Java'da Java.io.LineNumberInputStream Sınıfı
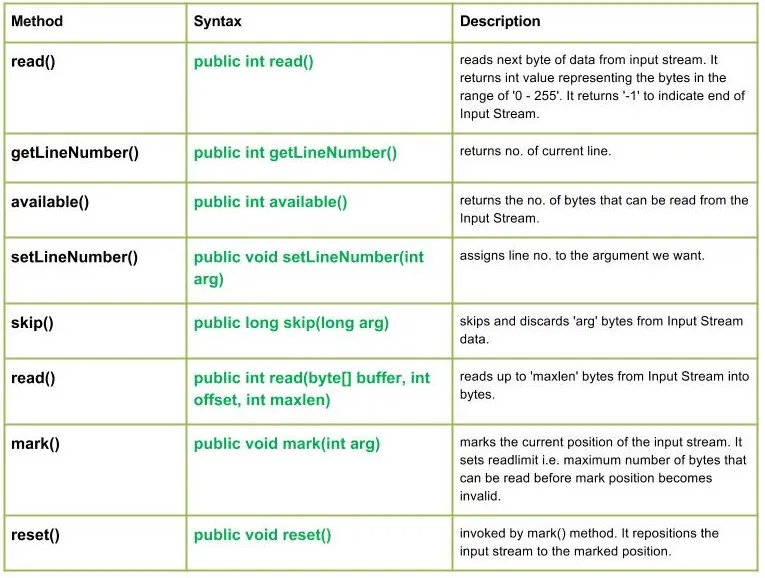
java.io.LineNumberInputStream sınıfı, mevcut satır numarasının kaydını tutmak için ekstra bir kolaylık sağlayan giriş akışının basit bir uzantısıdır.
Astar 'r' ile biten bir bayt dizisidir, yani bir satırbaşı karakteri veya yeni satır karakteri : 'n' veya satırbaşı karakterini takip eden bir satır besleme karakteri.
Beyan:
public class LineNumberInputStream extends Reader
Yapıcılar:
LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) : Constructs a newline no. stream that reads it's input from the specified Input Stream.
Yöntemler:
Sözdizimi:
public int read() Parameters : ------- Return : int value representing the bytes in the range of '0 - 255'. return -1 indicating end of Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Uygulama :
Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Not :
Çevrimiçi IDE'deki herhangi bir dosyaya erişemediğimiz için aşağıdaki Java Kodu burada çalışmayacaktır.
Yani programı sisteminize kopyalayın ve orada çalıştırın.
ABC.txt Programda kullanılan dosya şunları içerir:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Çıkış :
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Sözdizimi:
public int getLineNumber() Parameters : ------- Return : no. of current line
Uygulama :
Java // Java program illustrating the working of getLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of getLineNumber() : to print line no. a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( ' At line : ' + a ); System . out . print ( c ); } a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( ' at line: ' + a ); } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Not :
Çevrimiçi IDE'deki herhangi bir dosyaya erişemediğimiz için aşağıdaki Java Kodu burada çalışmayacaktır.
Yani programı sisteminize kopyalayın ve orada çalıştırın.
ABC.txt Programda kullanılan dosya şunları içerir:
no. of lines
Çıkış :
At line : 0 n At line : 0 o At line : 0 . At line : 0 At line : 0 o At line : 0 f At line : 1 At line : 1 l At line : 1 i At line : 1 n At line : 1 e At line : 1 s at line: 1
Sözdizimi:
public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Uygulama :
Java // Java program illustrating the working of available() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read a = geekline . available (); System . out . println ( c + ' Bytes available : ' + a ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Not :
Çevrimiçi IDE'deki herhangi bir dosyaya erişemediğimiz için aşağıdaki Java Kodu burada çalışmayacaktır.
Yani programı sisteminize kopyalayın ve orada çalıştırın.
ABC.txt Programda kullanılan dosya şunları içerir:
available
Çıkış :
a Bytes available : 4 v Bytes available : 3 a Bytes available : 3 i Bytes available : 2 l Bytes available : 2 a Bytes available : 1 b Bytes available : 1 l Bytes available : 0 e Bytes available : 0
Sözdizimi:
public void setLineNumber(int arg) Parameters : arg : line number to assign Return : void Exception: -----
Uygulama :
Java // Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b = 0 ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of setLineNumber() : to set the line no. geekline . setLineNumber ( 100 + b ); // getLineNumber() : returning the current line no. a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( c + ' Line No. Set : ' + a ); b ++ ; } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Not :
Çevrimiçi IDE'deki herhangi bir dosyaya erişemediğimiz için aşağıdaki Java Kodu burada çalışmayacaktır.
Yani programı sisteminize kopyalayın ve orada çalıştırın.
ABC.txt Programda kullanılan dosya şunları içerir:
LineNumber
Çıkış :
L Line No. Set : 100 i Line No. Set : 101 n Line No. Set : 102 e Line No. Set : 103 N Line No. Set : 104 u Line No. Set : 105 m Line No. Set : 106 b Line No. Set : 107 e Line No. Set : 108 r Line No. Set : 109
Sözdizimi:
public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of Input Stream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Uygulama:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b = 0 ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // skip() : to skip and discard 'arg' bytes // Here skip() will skip and discard 3 bytes. geekline . skip ( 3 ); System . out . println ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Not :
Çevrimiçi IDE'deki herhangi bir dosyaya erişemediğimiz için aşağıdaki Java Kodu burada çalışmayacaktır.
Yani programı sisteminize kopyalayın ve orada çalıştırın.
ABC.txt Programda kullanılan dosya şunları içerir:
Program Explaining Skip() method
Çıkış : '
P r E a n k ) t
Sözdizimi:
public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : buffer whose data to read offset : starting offset of the data maxlen : max. no. of bytes to read Return : total no. of bytes else return -1 if End of Input Stream is identified Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Uygulama :
Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while (( a = geekline . read ()) !=- 1 ) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Not :
Çevrimiçi IDE'deki herhangi bir dosyaya erişemediğimiz için aşağıdaki Java Kodu burada çalışmayacaktır.
Yani programı sisteminize kopyalayın ve orada çalıştırın.
ABC.txt Programda kullanılan dosya şunları içerir:
Read() method
yöntemin yaptığı şey ofset = r ve maxlen = 5... yani ---yani. 3 ofset sonra 5 bayt yani Read( sonra tekrar ofset yani --
Çıkış :
The number of char read: 5 ---Read(--
Sözdizimi:
public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
Sözdizimi:
public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
LineNumberInputStream Class yöntemlerini açıklayan Java Programı: reset() ve mark()
Java // Java program illustrating the working of LineNumberInputStream method // mark() and reset() import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geek = null ; try { geek = new FileInputStream ( 'GEEKS.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geek ); // read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); // mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream geekline . mark ( 0 ); // skip() : it results in reading of 'e' in G'e'eeks geekline . skip ( 1 ); System . out . println ( 'skip() method comes to play' ); System . out . println ( 'mark() method comes to play' ); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); boolean check = geekline . markSupported (); if ( geekline . markSupported ()) { // reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions. geekline . reset (); System . out . println ( 'reset() invoked' ); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); } else { System . out . println ( 'reset() method not supported.' ); } System . out . println ( 'geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : ' + check ); } catch ( Exception except ) { // in case of I/O error except . printStackTrace (); } finally { // releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes if ( geek != null ) geek . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Not :
Burada böyle bir dosya bulunmadığından bu kod çevrimiçi IDE'de çalışmayacaktır.
Çalışmasını kontrol etmek için bu kodu Sisteminizde çalıştırabilirsiniz.
ABC.txt kodda kullanılan dosya
HelloGeeks
Çıkış :
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() method not supported. geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : false