Wyszukiwanie w drzewie wyszukiwania binarnego (BST)
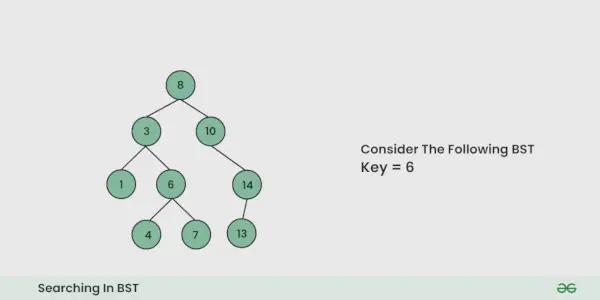
Dawać BST , zadaniem jest przeszukanie węzła w tym BST .
Aby wyszukać wartość w BST, rozważ ją jako posortowaną tablicę. Teraz możemy łatwo przeprowadzić operację wyszukiwania w BST za pomocą Algorytm wyszukiwania binarnego .
Algorytm wyszukiwania klucza w danym drzewie wyszukiwania binarnego:
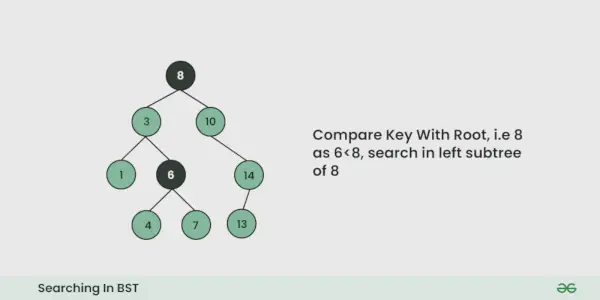
Załóżmy, że chcemy wyszukać numer X, Zaczynamy od korzenia. Następnie:
- Porównujemy szukaną wartość z wartością pierwiastka.
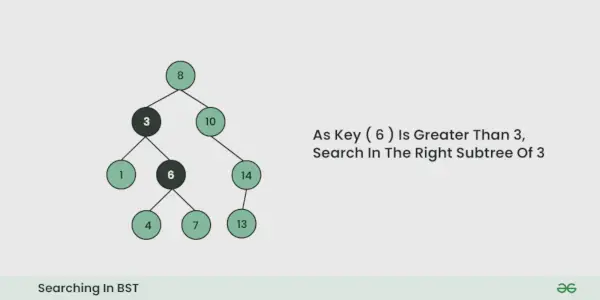
- Jeśli jest równa, kończymy wyszukiwanie, jeśli jest mniejsze, wiemy, że musimy przejść do lewego poddrzewa, ponieważ w drzewie wyszukiwania binarnego wszystkie elementy w lewym poddrzewie są mniejsze, a wszystkie elementy w prawym poddrzewie są większe.
- Powtarzaj powyższy krok, aż dalsze przejście nie będzie możliwe
- Jeśli w dowolnej iteracji zostanie znaleziony klucz, zwróć wartość True. Inaczej Fałsz.
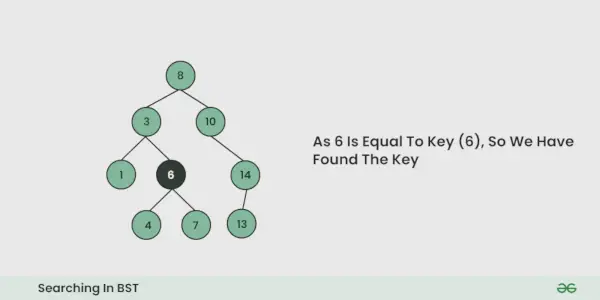
Ilustracja wyszukiwania w BST:
Aby lepiej zrozumieć, zobacz poniższą ilustrację:
Zalecana praktykaWyszukaj węzeł w BSTWypróbuj!

Program do implementacji wyszukiwania w BST:
C++
// C++ function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> using> namespace> std;> struct> node {> > int> key;> > struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(> int> item)> {> > struct> node* temp> > => new> struct> node;> > temp->klucz = element;> > temp->lewy = temp->prawy = NULL;> > return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(> struct> node* node,> int> key)> {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> newNode(key);> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key key)> > node->lewy = wstaw(węzeł->lewy, klawisz);> > else> if> (key>węzeł->klucz)> > node->prawo = wstaw(węzeł->prawo, klawisz);> > // Return the (unchanged) node pointer> > return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(> struct> node* root,> int> key)> > > // Base Cases: root is null or key is present at root> > if> (root == NULL> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> > struct> node* root = NULL;> > root = insert(root, 50);> > insert(root, 30);> > insert(root, 20);> > insert(root, 40);> > insert(root, 70);> > insert(root, 60);> > insert(root, 80);> > // Key to be found> > int> key = 6;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > cout < < key < <> ' not found'> < < endl;> > else> > cout < < key < <> ' found'> < < endl;> > key = 60;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > cout < < key < <> ' not found'> < < endl;> > else> > cout < < key < <> ' found'> < < endl;> > return> 0;> }> |
C
// C function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> #include> struct> node {> > int> key;> > struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(> int> item)> {> > struct> node* temp> > = (> struct> node*)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> struct> node));> > temp->klucz = element;> > temp->lewy = temp->prawy = NULL;> > return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(> struct> node* node,> int> key)> {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> newNode(key);> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key key)> > node->lewy = wstaw(węzeł->lewy, klawisz);> > else> if> (key>węzeł->klucz)> > node->prawo = wstaw(węzeł->prawo, klawisz);> > // Return the (unchanged) node pointer> > return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(> struct> node* root,> int> key)> > // Driver Code> int> main()> {> > struct> node* root = NULL;> > root = insert(root, 50);> > insert(root, 30);> > insert(root, 20);> > insert(root, 40);> > insert(root, 70);> > insert(root, 60);> > insert(root, 80);> > // Key to be found> > int> key = 6;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > printf> (> '%d not found
'> , key);> > else> > printf> (> '%d found
'> , key);> > key = 60;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > printf> (> '%d not found
'> , key);> > else> > printf> (> '%d found
'> , key);> > return> 0;> }> |
Jawa
// Java program to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node {> > int> key;> > Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item) {> > key = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> class> BinarySearchTree {> > Node root;> > // Constructor> > BinarySearchTree() {> > root => null> ;> > }> > // A utility function to insert> > // a new node with given key in BST> > Node insert(Node node,> int> key) {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node ==> null> ) {> > node => new> Node(key);> > return> node;> > }> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>węzeł.klucz) węzeł.prawo = wstaw(węzeł.prawo, klucz); // Zwraca (niezmieniony) wskaźnik węzła; zwraca węzeł; } // Funkcja narzędzia do wyszukiwania klucza w wyszukiwaniu węzła BST (główny węzeł, int klucz) // Kod sterownika public static void main(String[] args) { Drzewo BinarySearchTree = new BinarySearchTree(); // Wstawianie węzłów drzewo.root = drzewo.insert(drzewo.root, 50); drzewo.wstaw(drzewo.korzeń, 30); drzewo.wstaw(drzewo.korzeń, 20); drzewo.wstaw(korzeń drzewa, 40); drzewo.wstaw(korzeń drzewa, 70); drzewo.wstaw(korzeń drzewa, 60); drzewo.wstaw(drzewo.korzeń, 80); // Znaleziony klucz int klucz = 6; // Wyszukiwanie w BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' nie znaleziono'); else System.out.println(klucz + ' znaleziony'); klucz = 60; // Wyszukiwanie w BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' nie znaleziono'); else System.out.println(klucz + ' znaleziony'); } }> |
Python3
# Python3 function to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node:> > # Constructor to create a new node> > def> __init__(> self> , key):> > self> .key> => key> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # A utility function to insert> # a new node with the given key in BST> def> insert(node, key):> > # If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> node> is> None> :> > return> Node(key)> > # Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> key node.left = insert(node.left, key) elif key>node.key: node.right = wstaw(node.right, key) # Zwraca (niezmieniony) wskaźnik węzła return node # Funkcja narzędziowa do wyszukiwania klucza w BST def search(root, key): # Przypadki podstawowe: root is null lub klucz jest obecny w katalogu głównym, jeśli root to None lub root.key == klucz: return root # Klucz jest większy niż klucz root, jeśli root.key return search(root.right, key) # Klucz jest mniejszy niż root klawisz ' return search(root.left, key) # Kod sterownika if __name__ == '__main__': root = Brak root = wstaw(root, 50) wstaw(root, 30) wstaw(root, 20) wstaw (root, 40) wstaw(root, 70) wstaw(root, 60) wstaw(root, 80) # Klucz do znalezienia klucz = 6 # Wyszukiwanie w BST, jeśli search(root, klucz) ma wartość Brak: print(key, 'nie znaleziono') else: print(klucz, 'znaleziono') key = 60 # Wyszukiwanie w BST, jeśli search(root, klucz) to Brak: print(klucz, 'nie znaleziono') else: print(key, 'znaleziono')> |
C#
// C# function to search a given key in a given BST> using> System;> public> class> Node {> > public> int> key;> > public> Node left, right;> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> > // A utility function to create a new BST node> > public> Node NewNode(> int> item)> > {> > Node temp => new> Node();> > temp.key = item;> > temp.left = temp.right => null> ;> > return> temp;> > }> > // A utility function to insert> > // a new node with given key in BST> > public> Node Insert(Node node,> int> key)> > {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> NewNode(key);> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key node.left = Insert(node.left, key); else if (key>węzeł.klucz) węzeł.prawo = Wstaw(węzeł.prawo, klucz); // Zwraca (niezmieniony) wskaźnik węzła; zwraca węzeł; } // Funkcja narzędzia do wyszukiwania klucza w publicznym przeszukiwaniu węzła BST (korzeń węzła, klucz int) // Przypadki podstawowe: root ma wartość null lub klucz jest obecny w katalogu głównym if (root == null // Kod sterownika public static void Main () { Korzeń węzła = null; Drzewo binarne bt = nowe drzewo binarne(); root = bt.Insert(root, 50); bt.Insert(root, 20); , 40); bt.Insert(root, 70); bt.Insert(root, 60); bt.Insert(root, 80); // Klucz do znalezienia int klucz = 6; // Wyszukiwanie w BST if ( bt.Search(root, klucz) == null) Console.WriteLine(key + ' nie znaleziono'); else Console.WriteLine(key + ' znaleziono'); // Wyszukiwanie w BST if (bt.Search(root, klucz) == null) Console.WriteLine(key + ' nie znaleziono'); else Console.WriteLine(key + ' znaleziono'); |
>
// Javascript function to search a given key in a given BST>class Node {>>constructor(key) {>>this>.key = key;>>this>.left =>null>;>>this>.right =>null>;>>}>}>// A utility function to insert>// a new node with given key in BST>function>insert(node, key) {>>// If the tree is empty, return a new node>>if>(node ===>null>) {>>return>new>Node(key);>>}>>// Otherwise, recur down the tree>>if>(key node.left = insert(node.left, key); } else if (key>węzeł.klucz) { węzeł.prawy = wstaw(węzeł.prawy, klucz); } // Zwraca (niezmieniony) wskaźnik węzła; zwraca węzeł; } // Funkcja narzędziowa do wyszukiwania klucza w funkcji BST search(root, key) { // Przypadki podstawowe: root ma wartość null lub klucz jest obecny w katalogu głównym if (root === null || root.key === klucz ) {zwróć korzeń; } // Klucz jest większy niż klucz roota if (root.key return search(root.right, key); } // Klucz jest mniejszy niż klucz roota return search(root.left, key); } // Kod sterownika let root = null; wstaw (korzeń, 50); wstaw (korzeń, 20); wstaw (korzeń, 40); 60); wstaw(root, 80); // Znaleziono klucz niech klucz = 6; // Wyszukiwanie w BST if (search(root, klucz) === null) { console.log(key + ' not znaleziony'); } else { console.log(key + ' znaleziony' } key = 60; // Wyszukiwanie w BST if (search(root, klucz) === null) { console.log( klucz + ' nie znaleziono'); else { konsola.log(klucz + ' znaleziono');
>
Złożoność czasowa: O(h), gdzie h jest wysokością BST.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(h), gdzie h jest wysokością BST. Dzieje się tak, ponieważ maksymalna ilość miejsca potrzebna do przechowywania stosu rekurencji będzie wynosić H .Powiązane linki:
- Operacja wstawiania drzewa wyszukiwania binarnego
- Operacja usuwania drzewa wyszukiwania binarnego