Lista vinculada desenrolada | Conjunto 1 (Introdução)
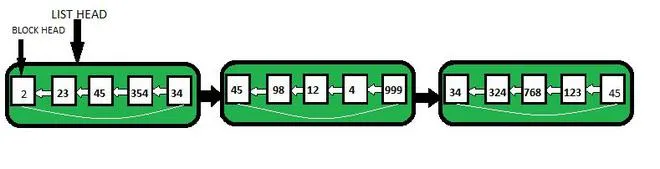
Assim como a matriz e a lista vinculada, a lista vinculada desenrolada também é uma estrutura de dados linear e é uma variante de uma lista vinculada.
Por que precisamos de uma lista vinculada desenrolada?
Uma das maiores vantagens das listas vinculadas em relação aos arrays é que a inserção de um elemento em qualquer local leva apenas O(1). No entanto, o problema aqui é que pesquisar um elemento em uma lista vinculada leva O(n). Assim, para resolver o problema de pesquisa, ou seja, reduzir o tempo de pesquisa do elemento, foi apresentado o conceito de listas encadeadas desenroladas. A lista vinculada desenrolada cobre as vantagens do array e da lista vinculada, pois reduz a sobrecarga de memória em comparação com listas vinculadas simples, armazenando vários elementos em cada nó e também tem a vantagem de inserção e exclusão rápida como uma lista vinculada.


Vantagens:
- Devido ao comportamento do cache, a pesquisa linear é muito mais rápida em listas vinculadas desenroladas.
- Em comparação com a lista vinculada comum, requer menos espaço de armazenamento para ponteiros/referências.
- Ele executa operações como inserção, exclusão e travessia mais rapidamente do que listas vinculadas comuns (porque a pesquisa é mais rápida).
Desvantagens:
- A sobrecarga por nó é comparativamente alta do que as listas vinculadas individualmente. Consulte um nó de exemplo no código abaixo
Exemplo: Digamos que temos 8 elementos, então sqrt(8)=2,82 que arredonda para 3. Portanto, cada bloco armazenará 3 elementos. Portanto, para armazenar 8 elementos, serão criados 3 blocos, dos quais os dois primeiros blocos armazenarão 3 elementos e o último bloco armazenará 2 elementos.
Como a pesquisa se torna melhor em listas vinculadas desenroladas?
Portanto, tomando o exemplo acima, se quisermos procurar o 7º elemento da lista, percorremos a lista de blocos até aquele que contém o 7º elemento. Leva apenas O(sqrt(n)) já que descobrimos que não ultrapassamos os blocos sqrt(n).
Implementação simples:
O programa abaixo cria uma lista vinculada simples desenrolada com 3 nós contendo um número variável de elementos em cada um. Ele também percorre a lista criada.
C++ // C++ program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include using namespace std ; #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public : int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) cout < < n -> array [ i ] < < ' ' ; // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { Node * head = NULL ; Node * second = NULL ; Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; } // This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C // C program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include #include #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node struct Node { int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; struct Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( struct Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' n -> array [ i ]); // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { struct Node * head = NULL ; struct Node * second = NULL ; struct Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); second = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); third = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static final int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node static class Node { int numElements ; int [] array = new int [ maxElements ] ; Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) System . out . print ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Python3 # Python3 program to implement unrolled # linked list and traversing it. maxElements = 4 # Unrolled Linked List Node class Node : def __init__ ( self ): self . numElements = 0 self . array = [ 0 for i in range ( maxElements )] self . next = None # Function to traverse an unrolled linked list # and print all the elements def printUnrolledList ( n ): while ( n != None ): # Print elements in current node for i in range ( n . numElements ): print ( n . array [ i ] end = ' ' ) # Move to next node n = n . next # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : head = None second = None third = None # Allocate 3 Nodes head = Node () second = Node () third = Node () # Let us put some values in second # node (Number of values must be # less than or equal to # maxElement) head . numElements = 3 head . array [ 0 ] = 1 head . array [ 1 ] = 2 head . array [ 2 ] = 3 # Link first Node with the second Node head . next = second # Let us put some values in second node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) second . numElements = 3 second . array [ 0 ] = 4 second . array [ 1 ] = 5 second . array [ 2 ] = 6 # Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third # Let us put some values in third node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 third . array [ 0 ] = 7 third . array [ 1 ] = 8 third . array [ 2 ] = 9 third . next = None printUnrolledList ( head ) # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# // C# program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. using System ; class GFG { static readonly int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public int numElements ; public int [] array = new int [ maxElements ]; public Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) Console . Write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void Main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. const maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { constructor () { this . numElements = 0 ; this . array = new Array ( maxElements ); this . next = null ; } } // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements function printUnrolledList ( n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( var i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) document . write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes var head = null ; var second = null ; var third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); < /script>
Saída
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Análise de Complexidade:
Neste artigo apresentamos uma lista desenrolada e suas vantagens. Também mostramos como percorrer a lista. No próximo artigo discutiremos a exclusão de inserção e os valores de maxElements/numElements em detalhes.
Inserção em lista vinculada desenrolada
Criar questionário