Minimalni stroški za rezanje deske na kvadrate

Glede na ploščo dimenzij n × m ki ga je treba razrezati na n × m kvadratov. Stroški reza vzdolž vodoravnega ali navpičnega roba so navedeni v dveh nizih:
- x[] : Zniževanje stroškov vzdolž navpičnih robov (po dolžini).
- in [] : Zniževanje stroškov vzdolž vodoravnih robov (po širini).
Poiščite minimalne skupne stroške, potrebne za optimalno rezanje deske na kvadrate.
Primeri:
Vnos: x[] = [2 1 3 1 4] y[] = [4 1 2] n = 4 m = 6
Izhod: 42
Pojasnilo:
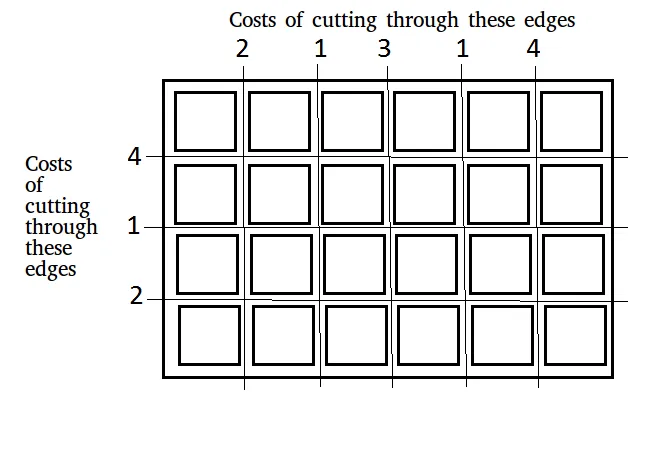
Sprva št. vodoravnih segmentov = 1 & št. navpičnih segmentov = 1.
Optimalen način rezanja na kvadrat je:
Izberite 4 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 4 × vodoravni segmenti = 4
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 1 navpični segmenti = 2.
Izberite 4 (od y) -> vodoravni rez Cena = 4 × navpični segmenti = 8
Sedaj vodoravni segmenti = 2 navpični segmenti = 2.
Izberite 3 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 3 × vodoravni segmenti = 6
Sedaj vodoravni segmenti = 2 navpični segmenti = 3.
Izberi 2 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 2 × vodoravni segmenti = 4
Sedaj vodoravni segmenti = 2 navpični segmenti = 4.
Izberite 2 (od y) -> vodoravni rez Cena = 2 × navpični segmenti = 8
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 3 navpični segmenti = 4.
Izberi 1 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 1 × vodoravni segmenti = 3
Sedaj vodoravni segmenti = 3 navpični segmenti = 5.
Izberi 1 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 1 × vodoravni segmenti = 3
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 3 navpični segmenti = 6.
Izberi 1 (od y) -> vodoravni rez Cena = 1 × navpični segmenti = 6
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 4 navpični segmenti = 6.
Torej skupni strošek = 4 + 8 + 6 + 4 + 8 + 3 + 3 + 6 = 42.Vnos: x[] = [1 1 1] y[] = [1 1 1] n = 4 m = 4
Izhod: 15
Pojasnilo:
Sprva št. vodoravnih segmentov = 1 & št. navpičnih segmentov = 1.
Optimalen način rezanja na kvadrat je:
Izberite 1 (od y) -> vodoravni rez Cena = 1 × navpični segmenti = 1
Sedaj vodoravni segmenti = 2 navpični segmenti = 1.
Izberite 1 (od y) -> vodoravni rez Cena = 1 × navpični segmenti = 1
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 3 navpični segmenti = 1.
Izberite 1 (od y) -> vodoravni rez Cena = 1 × navpični segmenti = 1
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 4 navpični segmenti = 1.
Izberi 1 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 1 × vodoravni segmenti = 4
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 4 navpični segmenti = 2.
Izberi 1 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 1 × vodoravni segmenti = 4
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 4 navpični segmenti = 3.
Izberi 1 (od x) -> navpični rez Cena = 1 × vodoravni segmenti = 4
Zdaj vodoravni segmenti = 4 navpični segmenti = 4
Torej skupni strošek = 1 + 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 15.
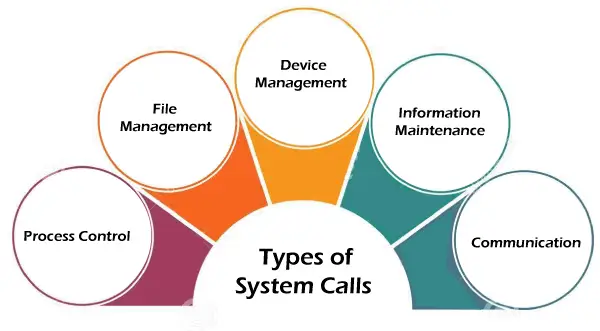
Kazalo vsebine
- [Naivni pristop] Preizkusite vse permutacije - O((n+m)!×(n+m)) čas in O(n+m) prostor
- [Pričakovani pristop] Uporaba pohlepne tehnike - O( n (log n)+m (log m)) čas in O(1) prostor
[Naivni pristop] Preizkusite vse permutacije - O((n+m)!×(n+m)) čas in O(n+m) prostor
Ideja je ustvariti vse možne permutacije danih kosov in nato izračunati stroške za vsako permutacijo. Končno med njimi vrnite minimalne stroške.
Opomba: Ta pristop ni izvedljiv za večje vložke, ker število permutacij faktorsko raste kot (m+n-2)!.
Za vsako permutacijo moramo izračunati stroške v O(m+n) času. Zato celotna časovna kompleksnost postane O((m+n−2)!×(m+n)).
[Pričakovani pristop] Uporaba pohlepne tehnike - O( n (log n)+m (log m)) čas in O(1) prostor
Ideja je, da najprej naredite najdražje kose z uporabo a pohlepen pristop . Opažamo, da izbira najvišjega znižanja stroškov na vsakem koraku zmanjša prihodnje stroške, saj vpliva na več kosov hkrati. Stroške navpičnega (x) in vodoravnega (y) zmanjšanja razvrstimo v padajočem vrstnem redu, nato pa iterativno izberemo večjega, da povečamo prihranke stroškov. Preostali kosi se obdelajo ločeno, da se zagotovi optimalno razdelitev vseh delov.
Kaj se zgodi, ko naredimo rez?
- Horizontalni rez → režete po širini, tako da se poveča število vodoravnih trakov (hCount++). Toda strošek se pomnoži z vCount (število navpičnih trakov), ker mora vodoravni rez potekati skozi vse navpične segmente.
- Vertikalni rez → režete po višini, tako da se poveča število navpičnih trakov (vCount++). Toda strošek se pomnoži s hCount (število vodoravnih trakov), ker mora navpični rez potekati skozi vse vodoravne segmente.
Koraki za rešitev težave:
- Razvrsti matri x in y v padajočem vrstnem redu.
- Uporabite dva kazalca, enega za x in enega za y, začenši od največje vrednosti in se pomaknite proti manjšim vrednostim.
- Vzdržujte hCount in vCount za sledenje, na koliko segmentov vpliva vsak rez, in jih ustrezno posodobite.
- Ponavljajte medtem ko imata oba x in y neobdelane kose, pri čemer vedno izberete večjo stroškovo, da zmanjšate skupne stroške.
- Če x ima preostale reze, jih obdelajte z množiteljem hCount; podobno obdelajte preostale y reze z vCount.
- Zberite skupne stroške v vsakem koraku z uporabo formule: znižajte stroške * število prizadetih kosov, kar zagotavlja minimalne stroške.
#include #include #include using namespace std ; int minCost ( int n int m vector < int >& x vector < int >& y ) { // Sort the cutting costs in ascending order sort ( x . begin () x . end ()); sort ( y . begin () y . end ()); int hCount = 1 vCount = 1 ; int i = x . size () - 1 j = y . size () - 1 ; int totalCost = 0 ; while ( i >= 0 && j >= 0 ) { // Choose the larger cost cut to // minimize future costs if ( x [ i ] >= y [ j ]) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } else { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } } // Process remaining vertical cuts while ( i >= 0 ) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } // Process remaining horizontal cuts while ( j >= 0 ) { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } return totalCost ; } int main () { int n = 4 m = 6 ; vector < int > x = { 2 1 3 1 4 }; vector < int > y = { 4 1 2 }; cout < < minCost ( n m x y ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Arrays ; class GfG { static int minCost ( int n int m int [] x int [] y ) { // Sort the cutting costs in ascending order Arrays . sort ( x ); Arrays . sort ( y ); int hCount = 1 vCount = 1 ; int i = x . length - 1 j = y . length - 1 ; int totalCost = 0 ; while ( i >= 0 && j >= 0 ) { // Choose the larger cost cut to // minimize future costs if ( x [ i ] >= y [ j ] ) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } else { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } } // Process remaining vertical cuts while ( i >= 0 ) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } // Process remaining horizontal cuts while ( j >= 0 ) { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } return totalCost ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 4 m = 6 ; int [] x = { 2 1 3 1 4 }; int [] y = { 4 1 2 }; System . out . println ( minCost ( n m x y )); } }
Python def minCost ( n m x y ): # Sort the cutting costs in ascending order x . sort () y . sort () hCount vCount = 1 1 i j = len ( x ) - 1 len ( y ) - 1 totalCost = 0 while i >= 0 and j >= 0 : # Choose the larger cost cut to # minimize future costs if x [ i ] >= y [ j ]: totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount vCount += 1 i -= 1 else : totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount hCount += 1 j -= 1 # Process remaining vertical cuts while i >= 0 : totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount vCount += 1 i -= 1 # Process remaining horizontal cuts while j >= 0 : totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount hCount += 1 j -= 1 return totalCost if __name__ == '__main__' : n m = 4 6 x = [ 2 1 3 1 4 ] y = [ 4 1 2 ] print ( minCost ( n m x y ))
C# using System ; class GfG { public static int minCost ( int n int m int [] x int [] y ) { // Sort the cutting costs in ascending order Array . Sort ( x ); Array . Sort ( y ); int hCount = 1 vCount = 1 ; int i = x . Length - 1 j = y . Length - 1 ; int totalCost = 0 ; // Process the cuts in greedy manner while ( i >= 0 && j >= 0 ) { // Choose the larger cost cut to // minimize future costs if ( x [ i ] >= y [ j ]) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } else { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } } // Process remaining vertical cuts while ( i >= 0 ) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } // Process remaining horizontal cuts while ( j >= 0 ) { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } return totalCost ; } public static void Main () { int n = 4 m = 6 ; int [] x = { 2 1 3 1 4 }; int [] y = { 4 1 2 }; Console . WriteLine ( minCost ( n m x y )); } }
JavaScript function minCost ( n m x y ) { // Sort the cutting costs in ascending order x . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); y . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); let hCount = 1 vCount = 1 ; let i = x . length - 1 j = y . length - 1 ; let totalCost = 0 ; while ( i >= 0 && j >= 0 ) { // Choose the larger cost cut to // minimize future costs if ( x [ i ] >= y [ j ]) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } else { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } } // Process remaining vertical cuts while ( i >= 0 ) { totalCost += x [ i ] * hCount ; vCount ++ ; i -- ; } // Process remaining horizontal cuts while ( j >= 0 ) { totalCost += y [ j ] * vCount ; hCount ++ ; j -- ; } return totalCost ; } // Driver Code let n = 4 m = 6 ; let x = [ 2 1 3 1 4 ]; let y = [ 4 1 2 ]; console . log ( minCost ( n m x y ));
Izhod
42Ustvari kviz