Rôzne spôsoby čítania textového súboru v jazyku Java
V jazyku Java existuje viacero spôsobov čítania textového súboru v závislosti od veľkosti údajov a prípadu použitia. The java.io a balíky java.nio.file poskytujú niekoľko tried na efektívne spracovanie čítania súborov. Poďme diskutovať o spoločných prístupoch jeden po druhom.
1. Použitie triedy BufferedReader
BufferedReader trieda číta text z prúdu znakov a ukladá znaky do vyrovnávacej pamäte pre efektívne čítanie. Často sa ovíja okolo a FileReader alebo InputStreamReader na zlepšenie výkonu.
Syntax
JavaBufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(čítačka vo veľkosti int);
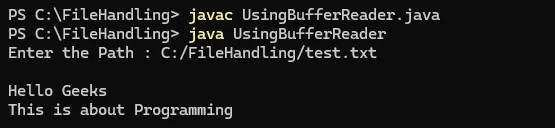
import java.io.* ; public class UsingBufferReader { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { // Creating BufferedReader for Input BufferedReader bfri = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader ( System . in )); System . out . print ( 'Enter the Path : ' ); // Reading File name String path = bfri . readLine (); BufferedReader bfro = new BufferedReader ( new FileReader ( path )); String st ; while (( st = bfro . readLine ()) != null ) System . out . println ( st ); } }
Výstup
 Výstup
Výstup 2. Trieda FileReader na čítanie textového súboru
The Trieda FileReader sa používa na čítanie textových súborov v jazyku Java. Číta znaky zo súboru a je vhodný na čítanie obyčajného textu. Konštruktéri tejto triedy predpokladajú, že predvolené kódovanie znakov a predvolená veľkosť bajtovej vyrovnávacej pamäte sú vhodné.
Konštruktory definované v tejto triede sú nasledovné:
- FileReader (súbor súboru): Vytvorí nový FileReader so súborom na čítanie
- FileReader (FileDescriptor fd): Vytvorí nový FileReader s FileDescriptorom na čítanie
- FileReader(String fileName): Vytvorí nový FileReader s názvom súboru, z ktorého sa má čítať
import java.io.* ; public class UsingFileReader { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader ( System . in )); System . out . print ( 'Enter the Path : ' ); // Reading File name String path = br . readLine (); FileReader fr = new FileReader ( path ); int i ; // Holds true till there is nothing to read while (( i = fr . read ()) != - 1 ) // Print all the content of a file System . out . print (( char ) i ); } }
Výstup
 Výstup
Výstup 3. Trieda skenera na čítanie textového súboru
Trieda skenera poskytuje jednoduchý spôsob, ako čítať textové súbory a analyzovať primitívne typy alebo reťazce pomocou regulárne výrazy . Rozdelí vstup na tokeny pomocou oddeľovača (v predvolenom nastavení biele miesto).
Príklad 1: S použitím slučiek
Java import java.io.* ; import java.util.Scanner ; public class UsingScannerClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader ( System . in )); System . out . print ( 'Enter the Path : ' ); // Reading File name String path = br . readLine (); // pass the path to the file as a parameter File file = new File ( path ); Scanner sc = new Scanner ( file ); while ( sc . hasNextLine ()) System . out . println ( sc . nextLine ()); } }
Výstup
 Výstup
Výstup Príklad 2: Bez použitia slučiek
Java import java.io.* ; import java.util.Scanner ; public class ReadingEntireFileWithoutLoop { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader ( System . in )); System . out . print ( 'Enter the Path : ' ); // Reading File name String path = br . readLine (); File file = new File ( path ); Scanner sc = new Scanner ( file ); // we just need to use \Z as delimiter sc . useDelimiter ( '\Z' ); System . out . println ( sc . next ()); } }
Výstup
 Výstup
Výstup 4. Čítanie celého súboru v zozname
Môžeme prečítať celý textový súbor do zoznamu pomocou Files.readAllLines() metóda z balík java.nio.file . Každý riadok v súbore sa stane jedným prvkom v zozname.
Syntax
public static List readAllLines(Path pathCharset cs) vyvolá IOException
Táto metóda rozpoznáva nasledovné ako zakončovače riadkov:
- u000Du000A -> Carriage Return + Line Feed
- u000A -> Line Feed
- u000D -> Carriage Return
import java.io.* ; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets ; import java.nio.file.* ; import java.util.* ; public class ReadFileIntoList { public static List < String > readFileInList ( String fileName ) { // Created List of String List < String > lines = Collections . emptyList (); try { lines = Files . readAllLines ( Paths . get ( fileName ) StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ); } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } return lines ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader ( System . in )); System . out . print ( 'Enter the Path : ' ); // Reading File name String path = br . readLine (); List l = readFileInList ( path ); // Iterator iterating over List Iterator < String > itr = l . iterator (); while ( itr . hasNext ()) System . out . println ( itr . next ()); } }
Výstup
 Výstup
Výstup 5. Čítajte textový súbor ako reťazec
V Jave môžeme čítať celý textový súbor ako jeden reťazec. Je to užitočné, keď chcete spracovať obsah súboru ako celok a nie riadok po riadku.
Syntax:
String data = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(fileName)));
Príklad:
Java package io ; import java.nio.file.* ; public class ReadTextAsString { public static String readFileAsString ( String fileName ) throws Exception { String data = '' ; data = new String ( Files . readAllBytes ( Paths . get ( fileName ))); return data ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader ( System . in )); System . out . print ( 'Enter the Path : ' ); // Reading File name String path = br . readLine (); String data = readFileAsString ( path ); System . out . println ( data ); } }
Výstup
 Výstup
Výstup