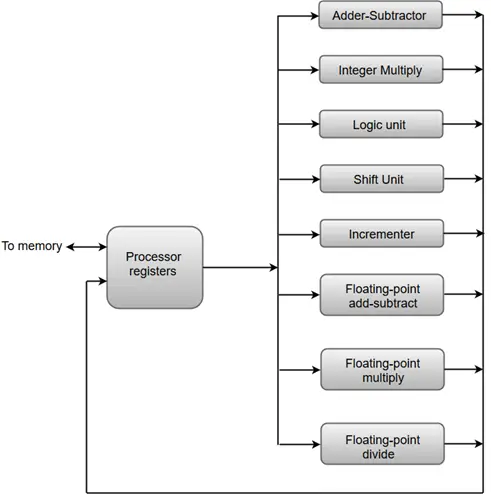
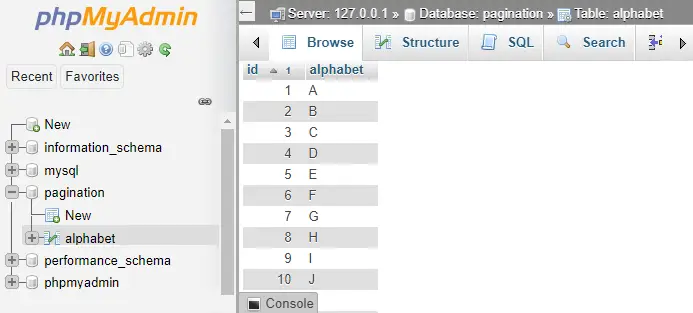
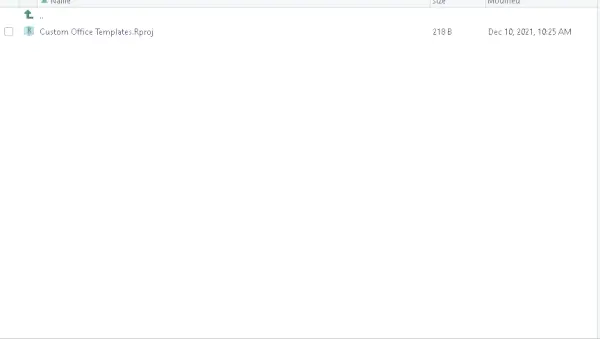
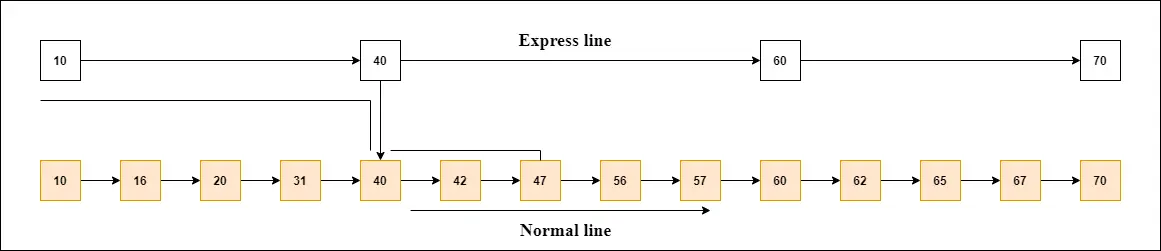
Ciąg Java jest pusty()
The Klasa ciągów Java isEmpty() Metoda sprawdza, czy ciąg wejściowy jest pusty, czy nie. Zauważ, że tutaj pusty oznacza, że liczba znaków zawartych w ciągu wynosi zero.
Podpis
Sygnaturę lub składnię metody string isEmpty() podano poniżej:
public boolean isEmpty()
Zwroty
true, jeśli długość wynosi 0, w przeciwnym razie false.
Od
1.6
Wdrożenie wewnętrzne
public boolean isEmpty() { return value.length == 0; } Przykład metody Java String isEmpty().
Nazwa pliku: StringIsEmptyExample.java
public class IsEmptyExample{ public static void main(String args[]){ String s1=''; String s2='javatpoint'; System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); System.out.println(s2.isEmpty()); }} Przetestuj teraz Wyjście:
true false
Metoda isEmpty() w języku Java Przykład 2
Nazwa pliku: StringIsEmptyExample2.java
public class IsEmptyExample2 { public static void main(String[] args) } Wyjście:
String s1 is empty Javatpoint
Puste vs. Ciągi zerowe
Wcześniej w tym samouczku omawialiśmy, że puste ciągi zawierają zero znaków. Jednak to samo dotyczy również łańcucha zerowego. Ciąg pusty to ciąg, który nie ma wartości.
String str = ''; // empty string String str1 = null; // null string. It is also not containing any characters.
Metoda isEmpty() nie nadaje się do sprawdzania ciągów zerowych. Poniższy przykład pokazuje to samo.
Nazwa pliku: StringIsEmptyExample3.java
public class StringIsEmptyExample3 { // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { String str = null; if(str.isEmpty()) { System.out.println('The string is null.'); } else { System.out.println('The string is not null.'); } } } Wyjście:
Exception in thread 'main' java.lang.NullPointerException at StringIsEmptyExample3.main(StringIsEmptyExample3.java:7)
Tutaj możemy użyć operatora ==, aby sprawdzić ciągi zerowe.
Nazwa pliku: StringIsEmptyExample4.java
class StringIsEmptyExample4 { // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { String str = null; if(str == null) { System.out.println('The string is null.'); } else { System.out.println('The string is not null.'); } } } Wyjście:
The string is null.
Puste ciągi
Puste ciągi to te ciągi, które zawierają tylko białe spacje. Metoda isEmpty() jest bardzo przydatna do sprawdzania pustych ciągów. Rozważ następujący przykład.
Nazwa pliku: StringIsEmptyExample5.java
public class StringIsEmptyExample5 { // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { // a blank string String str = ' '; int size = str.length(); // trim the white spaces and after that // if the string results in the empty string // then the string is blank; otherwise, not. if(size == 0) { System.out.println('The string is empty.
'); } else if(size > 0 && str.trim().isEmpty()) { System.out.println('The string is blank.
'); } else { System.out.println('The string is not blank.
'); } str = ' Welcome to JavaTpoint. '; size = str.length(); if(size == 0) { System.out.println('The string is empty.
'); } if(size > 0 && str.trim().isEmpty()) { System.out.println('The string is blank.
'); } else { System.out.println('The string is not blank.
'); } } } Wyjście:
The string is blank. The string is not blank.