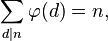Eulers Totient-funktion
Eulers Totientfunktion Φ(n) för en ingång n är antalet tal i {1, 2, 3, …, n-1} som är relativt primtal till n, d.v.s. de tal vars GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) med n är 1.
Exempel:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) är 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) är 1, men gcd(2, 2) är 2.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) är 1 och gcd(2, 3) är 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) är 1 och gcd(3, 4) är 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) är 1, gcd(2, 5) är 1,
gcd(3, 5) är 1 och gcd(4, 5) är 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) är 1 och gcd(5, 6) är 1,
Hur beräknar man Φ(n) för en ingång n?
A enkel lösning är att iterera genom alla tal från 1 till n-1 och räkna tal med gcd med n som 1. Nedan är implementeringen av den enkla metoden att beräkna Eulers Totient-funktion för ett inmatat heltal n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }> Java // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh> Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha> C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal> Javascript > PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout < < 'phi(' <
Ovanstående kod anropar gcd-funktionen O(n) gånger. Tidskomplexiteten för gcd-funktionen är O(h) där h är antalet siffror i ett mindre antal av givna två tal. Därför en övre gräns på tidskomplexitet av ovanstående lösning är O(N^2 log N) [Hur Φ det kan vara högst Log 10 n siffror i alla nummer från 1 till n] Hjälputrymme: O(log N)
Nedan är en Bättre lösning . Idén är baserad på Eulers produktformel som säger att värdet av totientfunktioner ligger under produktens övergripande primfaktorer p av n.
Formeln säger i grunden att värdet på Φ(n) är lika med n multiplicerad biprodukt av (1 – 1/p) för alla primfaktorer p av n. Till exempel värdet på Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Vi kan hitta alla primära faktorer med hjälp av idén som används i detta posta.
1) Initiera : resultat = n
2) Kör en slinga från 'p' = 2 till sqrt(n), gör följande för varje 'p'.
a) Om p delar n, då
Set: resultat = resultat * (1,0 - (1,0 / (flytande) p));
Dela alla förekomster av p i n.
3) Returnera resultat
Nedan är implementeringen av Eulers produktformel.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; //Eftersom i mängden {1,2,....,n-1} är alla tal relativt primtal med n //om n är ett primtal returnerar (int)resultat; } // Drivrutinskod int main() { int n; för(n = 1; n <= 10; n++) { cout < < 'Phi' < < '(' < < n < < ')' < < ' = ' < < phi(n) < C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; //Eftersom i mängden {1,2,....,n-1} är alla tal relativt primtal med n //om n är ett primtal returnerar (int)resultat; } // Drivrutinsprogram för att testa ovan funktion int main() { int n; för (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }> Java // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; //Eftersom i mängden {1,2,....,n-1} är alla tal relativt primtal med n //om n är ett primtal returnerar (int)resultat; } // Drivrutinsprogram för att testa ovan funktion public static void main(String args[]) { int n; för (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.> Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p <= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : resultat -= resultat // n #Eftersom i mängden {1,2,....,n-1} är alla tal relativt primtal med n #om n är ett primtal returnerar int(result) # Drivrutin program för att testa ovanstående funktion för n i intervallet(1, 11): print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Denna kod har bidragit # av Nikita Tiwari.> C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; //Eftersom i mängden {1,2,....,n-1} är alla tal relativt primtal med n //om n är ett primtal returnerar (int)resultat; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { int n; för (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.> Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; //Eftersom i mängden {1,2,....,n-1} är alla tal relativt primtal med n //om n är ett primtal returnerar parseInt(result); } // Förarkod för (låt n = 1; n <= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal> PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $result -= $result / $n; //Eftersom i mängden {1,2,....,n-1} är alla tal relativt primtal med n //om n är ett primtalsreturintervall($result); } // Drivrutinskod för ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>
Produktion Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Tidskomplexitet: O(Φ n log n)
Hjälputrymme: O(1)
Vi kan undvika flyttalsberäkningar i ovanstående metod. Tanken är att räkna alla primtalsfaktorer och deras multipler och subtrahera detta antal från n för att få det totientfunktionsvärde (primtalsfaktorer och multiplar av primtalsfaktorer kommer inte att ha gcd som 1)
1) Initiera resultatet som n
2) Betrakta varje tal 'p' (där 'p' varierar från 2 till Φ(n)).
Om p delar n, gör följande
a) Subtrahera alla multiplar av p från 1 till n [alla multiplar av p
kommer att ha gcd mer än 1 (minst p) med n]
b) Uppdatera n genom att upprepade gånger dividera det med p.
3) Om det reducerade n är mer än 1, ta bort alla multiplar
av n från resultat.
Nedan är implementeringen av ovanstående algoritm.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; returnera resultat; } // Drivrutinskod int main() { int n; för(n = 1; n <= 10; n++) { cout < < 'Phi' < < '(' < < n < < ')' < < ' = ' < < phi(n) < < endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu> C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; returnera resultat; } // Drivrutinsprogram för att testa ovan funktion int main() { int n; för (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }> Java // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; returnera resultat; } // Driver Code public static void main (String[] args) { int n; för (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit> Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): resultat -= int(resultat / n); returnera resultat; # Drivrutinskod för n inom intervallet(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Denna kod har bidragit # av mits> C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= resultat /n; returnera resultat; } // Driver Code static public void Main () { int n; för (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit> Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) resultat -= parseInt(result / n); returnera resultat; } // Förarkod för (låt n = 1; n <= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal> PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $result -= (int)$result / $n; returnera $resultat; } // Drivrutinskod för ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>>
Produktion Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Tidskomplexitet: O(Φ n log n)
Hjälputrymme: O(1)
Låt oss ta ett exempel för att förstå ovanstående algoritm.
n = 10.
Initiera: resultat = 10
2 är en primfaktor, så n = n/i = 5, resultat = 5
3 är inte en primär faktor.
For-slingan stannar efter 3 eftersom 4*4 inte är mindre än eller lika
till 10.
Efter för loop, resultat = 5, n = 5
Eftersom n> 1, resultat = resultat - resultat/n = 4
Några intressanta egenskaper hos Eulers Totient-funktion
1) För en primtal p , phi(p) = p – 1
Bevis :
phi(p) = p - 1 , där p är vilket primtal som helst. Det vet vi gcd(p, k) = 1 där k är vilket slumptal som helst och k
eq p Totalt antal från 1 till p = p Antal för vilket gcd(p, k) = 1 är 1 , det vill säga själva talet p, så subtrahera 1 från p phi(p) = p - 1
Exempel:
phi(5) = 5 - 1 = 4 phi(13) = 13 - 1 = 12 phi(29) = 29 - 1 = 28
2) För två primtal a och b phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) = (a – 1) cdot (b – 1) , Använd i RSA-algoritm
Bevis :
phi(acdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) , där a och b är primtal phi(a) = a - 1 , phi(b) = b - 1 Totalt antal från 1 till ab = ab Totala multiplar av a från 1 till ab = frac{a cdot b} {a} = b Totala multiplar av b från 1 till ab = frac{a cdot b} {b} = a Exempel: a = 5, b = 7, ab = 35Multiplar av a = frac {35} {5} = 7 {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35}Multipel av b = frac {35} {7} = 5 {7, 14, 21, 28, 35} Kan det bli någon dubbelräkning? (se ovanstående exempel noggrant, försök med andra primtal också för mer grepp) Naturligtvis har vi räknat ab dubbelt i multipler av a och multiplar av b så, Totala multipler = a + b - 1 (med vilken gcd
eq 1 med ab ) phi(ab) = ab - (a + b - 1) , tar bort alla nummer med gcd
eq 1 med ab phi(ab) = a(b - 1) - (b - 1) phi(ab) = (a - 1) cdot (b - 1) phi(ab) = phi(a) cdot phi(b)
Exempel:
phi(5 cdot 7) = phi(5) cdot phi(7) = (5 - 1) cdot (7 - 1) = 24 phi(3 cdot 5) = phi(3) cdot phi(5) = (3 - 1) cdot (5 - 1) = 8 phi(3 cdot 7) = phi(3) cdot phi(7) = (3 - 1) cdot (7 - 1) = 12
3) För ett primtal p , phi(p ^ k) = p ^ k – p ^ {k – 1}
Bevis :
phi(p^k) = p ^ k - p ^{k - 1} , där p är ett primtal Totalt antal från 1 till p ^ k = p ^ k Totala multiplar av p = frac {p ^ k} {p} = p ^ {k - 1} Ta bort dessa multiplar som med dem gcd
eq 1 Exempel: p = 2, k = 5, p ^ k = 32Multiplar av 2 (som med dem gcd
eq 1 ) = 32 / 2 = 16 {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32} phi(p ^ k) = p ^ k - p ^ {k - 1}
Exempel:
phi(2 ^ 5) = 2 ^ 5 - 2 ^ {5 - 1} = 32 - 16 = 16 phi(5 ^ 3) = 5 ^ 3 - 5 ^ {3 - 1} = 125 - 25 = 100 phi(3 ^ 5) = 3 ^ 5 - 3 ^ {5 - 1} = 243 - 81 = 162
4) För två nummer a och b phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {gcd(a, b)} {phi(gcd(a, b))}
Specialfall : gcd(a, b) = 1
phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {1} {phi(1)} = phi(a) cdot phi(b)
Exempel:
Specialfall : gcd(a, b) = 1 , phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) phi(2 cdot 9) = phi(2) cdot phi(9) = 1 cdot 6 = 6 phi(8 cdot 9) = phi(8) cdot phi(9) = 4 cdot 6 = 24 phi(5 cdot 6) = phi(5) cdot phi(6) = 4 cdot 2 = 8 Normalt fall: gcd(a, b)
eq 1 , phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {gcd(a, b)} {phi(gcd(a, b))} phi(4 cdot 6) = phi(4) cdot phi(6) cdot frac {gcd(4, 6)} {phi(gcd(4, 6))} = 2 cdot 2 cdot frac{2}{1} = 2 cdot 2 cdot 2 = 8 phi(4 cdot 8) = phi(4) cdot phi(8) cdot frac {gcd(4, 8)} {phi(gcd(4, 8))} = 2 cdot 4 cdot frac{4}{2} = 2 cdot 4 cdot 2 = 16 phi(6 cdot 8) = phi(6) cdot phi(8) cdot frac {gcd(6, 8)} {phi(gcd(6, 8))} = 2 cdot 4 cdot frac{2}{1} = 2 cdot 4 cdot 2 = 16
5) Summan av värdena för totientfunktioner för alla divisorer av n är lika med n.
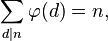
Exempel:
n = 6
faktorer = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n = phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(3) + phi(6) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 6 n = 8faktorer = {1, 2, 4, 8}n = phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(4) + phi(8) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 8 n = 10faktorer = {1, 2, 5, 10}n = phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(5) + phi(10) = 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 10
6) Den mest kända och viktigaste egenskapen uttrycks i Eulers teorem :
Teoremet säger att om n och a är coprime
(eller relativt primtal) positiva heltal, alltså
a Φ(n) Φ 1 (mod n)
De RSA-kryptosystem bygger på detta teorem:
I det speciella fallet när m är primtal, säg p, förvandlas Eulers sats till den sk Fermats lilla teorem :
a p-1 Φ 1 (mot p)
7) Antalet generatorer av en ändlig cyklisk grupp under modulo n addition är Φ(n) .
Relaterad artikel:
Eulers Totient-funktion för alla tal mindre än eller lika med n
Optimerad Euler Totient-funktion för flera utvärderingar
Referenser:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/