Razred Java.io.PipedOutputStream v Javi

Razred Java.io.PipedInputStream v Javi

Cevi v IO zagotavljajo povezavo med dvema nitima, ki se hkrati izvajata v JVM. Tako se cevi uporabljajo kot vir ali cilj.
- PipedInputStream je prav tako povezan s PipedOutputStream. Podatke je torej mogoče zapisati s PipedOutputStream in PipedInputStream. Toda uporaba obeh niti hkrati povzroči zastoj za niti.
- PipedOutputStream pošilja konec cevi. Podatki se zapišejo v PipedOutputStream. Cev naj bi bila prekinjena, če PipedInputStream, ki je bral podatke, ni več.
Izjava:
public class PipedOutputStream
extends OutputStream
Konstruktor:
- PipedOutputStream() : ustvari PipedOutputStream, ki ni povezan.
- PipedOutputStream(PipedOutputStream inStream) : ustvari PipedOutputStream, ki ga
je povezan s PipedInputStream - 'inStream'.
Metode:
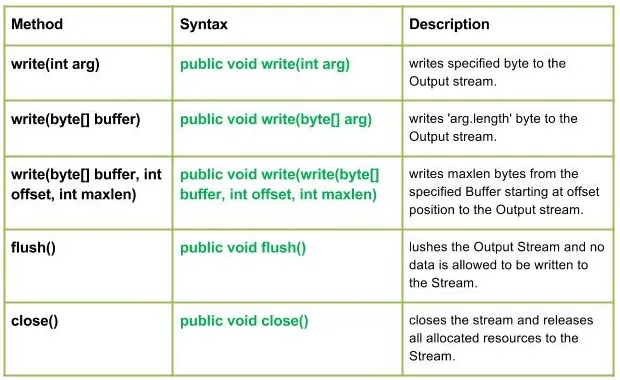
write() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(int byte) zapiše določen bajt v cevni izhodni tok.
Sintaksa:
public void write(int byte)
Parameters :
byte : byte to be written
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) zapiše maxlen bajtov podatkov iz medpomnilnika v cevni izhodni tok. Metoda se blokira, če v tok ni zapisan noben bajt.
Sintaksa:
public void write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen)
Parameters :
buffer : data of the buffer
offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'.
maxlen : maximum length of array to be read
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. JavaIzhod:
Use of write(buffer offset maxlen) : J A V A
- close() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.close() zapre cevovodni izhodni tok in sprosti dodeljena sredstva.
Sintaksa:
public void close()
Parameters :
--------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- povezava (destinacija PipedInputStream) : java.io.PipedOutputStream.connect (destinacija PipedInputStream poveže cevovodni izhodni tok z 'ciljnim' cevovodnim vhodnim tokom in v primeru, da so 'cilj' cevi z nekim drugim tokom, se vrže izjema IO
Sintaksa:
public void connect(PipedInputStream destination)
Parameters :
destination : the Piped Input Stream to be connected to
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- flush(): java.io.PipedOutputStream.flush() splakne izhodni tok.
Sintaksa:
public void flush()
Parameters :
------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
Koda Java, ki ponazarja delovanje metod razreda PipedOutputStream:
JavaIzhod:
Use of flush() method :
G E E K S
Closing the Output stream
Ustvari kviz