R – Matrice
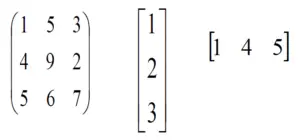
R-matica je dvojrozmerné usporiadanie údajov v riadkoch a stĺpcoch.
V matici sú riadky tie, ktoré prebiehajú vodorovne a stĺpce sú tie, ktoré prebiehajú vertikálne. In R programovanie matice sú dvojrozmerné, homogénne dátové štruktúry. Tu je niekoľko príkladov matríc:

R – Matrice
Vytvorenie matice v R
Na vytvorenie matice v R je potrebné použiť funkciu tzv matica() .
Argumenty k tomu matica() sú množinou prvkov vo vektore. Musíte zadať, koľko riadkov a koľko stĺpcov chcete mať vo svojej matici.
Poznámka: Štandardne sú matice usporiadané podľa stĺpcov.
Syntax na vytvorenie R-matice
matrix(data, nrow, ncol, byrow, dimnames)
Parametre:
- údaje – hodnoty, ktoré chcete zadať
- teraz - č. riadkov
- ncol – č. stĺpcov
- vedľa – logická stopa, ak bude hodnota „true“ priradená riadkami
- dimnames – názvy riadkov a stĺpcov
Príklad:
R
# R program to create a matrix> > A => matrix> (> > > # Taking sequence of elements> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > > # No of rows> > nrow = 3,> > > # No of columns> > ncol = 3,> > > # By default matrices are in column-wise order> > # So this parameter decides how to arrange the matrix> > byrow => TRUE> )> > # Naming rows> rownames> (A) => c> (> 'a'> ,> 'b'> ,> 'c'> )> > # Naming columns> colnames> (A) => c> (> 'c'> ,> 'd'> ,> 'e'> )> > cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: c d e a 1 2 3 b 4 5 6 c 7 8 9
Vytvorenie špeciálnych matíc v R
R umožňuje vytváranie rôznych rôznych typov matíc s použitím argumentov odovzdaných funkcii matrix().
1. Matica, kde sú všetky riadky a stĺpce vyplnené jednou konštantou „k“:
Na vytvorenie takejto matice R je syntax uvedená nižšie:
Syntax: matica(k, m, n)
Parametre:
k: konštanta
m: počet riadkov
n: počet stĺpcov
Príklad:
R
# R program to illustrate> # special matrices> # Matrix having 3 rows and 3 columns> # filled by a single constant 5> print> (> matrix> (5, 3, 3))> |
Výkon
[,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 5 5 5 [2,] 5 5 5 [3,] 5 5 5
2. Diagonálna matica:
Diagonálna matica je matica, v ktorej sú všetky položky mimo hlavnej diagonály nulové. Na vytvorenie takejto matice R je syntax uvedená nižšie:
Syntax: diag(k, m, n)
Parametre:
k: konštanty/pole
m: počet riadkov
n: počet stĺpcov
Príklad:
R
# R program to illustrate> # special matrices> # Diagonal matrix having 3 rows and 3 columns> # filled by array of elements (5, 3, 3)> print> (> diag> (> c> (5, 3, 3), 3, 3))> |
Výkon
[,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 5 0 0 [2,] 0 3 0 [3,] 0 0 3
3. Matica identity:
Matica identity, v ktorej sú všetky prvky hlavnej uhlopriečky jednotky a všetky ostatné prvky sú nuly. Na vytvorenie takejto matice R je syntax uvedená nižšie:
Syntax: diag(k, m, n)
Parametre:
k: 1
m: počet riadkov
n: počet stĺpcov
Príklad:
R
# R program to illustrate> # special matrices> # Identity matrix having> # 3 rows and 3 columns> print> (> diag> (1, 3, 3))> |
Výkon
[,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 0 0 [2,] 0 1 0 [3,] 0 0 1
4. Maticové metriky
Matrixové metriky vám povedia o Matrixe, ktorú ste vytvorili. Možno budete chcieť vedieť počet riadkov, počet stĺpcov, rozmery matice.
Nižšie uvedený príklad vám pomôže zodpovedať nasledujúce otázky:
- Ako môžete poznať rozmer matice?
- Ako môžete vedieť, koľko riadkov je v matici?
- Koľko stĺpcov je v matici?
- Koľko prvkov je v matici?
Príklad:
R
# R program to illustrate> # matrix metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> cat> (> 'Dimension of the matrix:
'> )> print> (> dim> (A))> cat> (> 'Number of rows:
'> )> print> (> nrow> (A))> cat> (> 'Number of columns:
'> )> print> (> ncol> (A))> cat> (> 'Number of elements:
'> )> print> (> length> (A))> # OR> print> (> prod> (> dim> (A)))> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Dimension of the matrix: [1] 3 3 Number of rows: [1] 3 Number of columns: [1] 3 Number of elements: [1] ...
Prístup k prvkom R-Matrix
K prvkom v maticiach R môžeme pristupovať pomocou rovnakej konvencie, ktorá sa dodržiava v dátových rámcoch. Takže budete mať maticu a za ňou hranatú zátvorku s čiarkou medzi poľom.
Hodnota pred čiarkou sa používa na prístup k riadkom a hodnota, ktorá je za čiarkou, sa používa na prístup k stĺpcom. Ukážme si to jednoduchým R kódom.
Prístup k riadkom:
R
# R program to illustrate> # access rows in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> # Accessing first and second row> cat> (> 'Accessing first and second row
'> )> print> (A[1:2, ])> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Accessing first and second row [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6
Prístup k stĺpcom:
R
# R program to illustrate> # access columns in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> # Accessing first and second column> cat> (> 'Accessing first and second column
'> )> print> (A[, 1:2])> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Accessing first and second column [,1] [,2] [1,] 1 2 [2,] 4 5 [3,] 7 8
Ďalší príklad prístupu k prvkom R-matice:
R
# R program to illustrate> # access an entry in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> # Accessing 2> print> (A[1, 2])> # Accessing 6> print> (A[2, 3])> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 [1] 2 [1] 6
Prístup k podmaticiam v jazyku R:
K podmatici v matici môžeme pristupovať pomocou dvojbodka(:) operátor.
R
# R program to illustrate> # access submatrices in a matrix> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> cat> (> 'Accessing the first three rows and the first two columns
'> )> print> (A[1:3, 1:2])> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Accessing the first three rows and the first two columns [,1] [,2] [1,] 1 2 [2,] 4 5 [3...
Úprava prvkov R-matice
V R môžete upravovať prvky matíc priamym priradením.
Príklad:
R
# R program to illustrate> # editing elements in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> # Editing the 3rd rows and 3rd column element> # from 9 to 30> # by direct assignments> A[3, 3] = 30> cat> (> 'After edited the matrix
'> )> print> (A)> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After edited the matrix [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 30
R-matice zreťazenie
Zreťazenie matice sa vzťahuje na zlúčenie riadkov alebo stĺpcov existujúcej matice R.
Reťazenie riadku:
Reťazenie riadku do matice sa vykonáva pomocou rbind() .
R
# R program to illustrate> # concatenation of a row in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> # Creating another 1x3 matrix> B => matrix> (> > c> (10, 11, 12),> > nrow = 1,> > ncol = 3> )> cat> (> 'The 1x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (B)> # Add a new row using rbind()> C => rbind> (A, B)> cat> (> 'After concatenation of a row:
'> )> print> (C)> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 The 1x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 10 11 12 After concatenation of a row: [,1] [,2] [,3...
Reťazenie stĺpca:
Reťazenie stĺpca na maticu sa vykonáva pomocou cbind() .
R
# R program to illustrate> # concatenation of a column in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> # Creating another 3x1 matrix> B => matrix> (> > c> (10, 11, 12),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 1,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x1 matrix:
'> )> print> (B)> # Add a new column using cbind()> C => cbind> (A, B)> cat> (> 'After concatenation of a column:
'> )> print> (C)> |
Výkon
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 The 3x1 matrix: [,1] [1,] 10 [2,] 11 [3,] 12 After concatenation of a column: [,1] [,2] ...
Nekonzistentnosť rozmerov: Všimnite si, že pred týmto zreťazením matice sa musíte uistiť o konzistencii rozmerov medzi maticou.
R
# R program to illustrate> # Dimension inconsistency in metrics concatenation> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'The 3x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (A)> # Creating another 1x3 matrix> B => matrix> (> > c> (10, 11, 12),> > nrow = 1,> > ncol = 3,> )> cat> (> 'The 1x3 matrix:
'> )> print> (B)> # This will give an error> # because of dimension inconsistency> C => cbind> (A, B)> cat> (> 'After concatenation of a column:
'> )> print> (C)> |
Výkon:
The 3x3 matrix: [, 1] [, 2] [, 3] [1, ] 1 2 3 [2, ] 4 5 6 [3, ] 7 8 9 The 1x3 matrix: [, 1] [, 2] [, 3] [1, ] 10 11 12 Error in cbind(A, B) : number of rows of matrices must match (see arg 2)
Pridávanie riadkov a stĺpcov do R-matice
Ak chcete pridať riadok do R-matice, môžete použiť rbind() a na pridanie stĺpca do R-matice môžete použiť cbind () funkcia.
Pridáva sa riadok
Pozrime sa nižšie na príklad, ako pridať riadok do R-matice?
Príklad:
R
# Create a 3x3 matrix> number <-> matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'Before inserting a new row:
'> )> print> (number)> # New row to be inserted> new_row <-> c> (10, 11, 12)> # Define the new row> # Inserting the new row at the second position> A <-> rbind> (number[1, ], new_row, number[-1, ])> cat> (> '
After inserting a new row:
'> )> print> (number)> |
Výkon
Before inserting a new row: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After inserting a new row: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,]...
Pridanie stĺpca
Pozrime sa nižšie na príklad, ako pridať stĺpec do R-matice?
R
# Create a 3x3 matrix> number <-> matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'Before adding a new column:
'> )> print> (number)> # New column to be added> new_column <-> c> (10, 11, 12)> # Define the new column> # Adding the new column at the end> number <-> cbind> (number, new_column)> cat> (> '
After adding a new column:
'> )> print> (number)> |
Výkon
Before adding a new column: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After adding a new column: new_column [1,] 1 2 3 10 [2,] 4 5 6 1...
Odstránenie riadkov a stĺpcov R-matice
Ak chcete odstrániť riadok alebo stĺpec, musíte najprv získať prístup k tomuto riadku alebo stĺpcu a potom pred tento riadok alebo stĺpec vložiť znamienko mínus. Znamená to, že ste museli odstrániť daný riadok alebo stĺpec.
Odstránenie riadkov:
R
# R program to illustrate> # row deletion in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'Before deleting the 2nd row
'> )> print> (A)> # 2nd-row deletion> A = A[-2, ]> cat> (> 'After deleted the 2nd row
'> )> print> (A)> |
Výkon
Before deleting the 2nd row [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After deleted the 2nd row [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 7 8 9
Odstránenie stĺpca:
R
# R program to illustrate> # column deletion in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A => matrix> (> > c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > nrow = 3,> > ncol = 3,> > byrow => TRUE> )> cat> (> 'Before deleting the 2nd column
'> )> print> (A)> # 2nd-row deletion> A = A[, -2]> cat> (> 'After deleted the 2nd column
'> )> print> (A)> |
Výkon
Before deleting the 2nd column [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After deleted the 2nd column [,1] [,2] [1,] 1 3 [2,] 4 6 [3,] 7 9
Diskutovali sme o R-maticách a ich základných operáciách, ako je pridávanie nových riadkov a stĺpcov, odstraňovanie riadkov a stĺpcov, zlučovanie matíc atď.
Dúfame, že vám to pomohlo pochopiť matice v R a teraz môžete pohodlne používať matice R vo svojich projektoch.
Skontrolujte tiež:
- R – Pole
- R – zoznamy
- R – Tuples