Znajdź, czy podtablica ma postać góry, czy nie

Wypróbuj w praktyce GfG  #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; } Dana jest tablica liczb całkowitych i zakres, który musimy sprawdzić, czy podtablica mieszcząca się w tym zakresie ma wartości w postaci góry, czy nie. Mówi się, że wszystkie wartości podtablicy mają postać góry, jeśli wszystkie wartości rosną lub maleją, albo najpierw rosną, a następnie maleją.
Bardziej formalnie podtablica [a1 a2 a3…aN] mówi się, że ma postać góry, jeśli istnieje liczba całkowita K 1 <= K <= N such that
a1 <= a2 <= a3 .. <= aK >= a(K+1) >= a(K+2) …. >= N
Przykłady:
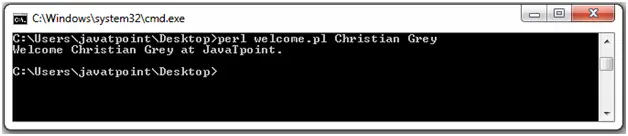
Input : Arr[] = [2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2] Range = [0 2] Output : Yes Explanation: The output is yes subarray is [2 3 2] so subarray first increases and then decreases Input: Arr[] = [2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2] Range = [2 7] Output: Yes Explanation: The output is yes subarray is [2 4 4 6 3 2] so subarray first increases and then decreases Input: Arr[]= [2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2] Range = [1 3] Output: no Explanation: The output is no subarray is [3 2 4] so subarray is not in the form above statedRecommended Practice Problem z podtablicą górską Spróbuj!
Rozwiązanie:
- Utwórz dwie dodatkowe przestrzenie o długości N lewy I Prawidłowy i dodatkowa zmienna ostatniptr
- Zainicjuj lewo[0] = 0 i ostatniptr = 0
- Przejdź przez oryginalną tablicę od drugiego indeksu do końca
- Dla każdego indeksu sprawdź, czy jest większy niż poprzedni element, jeśli tak, zaktualizuj plik ostatniptr z aktualnym indeksem.
- Dla każdego magazynu indeksów ostatniptr W lewo [i]
- zainicjować prawy[N-1] = N-1 i ostatniptr = N-1
- Przejdź przez oryginalną tablicę od przedostatniego indeksu do początku
- Dla każdego indeksu sprawdź, czy jest większy niż następny element, jeśli tak, zaktualizuj plik ostatniptr z aktualnym indeksem.
- Dla każdego magazynu indeksów ostatniptr W prawda [ja]
- Teraz przetwórz zapytania
- dla każdego zapytania l r Jeśli prawy[l] >= lewy[r] następnie wydrukuj Tak w przeciwnym razie NIE
// C++ program to check whether a subarray is in // mountain form or not #include using namespace std ; // Utility method to construct left and right array int preprocess ( int arr [] int N int left [] int right []) { // Initialize first left index as that index only left [ 0 ] = 0 ; int lastIncr = 0 ; for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // if current value is greater than previous // update last increasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i - 1 ]) lastIncr = i ; left [ i ] = lastIncr ; } // Initialize last right index as that index only right [ N - 1 ] = N - 1 ; int firstDecr = N - 1 ; for ( int i = N - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { // if current value is greater than next // update first decreasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i + 1 ]) firstDecr = i ; right [ i ] = firstDecr ; } } // Method returns true if arr[L..R] is in mountain form bool isSubarrayMountainForm ( int arr [] int left [] int right [] int L int R ) { // return true only if right at starting range is // greater than left at ending range return ( right [ L ] >= left [ R ]); } // Driver code to test above methods int main () { int arr [] = { 2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2 }; int N = sizeof ( arr ) / sizeof ( int ); int left [ N ] right [ N ]; preprocess ( arr N left right ); int L = 0 ; int R = 2 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) cout < < 'Subarray is in mountain form n ' ; else cout < < 'Subarray is not in mountain form n ' ; L = 1 ; R = 3 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) cout < < 'Subarray is in mountain form n ' ; else cout < < 'Subarray is not in mountain form n ' ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to check whether a subarray is in // mountain form or not class SubArray { // Utility method to construct left and right array static void preprocess ( int arr [] int N int left [] int right [] ) { // initialize first left index as that index only left [ 0 ] = 0 ; int lastIncr = 0 ; for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // if current value is greater than previous // update last increasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i - 1 ] ) lastIncr = i ; left [ i ] = lastIncr ; } // initialize last right index as that index only right [ N - 1 ] = N - 1 ; int firstDecr = N - 1 ; for ( int i = N - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { // if current value is greater than next // update first decreasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i + 1 ] ) firstDecr = i ; right [ i ] = firstDecr ; } } // method returns true if arr[L..R] is in mountain form static boolean isSubarrayMountainForm ( int arr [] int left [] int right [] int L int R ) { // return true only if right at starting range is // greater than left at ending range return ( right [ L ] >= left [ R ] ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int arr [] = { 2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2 }; int N = arr . length ; int left [] = new int [ N ] ; int right [] = new int [ N ] ; preprocess ( arr N left right ); int L = 0 ; int R = 2 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) System . out . println ( 'Subarray is in mountain form' ); else System . out . println ( 'Subarray is not in mountain form' ); L = 1 ; R = 3 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) System . out . println ( 'Subarray is in mountain form' ); else System . out . println ( 'Subarray is not in mountain form' ); } } // This Code is Contributed by Saket Kumar
Python3 # Python 3 program to check whether a subarray is in # mountain form or not # Utility method to construct left and right array def preprocess ( arr N left right ): # initialize first left index as that index only left [ 0 ] = 0 lastIncr = 0 for i in range ( 1 N ): # if current value is greater than previous # update last increasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i - 1 ]): lastIncr = i left [ i ] = lastIncr # initialize last right index as that index only right [ N - 1 ] = N - 1 firstDecr = N - 1 i = N - 2 while ( i >= 0 ): # if current value is greater than next # update first decreasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i + 1 ]): firstDecr = i right [ i ] = firstDecr i -= 1 # method returns true if arr[L..R] is in mountain form def isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R ): # return true only if right at starting range is # greater than left at ending range return ( right [ L ] >= left [ R ]) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2 ] N = len ( arr ) left = [ 0 for i in range ( N )] right = [ 0 for i in range ( N )] preprocess ( arr N left right ) L = 0 R = 2 if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )): print ( 'Subarray is in mountain form' ) else : print ( 'Subarray is not in mountain form' ) L = 1 R = 3 if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )): print ( 'Subarray is in mountain form' ) else : print ( 'Subarray is not in mountain form' ) # This code is contributed by # Surendra_Gangwar
C# // C# program to check whether // a subarray is in mountain // form or not using System ; class GFG { // Utility method to construct // left and right array static void preprocess ( int [] arr int N int [] left int [] right ) { // initialize first left // index as that index only left [ 0 ] = 0 ; int lastIncr = 0 ; for ( int i = 1 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // if current value is // greater than previous // update last increasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i - 1 ]) lastIncr = i ; left [ i ] = lastIncr ; } // initialize last right // index as that index only right [ N - 1 ] = N - 1 ; int firstDecr = N - 1 ; for ( int i = N - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { // if current value is // greater than next // update first decreasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i + 1 ]) firstDecr = i ; right [ i ] = firstDecr ; } } // method returns true if // arr[L..R] is in mountain form static bool isSubarrayMountainForm ( int [] arr int [] left int [] right int L int R ) { // return true only if right at // starting range is greater // than left at ending range return ( right [ L ] >= left [ R ]); } // Driver Code static public void Main () { int [] arr = { 2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2 }; int N = arr . Length ; int [] left = new int [ N ]; int [] right = new int [ N ]; preprocess ( arr N left right ); int L = 0 ; int R = 2 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) Console . WriteLine ( 'Subarray is in ' + 'mountain form' ); else Console . WriteLine ( 'Subarray is not ' + 'in mountain form' ); L = 1 ; R = 3 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) Console . WriteLine ( 'Subarray is in ' + 'mountain form' ); else Console . WriteLine ( 'Subarray is not ' + 'in mountain form' ); } } // This code is contributed by aj_36
JavaScript < script > // Javascript program to check whether // a subarray is in mountain // form or not // Utility method to construct // left and right array function preprocess ( arr N left right ) { // initialize first left // index as that index only left [ 0 ] = 0 ; let lastIncr = 0 ; for ( let i = 1 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // if current value is // greater than previous // update last increasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i - 1 ]) lastIncr = i ; left [ i ] = lastIncr ; } // initialize last right // index as that index only right [ N - 1 ] = N - 1 ; let firstDecr = N - 1 ; for ( let i = N - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { // if current value is // greater than next // update first decreasing if ( arr [ i ] > arr [ i + 1 ]) firstDecr = i ; right [ i ] = firstDecr ; } } // method returns true if // arr[L..R] is in mountain form function isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R ) { // return true only if right at // starting range is greater // than left at ending range return ( right [ L ] >= left [ R ]); } let arr = [ 2 3 2 4 4 6 3 2 ]; let N = arr . length ; let left = new Array ( N ); let right = new Array ( N ); preprocess ( arr N left right ); let L = 0 ; let R = 2 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) document . write ( 'Subarray is in ' + 'mountain form' + ' ' ); else document . write ( 'Subarray is not ' + 'in mountain form' + ' ' ); L = 1 ; R = 3 ; if ( isSubarrayMountainForm ( arr left right L R )) document . write ( 'Subarray is in ' + 'mountain form' ); else document . write ( 'Subarray is not ' + 'in mountain form' ); < /script>
Subarray is in mountain form Subarray is not in mountain form
Potrzebne są tylko dwa przejścia, więc złożoność czasowa wynosi O (n).
Wymagane są dwie dodatkowe przestrzenie o długości n, więc złożoność przestrzeni wynosi O (n).
Może Ci Się Spodobać
Najpopularniejsze Artykuły
Kategoria
Ciekawe Artykuły