu RSS beslemesini (veya XML dosyasını) işleyip ileride kullanmak üzere başka bir formatta kaydetmektir.
#Python code to illustrate parsing of XML files # importing the required modules import csv import requests import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET def loadRSS (): # url of rss feed url = 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rss/topnews/rssfeed.xml' # creating HTTP response object from given url resp = requests . get ( url ) # saving the xml file with open ( 'topnewsfeed.xml' 'wb' ) as f : f . write ( resp . content ) def parseXML ( xmlfile ): # create element tree object tree = ET . parse ( xmlfile ) # get root element root = tree . getroot () # create empty list for news items newsitems = [] # iterate news items for item in root . findall ( './channel/item' ): # empty news dictionary news = {} # iterate child elements of item for child in item : # special checking for namespace object content:media if child . tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss' : news [ 'media' ] = child . attrib [ 'url' ] else : news [ child . tag ] = child . text . encode ( 'utf8' ) # append news dictionary to news items list newsitems . append ( news ) # return news items list return newsitems def savetoCSV ( newsitems filename ): # specifying the fields for csv file fields = [ 'guid' 'title' 'pubDate' 'description' 'link' 'media' ] # writing to csv file with open ( filename 'w' ) as csvfile : # creating a csv dict writer object writer = csv . DictWriter ( csvfile fieldnames = fields ) # writing headers (field names) writer . writeheader () # writing data rows writer . writerows ( newsitems ) def main (): # load rss from web to update existing xml file loadRSS () # parse xml file newsitems = parseXML ( 'topnewsfeed.xml' ) # store news items in a csv file savetoCSV ( newsitems 'topnews.csv' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : # calling main function main ()
Above code will: - Belirtilen URL'den RSS beslemesini yükleyin ve XML dosyası olarak kaydedin.
- Haberleri, her sözlüğün tek bir haber öğesi olduğu bir sözlük listesi olarak kaydetmek için XML dosyasını ayrıştırın.
- Haber öğelerini bir CSV dosyasına kaydedin.
- Yukarıdaki örnekte kullanılan haber sitesinin daha fazla rss beslemesine göz atabilirsiniz. Diğer rss akışlarını da ayrıştırarak yukarıdaki örneğin genişletilmiş bir sürümünü oluşturmayı deneyebilirsiniz.
- Kriket hayranı mısınız? Daha sonra Bu rss beslemesi ilginizi çekmelidir! Canlı kriket maçları hakkındaki bilgileri almak için bu XML dosyasını ayrıştırabilir ve bir masaüstü bildirimi yapmak için kullanabilirsiniz!
def loadRSS(): # url of rss feed url = 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rss/topnews/rssfeed.xml' # creating HTTP response object from given url resp = requests.get(url) # saving the xml file with open('topnewsfeed.xml' 'wb') as f: f.write(resp.content) Here we first created a HTTP response object by sending an HTTP request to the URL of the RSS feed. The content of response now contains the XML file data which we save as topnewsfeed.xml yerel rehberimizde. İstek modülünün nasıl çalıştığı hakkında daha fazla bilgi için şu makaleyi izleyin: Python kullanarak GET ve POST istekleri  Burada kullanıyoruz xml.etree.ElementTree (kısaca ET olarak adlandırın) modülü. Element Ağacı'nın bu amaç için iki sınıfı vardır: Element Ağacı XML belgesinin tamamını bir ağaç olarak temsil eder ve Öğe bu ağaçtaki tek bir düğümü temsil eder. Belgenin tamamıyla etkileşimler (dosyalara okuma ve dosyalardan yazma) genellikle Element Ağacı seviye. Tek bir XML öğesi ve onun alt öğeleriyle etkileşimler, Öğe seviye. Tamam öyleyse hadi üzerinden geçelim ayrıştırmaXML() function now:
Burada kullanıyoruz xml.etree.ElementTree (kısaca ET olarak adlandırın) modülü. Element Ağacı'nın bu amaç için iki sınıfı vardır: Element Ağacı XML belgesinin tamamını bir ağaç olarak temsil eder ve Öğe bu ağaçtaki tek bir düğümü temsil eder. Belgenin tamamıyla etkileşimler (dosyalara okuma ve dosyalardan yazma) genellikle Element Ağacı seviye. Tek bir XML öğesi ve onun alt öğeleriyle etkileşimler, Öğe seviye. Tamam öyleyse hadi üzerinden geçelim ayrıştırmaXML() function now: tree = ET.parse(xmlfile)Here we create an Element Ağacı iletilenleri ayrıştırarak nesne xmlfile.xml dosyası
root = tree.getroot()rootlanmış() fonksiyon kökünü döndürür ağaç olarak Öğe object.
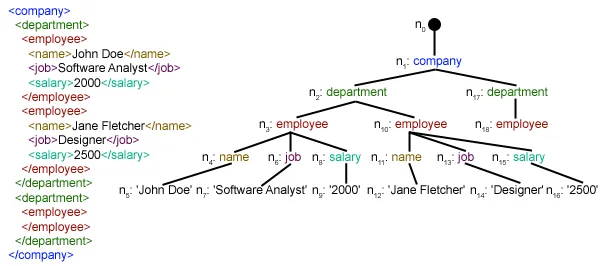
for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): Now once you have taken a look at the structure of your XML file you will notice that we are interested only in öğe eleman. ./kanal/öğe aslında XPath sözdizimi (XPath, bir XML belgesinin bölümlerini adreslemek için kullanılan bir dildir). Burada hepsini bulmak istiyoruz öğe torunları kanal çocukları kök ('.' ile gösterilir) öğesi. Desteklenen XPath sözdizimi hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinebilirsiniz Burada . for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): # empty news dictionary news = {} # iterate child elements of item for child in item: # special checking for namespace object content:media if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] else: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') # append news dictionary to news items list newsitems.append(news) Now we know that we are iterating through öğe elemanların her biri öğe öğesi bir haber içeriyor. Böylece boş bir alan oluşturuyoruz haberler dictionary in which we will store all data available about news item. To iterate though each child element of an element we simply iterate through it like this: for child in item:Now notice a sample item element here:
 We will have to handle namespace tags separately as they get expanded to their original value when parsed. So we do something like this:
We will have to handle namespace tags separately as they get expanded to their original value when parsed. So we do something like this: if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] çocuk.attrib Bir elemente ilişkin tüm niteliklerin sözlüğüdür. Burada ilgilendiğimiz URL niteliği medya:içerik namespace tag. Now for all other children we simply do: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') çocuk.etiketi alt öğenin adını içerir. çocuk.metin stores all the text inside that child element. So finally a sample item element is converted to a dictionary and looks like this: {'description': 'Ignis has a tough competition already from Hyun.... 'guid': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/autos/maruti-ignis-launch.... 'link': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/autos/maruti-ignis-launch.... 'media': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rf/image_size_630x354/HT/... 'pubDate': 'Thu 12 Jan 2017 12:33:04 GMT ' 'title': 'Maruti Ignis launches on Jan 13: Five cars that threa..... } Then we simply append this dict element to the list yeni siteler . Sonunda bu liste döndürülür.  Gördüğünüz gibi hiyerarşik XML dosyası verileri basit bir CSV dosyasına dönüştürüldü, böylece tüm haberler bir tablo biçiminde saklandı. Bu, veritabanını genişletmeyi de kolaylaştırır. Ayrıca JSON benzeri veriler doğrudan uygulamalarında kullanılabilir! Bu, genel bir API sağlamayan ancak bazı RSS beslemeleri sağlayan web sitelerinden veri çıkarmak için en iyi alternatiftir. Yukarıdaki makalede kullanılan tüm kod ve dosyaları bulabilirsiniz Burada . Sırada ne var?
Gördüğünüz gibi hiyerarşik XML dosyası verileri basit bir CSV dosyasına dönüştürüldü, böylece tüm haberler bir tablo biçiminde saklandı. Bu, veritabanını genişletmeyi de kolaylaştırır. Ayrıca JSON benzeri veriler doğrudan uygulamalarında kullanılabilir! Bu, genel bir API sağlamayan ancak bazı RSS beslemeleri sağlayan web sitelerinden veri çıkarmak için en iyi alternatiftir. Yukarıdaki makalede kullanılan tüm kod ve dosyaları bulabilirsiniz Burada . Sırada ne var?