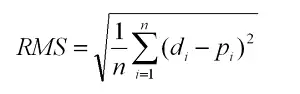Wstawienie do cyklicznej listy pojedynczo połączonej

W tym artykule dowiemy się, jak wstawić węzeł do cyklicznej listy połączonej. Wstawianie to podstawowa operacja na listach połączonych, która polega na dodaniu nowego węzła do listy. Na liście połączonej cyklicznie ostatni węzeł łączy się z pierwszym węzłem, tworząc pętlę.
Istnieją cztery główne sposoby dodawania elementów:
- Wstawienie na pustą listę
- Wstawienie na początku listy
- Wstawienie na końcu listy
- Wstawienie na konkretną pozycję na liście
Zalety używania wskaźnika ogona zamiast wskaźnika głowy
Musimy przeszukać całą listę, żeby na początku wstawić węzeł. Również w celu wstawienia na końcu należy przejść całą listę. Jeżeli zamiast start pointer, przenosimy wskaźnik do ostatniego węzła, wtedy w obu przypadkach nie będzie potrzeby przeglądania całej listy. Zatem wstawienie na początku lub na końcu zajmuje stały czas, niezależnie od długości listy.
1. Wstawienie do pustej listy w okrągłej liście połączonej
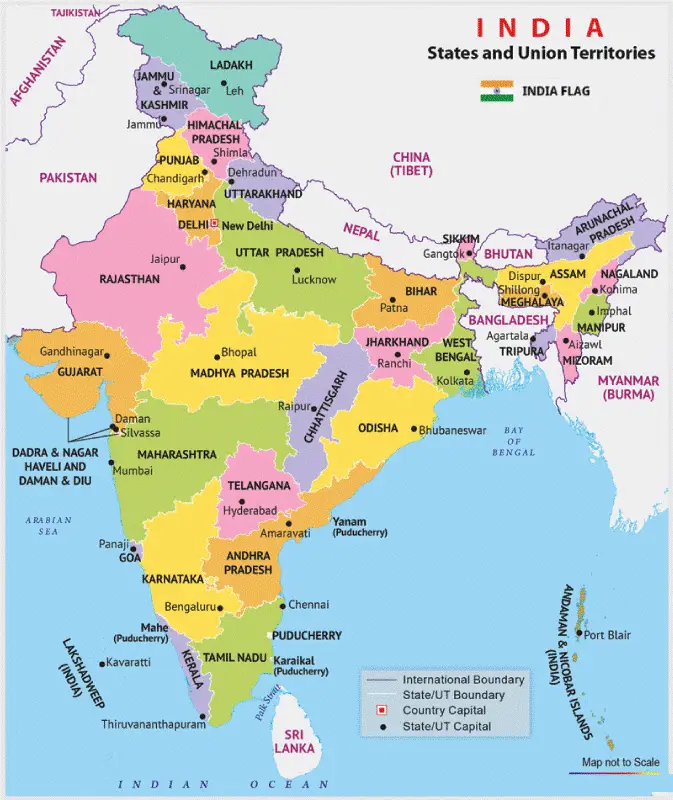
Aby wstawić węzeł do pustej listy połączonej cyklicznie, tworzy się plik nowy węzeł z podanymi danymi ustawia swój następny wskaźnik tak, aby wskazywał na siebie i aktualizuje ostatni wskaźnik, aby się do tego odnieść nowy węzeł .
 Wstawienie do pustej listy
Wstawienie do pustej listy Podejście krok po kroku:
- Sprawdź, czy ostatni nie jest nullptr . Jeśli PRAWDA powrót ostatni (lista nie jest pusta).
- W przeciwnym razie utwórz nowy węzeł z podanymi danymi.
- Ustaw nowy węzeł następny wskaźnik wskazujący na siebie (link cykliczny).
- Aktualizacja ostatni wskazać na nowy węzeł i zwróć to.
Aby przeczytać więcej na temat wstawiania na pustą listę, zobacz: Wstawienie do pustej listy w cyklicznej liście połączonej
2. Wstawienie na początku w cyklicznie połączonej liście
Aby wstawić nowy węzeł na początku listy połączonej cyklicznie
- Najpierw tworzymy nowy węzeł i przydziel mu pamięć.
- Jeśli lista jest pusta (na co wskazuje ostatni wskaźnik NIEWAŻNY ) robimy nowy węzeł wskazywać na siebie.
- Jeśli lista zawiera już węzły, ustawiamy nowy węzeł następny wskaźnik wskazujący na obecna głowa z listy (tzn ostatni -> następny )
- Następnie zaktualizuj następny wskaźnik ostatniego węzła, aby wskazywał na nowy węzeł . Zachowuje to cykliczną strukturę listy.
 Wstawienie na początku w cyklicznej liście połączonej
Wstawienie na początku w cyklicznej liście połączonej Aby przeczytać więcej o wstawianiu na początku, zobacz: Wstawienie na początku w cyklicznej liście połączonej
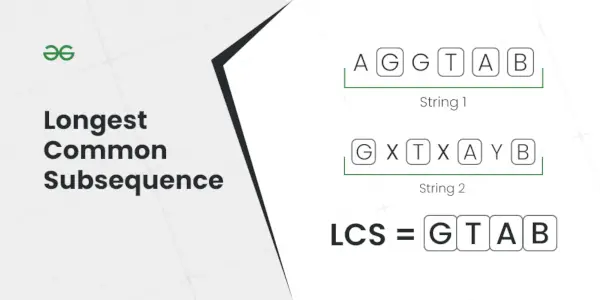
3. Wstawienie na końcu listy z linkami cyklicznymi
Aby wstawić nowy węzeł na końcu listy połączonej cyklicznie, najpierw tworzymy nowy węzeł i przydzielamy mu pamięć.
- Jeśli lista jest pusta (tzn ostatni Lub ogon istota wskazująca NIEWAŻNY ) inicjujemy listę za pomocą nowy węzeł i skierowanie go na siebie, tworząc okrągłą strukturę.
- Jeśli lista zawiera już węzły, ustawiamy nowy węzeł następny wskaźnik wskazujący na obecna głowa (czyli ogon->dalej )
- Następnie zaktualizuj obecny ogon następny wskaźnik wskazujący na nowy węzeł .
- Na koniec aktualizujemy wskaźnik ogona do nowy węzeł.
- Zapewni to, że nowy węzeł jest teraz ostatni węzeł na liście, zachowując powiązanie cykliczne.
 Wstawienie na końcu okrągłej listy połączonej
Wstawienie na końcu okrągłej listy połączonej Aby przeczytać więcej o wstawianiu na końcu, zobacz: Wstawienie na końcu okrągłej listy połączonej
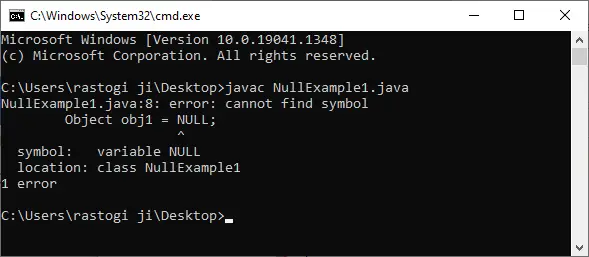
4. Wstawienie w określonej pozycji na liście połączonej cyklicznie
Aby wstawić nowy węzeł w określonej pozycji na liście połączonej cyklicznie, najpierw sprawdzamy, czy lista jest pusta.
- Jeśli tak jest i pozycja nie jest 1 następnie wypisujemy komunikat o błędzie, ponieważ pozycja nie istnieje na liście. I
- f pozycja Jest 1 następnie tworzymy nowy węzeł i sprawić, że będzie to wskazywało na siebie.
- Jeżeli lista nie jest pusta tworzymy plik nowy węzeł i przejrzyj listę, aby znaleźć właściwy punkt wstawiania.
- Jeśli pozycja Jest 1 wstawiamy nowy węzeł na początku, odpowiednio dostosowując wskazówki.
- W przypadku innych pozycji przeglądamy listę, aż dotrzemy do żądanej pozycji i wstawiamy nowy węzeł poprzez aktualizację wskaźników.
- Jeśli na końcu zostanie wstawiony nowy węzeł, aktualizujemy również plik ostatni wskaźnik odnoszący się do nowego węzła, zachowując cykliczną strukturę listy.
 Wstawienie w określonej pozycji na liście połączonej cyklicznie
Wstawienie w określonej pozycji na liście połączonej cyklicznie Podejście krok po kroku:
- Jeśli ostatni Jest nullptr I poz nie jest 1 drukuj ' Nieprawidłowa pozycja! '.
- W przeciwnym razie Utwórz nowy węzeł z podanymi danymi.
- Wstaw na początku: Jeśli poz ma wartość 1, zaktualizuj wskaźniki i wróć jako ostatni.
- Lista trawersów: Pętla, aby znaleźć punkt wstawienia; print 'Nieprawidłowa pozycja!' jeśli poza granicami.
- Wstaw węzeł: Zaktualizuj wskaźniki, aby wstawić nowy węzeł.
- Aktualizacja ostatnia: Jeśli wstawiono na końcu aktualizacji ostatni .
#include using namespace std ; struct Node { int data ; Node * next ; Node ( int value ){ data = value ; next = nullptr ; } }; // Function to insert a node at a specific position in a circular linked list Node * insertAtPosition ( Node * last int data int pos ){ if ( last == nullptr ){ // If the list is empty if ( pos != 1 ){ cout < < 'Invalid position!' < < endl ; return last ; } // Create a new node and make it point to itself Node * newNode = new Node ( data ); last = newNode ; last -> next = last ; return last ; } // Create a new node with the given data Node * newNode = new Node ( data ); // curr will point to head initially Node * curr = last -> next ; if ( pos == 1 ){ // Insert at the beginning newNode -> next = curr ; last -> next = newNode ; return last ; } // Traverse the list to find the insertion point for ( int i = 1 ; i < pos - 1 ; ++ i ) { curr = curr -> next ; // If position is out of bounds if ( curr == last -> next ){ cout < < 'Invalid position!' < < endl ; return last ; } } // Insert the new node at the desired position newNode -> next = curr -> next ; curr -> next = newNode ; // Update last if the new node is inserted at the end if ( curr == last ) last = newNode ; return last ; } void printList ( Node * last ){ if ( last == NULL ) return ; Node * head = last -> next ; while ( true ){ cout < < head -> data < < ' ' ; head = head -> next ; if ( head == last -> next ) break ; } cout < < endl ; } int main (){ // Create circular linked list: 2 3 4 Node * first = new Node ( 2 ); first -> next = new Node ( 3 ); first -> next -> next = new Node ( 4 ); Node * last = first -> next -> next ; last -> next = first ; cout < < 'Original list: ' ; printList ( last ); // Insert elements at specific positions int data = 5 pos = 2 ; last = insertAtPosition ( last data pos ); cout < < 'List after insertions: ' ; printList ( last ); return 0 ; }
C #include #include // Define the Node structure struct Node { int data ; struct Node * next ; }; struct Node * createNode ( int value ); // Function to insert a node at a specific position in a circular linked list struct Node * insertAtPosition ( struct Node * last int data int pos ) { if ( last == NULL ) { // If the list is empty if ( pos != 1 ) { printf ( 'Invalid position! n ' ); return last ; } // Create a new node and make it point to itself struct Node * newNode = createNode ( data ); last = newNode ; last -> next = last ; return last ; } // Create a new node with the given data struct Node * newNode = createNode ( data ); // curr will point to head initially struct Node * curr = last -> next ; if ( pos == 1 ) { // Insert at the beginning newNode -> next = curr ; last -> next = newNode ; return last ; } // Traverse the list to find the insertion point for ( int i = 1 ; i < pos - 1 ; ++ i ) { curr = curr -> next ; // If position is out of bounds if ( curr == last -> next ) { printf ( 'Invalid position! n ' ); return last ; } } // Insert the new node at the desired position newNode -> next = curr -> next ; curr -> next = newNode ; // Update last if the new node is inserted at the end if ( curr == last ) last = newNode ; return last ; } // Function to print the circular linked list void printList ( struct Node * last ) { if ( last == NULL ) return ; struct Node * head = last -> next ; while ( 1 ) { printf ( '%d ' head -> data ); head = head -> next ; if ( head == last -> next ) break ; } printf ( ' n ' ); } // Function to create a new node struct Node * createNode ( int value ) { struct Node * newNode = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); newNode -> data = value ; newNode -> next = NULL ; return newNode ; } int main () { // Create circular linked list: 2 3 4 struct Node * first = createNode ( 2 ); first -> next = createNode ( 3 ); first -> next -> next = createNode ( 4 ); struct Node * last = first -> next -> next ; last -> next = first ; printf ( 'Original list: ' ); printList ( last ); // Insert elements at specific positions int data = 5 pos = 2 ; last = insertAtPosition ( last data pos ); printf ( 'List after insertions: ' ); printList ( last ); return 0 ; }
Java class Node { int data ; Node next ; Node ( int value ){ data = value ; next = null ; } } public class GFG { // Function to insert a node at a specific position in a // circular linked list static Node insertAtPosition ( Node last int data int pos ){ if ( last == null ) { // If the list is empty if ( pos != 1 ) { System . out . println ( 'Invalid position!' ); return last ; } // Create a new node and make it point to itself Node newNode = new Node ( data ); last = newNode ; last . next = last ; return last ; } // Create a new node with the given data Node newNode = new Node ( data ); // curr will point to head initially Node curr = last . next ; if ( pos == 1 ) { // Insert at the beginning newNode . next = curr ; last . next = newNode ; return last ; } // Traverse the list to find the insertion point for ( int i = 1 ; i < pos - 1 ; ++ i ) { curr = curr . next ; // If position is out of bounds if ( curr == last . next ) { System . out . println ( 'Invalid position!' ); return last ; } } // Insert the new node at the desired position newNode . next = curr . next ; curr . next = newNode ; // Update last if the new node is inserted at the // end if ( curr == last ) last = newNode ; return last ; } static void printList ( Node last ){ if ( last == null ) return ; Node head = last . next ; while ( true ) { System . out . print ( head . data + ' ' ); head = head . next ; if ( head == last . next ) break ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create circular linked list: 2 3 4 Node first = new Node ( 2 ); first . next = new Node ( 3 ); first . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); Node last = first . next . next ; last . next = first ; System . out . print ( 'Original list: ' ); printList ( last ); // Insert elements at specific positions int data = 5 pos = 2 ; last = insertAtPosition ( last data pos ); System . out . print ( 'List after insertions: ' ); printList ( last ); } }
Python class Node : def __init__ ( self value ): self . data = value self . next = None # Function to insert a node at a specific position in a circular linked list def insertAtPosition ( last data pos ): if last is None : # If the list is empty if pos != 1 : print ( 'Invalid position!' ) return last # Create a new node and make it point to itself new_node = Node ( data ) last = new_node last . next = last return last # Create a new node with the given data new_node = Node ( data ) # curr will point to head initially curr = last . next if pos == 1 : # Insert at the beginning new_node . next = curr last . next = new_node return last # Traverse the list to find the insertion point for i in range ( 1 pos - 1 ): curr = curr . next # If position is out of bounds if curr == last . next : print ( 'Invalid position!' ) return last # Insert the new node at the desired position new_node . next = curr . next curr . next = new_node # Update last if the new node is inserted at the end if curr == last : last = new_node return last # Function to print the circular linked list def print_list ( last ): if last is None : return head = last . next while True : print ( head . data end = ' ' ) head = head . next if head == last . next : break print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create circular linked list: 2 3 4 first = Node ( 2 ) first . next = Node ( 3 ) first . next . next = Node ( 4 ) last = first . next . next last . next = first print ( 'Original list: ' end = '' ) print_list ( last ) # Insert elements at specific positions data = 5 pos = 2 last = insertAtPosition ( last data pos ) print ( 'List after insertions: ' end = '' ) print_list ( last )
JavaScript class Node { constructor ( value ){ this . data = value ; this . next = null ; } } // Function to insert a node at a specific position in a // circular linked list function insertAtPosition ( last data pos ) { if ( last === null ) { // If the list is empty if ( pos !== 1 ) { console . log ( 'Invalid position!' ); return last ; } // Create a new node and make it point to itself let newNode = new Node ( data ); last = newNode ; last . next = last ; return last ; } // Create a new node with the given data let newNode = new Node ( data ); // curr will point to head initially let curr = last . next ; if ( pos === 1 ) { // Insert at the beginning newNode . next = curr ; last . next = newNode ; return last ; } // Traverse the list to find the insertion point for ( let i = 1 ; i < pos - 1 ; ++ i ) { curr = curr . next ; // If position is out of bounds if ( curr === last . next ) { console . log ( 'Invalid position!' ); return last ; } } // Insert the new node at the desired position newNode . next = curr . next ; curr . next = newNode ; // Update last if the new node is inserted at the end if ( curr === last ) last = newNode ; return last ; } // Function to print the circular linked list function printList ( last ){ if ( last === null ) return ; let head = last . next ; while ( true ) { console . log ( head . data + ' ' ); head = head . next ; if ( head === last . next ) break ; } console . log (); } // Create circular linked list: 2 3 4 let first = new Node ( 2 ); first . next = new Node ( 3 ); first . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); let last = first . next . next ; last . next = first ; console . log ( 'Original list: ' ); printList ( last ); // Insert elements at specific positions let data = 5 ; let pos = 2 ; last = insertAtPosition ( last data pos ); console . log ( 'List after insertions: ' ); printList ( last );
Wyjście
Original list: 2 3 4 List after insertions: 2 5 3 4
Złożoność czasowa: O(n) musimy przeszukać listę, aby znaleźć konkretną pozycję.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(1)