Achatar uma lista vinculada de vários níveis (em termos de profundidade)
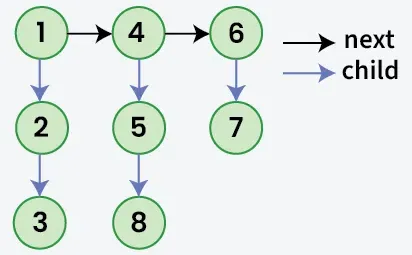
Dada uma lista vinculada onde, além do próximo ponteiro cada nó tem um criança ponteiro que pode ou não apontar para uma lista separada. Essas listas secundárias podem ter um ou mais seus próprios filhos para produzir multinível lista vinculada. Considerando a cabeça do da lista. A tarefa é achatar a lista para que todos os nós apareçam em um nível único lista vinculada. Achate a lista de forma que todos os nós no primeiro nível deveria vir primeiro então nós do segundo nível e assim por diante.
Exemplos:
Entrada:

Saída: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
Explicação: A lista vinculada multinível é nivelada porque não possui ponteiros filhos.
Nós discutimos nivelamento de uma lista vinculada de vários níveis onde os nós têm dois ponteiros para baixo e próximo. No post anterior nós achatado a lista vinculada em termos de nível. Como nivelar uma lista vinculada quando sempre precisamos processar o ponteiro para baixo antes do próximo em cada nó.
Índice
- [Abordagem esperada] Usando recursão - O(n) Tempo e O(n) Espaço
- [Abordagem alternativa] Usando pilha - O(n) Tempo e O(n) Espaço
[Abordagem esperada] Usando recursão - O(n) Tempo e O(n) Espaço
C++A abordagem é achatar um vinculado multinível list percorrendo cada nó e seus nós filhos. Primeiro achatar a lista infantil usando recursão. Depois que a lista filho estiver nivelada, prossiga para o próximo nó na sequência. Durante a travessia mantenha um referência para o nó visitado anteriormente and link it to the current node. Este processo garante que todos os nós de diferentes níveis estejam conectados em um lista linear única preservando ao mesmo tempo o ordem em profundidade.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * curr Node *& prev ) { if ( curr == nullptr ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node * next = curr -> next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr -> down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); Node * prev = nullptr ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node curr Node [] prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] != null ) prev [ 0 ] . next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node [] prev = new Node [ 1 ] ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( curr prev ): if curr is None : return # Add the current element to the list. if prev [ 0 ] is not None : prev [ 0 ] . next = curr prev [ 0 ] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr . next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list ( curr . down prev ) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list ( next_node prev ) def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr is not None : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) prev = [ None ] flatten_list ( head prev ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node curr ref Node prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList ( curr . down ref prev ); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList ( next ref prev ); } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node prev = null ; FlattenList ( head ref prev ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( curr prev ) { if ( curr === null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] !== null ) prev [ 0 ]. next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer let next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); let prev = [ null ]; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head );
Saída
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[Abordagem Alternativa] Usando Pilha - O(n) Tempo e O(n) Espaço
C++A abordagem consiste em percorrer lista vinculada multinível usando um pilha . Comece por empurrando o nó principal na pilha. Então enquanto o a pilha não está vazia pop o nó superior e processe-o. Para cada nó empurrar isso é ponteiros para próximo e para baixo (se existirem) na pilha. Durante este processo vincular o nó atual ao nó anterior mantendo a lista de forma achatada. A travessia garante que nós de todos os níveis estejam conectados em um lista vinculada de nível único preservando a ordem em profundidade.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * head ) { if ( head == nullptr ) return ; stack < Node *> st ; st . push ( head ); Node * prev = nullptr ; while ( ! st . empty ()) { Node * curr = st . top (); st . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr -> next != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr -> down != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack ; class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack <> (); stack . push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( ! stack . isEmpty ()) { Node curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( head ): if head is None : return stack = [ head ] prev = None while stack : curr = stack . pop () # Push the next node first if curr . next : stack . append ( curr . next ) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr . down : stack . append ( curr . down ) # Add the current element to the list if prev : prev . next = curr prev = curr def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) flatten_list ( head ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack < Node > (); stack . Push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( stack . Count > 0 ) { Node curr = stack . Pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . Push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . Push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); FlattenList ( head ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( head ) { if ( head === null ) return ; let stack = [ head ]; let prev = null ; while ( stack . length > 0 ) { let curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next !== null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down !== null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev !== null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head );
Saída
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28