Platta till en länkad lista på flera nivåer (djupgående)
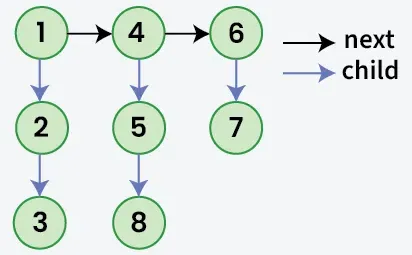
Givet en länkad lista där förutom den nästa pekare varje nod har en barn pekare som eventuellt pekar på en separat lista. Dessa underordnade listor kan ha en eller flera egna barn att producera en flera nivåer länkad lista. Med tanke på huvud av första nivån av listan. Uppgiften är att platta till listan så att alla noder visas i en en-nivå länkad lista. Platta ut listan på ett sätt som alla noder vid första nivån borde komma första sedan noder av andra nivå och så vidare.
Exempel:
Input:

Produktion: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
Förklaring: Den länkade listan på flera nivåer är tillplattad eftersom den inte har några underordnade pekare.
Vi har diskuterat utjämning av en länkad lista på flera nivåer där noder har två pekare ner och nästa. I förra inlägget vi tillplattade den länkade listan nivåmässigt. Hur man plattar ut en länkad lista när vi alltid behöver bearbeta nedåtpekare före nästa vid varje nod.
Innehållsförteckning
- [Förväntad tillvägagångssätt] Använda rekursion - O(n) Tid och O(n) Mellanrum
- [Alternativ tillvägagångssätt] Använda stack - O(n) tid och O(n) mellanrum
[Förväntad tillvägagångssätt] Använda rekursion - O(n) Tid och O(n) Mellanrum
C++Tillvägagångssättet är att rekursivt platta ut a länkad på flera nivåer lista genom att korsa varje nod och dess undernoder. Första platta till barnlistan med hjälp av rekursion. När barnlistan är tillplattad fortsätt till nästa nod i sekvensen. Under korsning bibehålla en hänvisning till tidigare besökt nod och länka den till den aktuella noden. Denna process säkerställer att alla noder från olika nivåer är anslutna i en enda linjär lista samtidigt som man bevarar djupgående ordning.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * curr Node *& prev ) { if ( curr == nullptr ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node * next = curr -> next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr -> down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); Node * prev = nullptr ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node curr Node [] prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] != null ) prev [ 0 ] . next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node [] prev = new Node [ 1 ] ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( curr prev ): if curr is None : return # Add the current element to the list. if prev [ 0 ] is not None : prev [ 0 ] . next = curr prev [ 0 ] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr . next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list ( curr . down prev ) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list ( next_node prev ) def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr is not None : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) prev = [ None ] flatten_list ( head prev ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node curr ref Node prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList ( curr . down ref prev ); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList ( next ref prev ); } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node prev = null ; FlattenList ( head ref prev ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( curr prev ) { if ( curr === null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] !== null ) prev [ 0 ]. next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer let next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); let prev = [ null ]; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head );
Produktion
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[Alternativ tillvägagångssätt] Använda stack - O(n) tid och O(n) mellanrum
C++Tillvägagångssättet är att korsa länkad lista på flera nivåer med hjälp av en stack . Börja med tryckande de huvudnod upp på traven. Sedan medan stacken är inte tom pop toppnoden och bearbeta den. För varje nod tryck dess nästa och nedåtpekare (om de finns) på traven. Under denna process länka den nuvarande noden till den föregående noden upprätthålla listan i en tillplattad form. Traverseringen säkerställer att noder från alla nivåer är anslutna i en länkad lista på en nivå bevara den djupgående ordningen.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * head ) { if ( head == nullptr ) return ; stack < Node *> st ; st . push ( head ); Node * prev = nullptr ; while ( ! st . empty ()) { Node * curr = st . top (); st . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr -> next != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr -> down != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack ; class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack <> (); stack . push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( ! stack . isEmpty ()) { Node curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( head ): if head is None : return stack = [ head ] prev = None while stack : curr = stack . pop () # Push the next node first if curr . next : stack . append ( curr . next ) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr . down : stack . append ( curr . down ) # Add the current element to the list if prev : prev . next = curr prev = curr def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) flatten_list ( head ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack < Node > (); stack . Push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( stack . Count > 0 ) { Node curr = stack . Pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . Push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . Push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); FlattenList ( head ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( head ) { if ( head === null ) return ; let stack = [ head ]; let prev = null ; while ( stack . length > 0 ) { let curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next !== null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down !== null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev !== null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head );
Produktion
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28