Dynamiczna tablica w Javie
Tablica ma stały rozmiar i jest jednorodna struktura danych . Ograniczeniem tablic jest to, że mają stały rozmiar. Oznacza to, że deklarując tablicę musimy określić liczbę jej elementów. Tutaj pojawia się pytanie, co jeśli chcemy wstawić element i nie ma już miejsca na nowy element? Tutaj koncepcja tablica dynamiczna powstaje. Dynamicznie zwiększa rozmiar tablicy.
W tej części zrozumiemy co to jest tablica dynamiczna, cechy tablicy dynamicznej, jak zmienić rozmiar tablicy dynamicznej, I jak zaimplementować tablicę dynamiczną w Javie .
Co to jest tablica dynamiczna?
Tablica dynamiczna to a zmienny rozmiar lista struktur danych. Rośnie automatycznie, gdy próbujemy wstawić element, jeśli nie ma już miejsca na nowy element. Pozwala nam dodawać i usuwać elementy. Przydziela pamięć w czasie wykonywania za pomocą sterty. Może zmieniać swój rozmiar w czasie działania.
W Jawa , Lista tablic jest implementacją o zmiennym rozmiarze. Implementuje interfejs List i udostępnia wszystkie metody związane z operacjami na listach. Siła tablicy dynamicznej wynosi:
- Szybkie wyszukiwanie
- Zmienny rozmiar
- Przyjazny dla pamięci podręcznej
Działanie tablicy dynamicznej
W tablicy dynamicznej elementy są przechowywane w sposób ciągły od początku tablicy, a pozostała przestrzeń pozostaje niewykorzystana. Możemy dodawać elementy, aż zarezerwowane odstępy zostaną całkowicie wykorzystane. Kiedy zarezerwowana przestrzeń jest wykorzystana i konieczne jest dodanie niektórych elementów. W takim przypadku należy zwiększyć rozmiar tablicy o stałym rozmiarze. Pamiętaj, że przed dołączeniem elementu alokujemy większą tablicę, kopiujemy elementy z tablicy i zwracamy nowo utworzoną tablicę.
Innym sposobem dodania elementu jest utworzenie najpierw funkcji, która utworzy nową tablicę o podwójnym rozmiarze, skopiuje wszystkie elementy ze starej tablicy i zwróci nową tablicę. Podobnie możemy również zmniejszyć rozmiar tablicy dynamicznej.
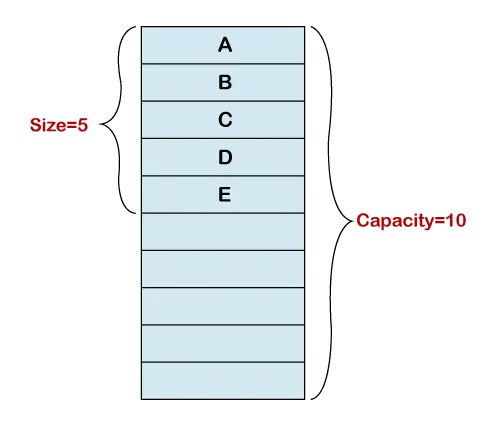
Rozmiar a pojemność
Inicjalizacja tablicy dynamicznej tworzy tablicę o stałym rozmiarze. Na poniższym rysunku implementacja tablicy ma 10 indeksów. Dodaliśmy pięć elementów do tablicy. Teraz podstawowa tablica ma długość pięć. Dlatego długość tablicy dynamicznej wynosi 5, a jej pojemność wynosi 10. Tablica dynamiczna śledzi punkt końcowy.

Funkcje tablicy dynamicznej
W Javie tablica dynamiczna ma trzy kluczowe cechy: Dodaj element, usuń element i zmień rozmiar tablicy.
Dodaj element do tablicy dynamicznej
W tablicy dynamicznej możemy utworzyć tablicę o stałym rozmiarze, jeśli zajdzie potrzeba dodania większej liczby elementów do tablicy. Zwykle tworzy nową tablicę o podwójnym rozmiarze. Następnie kopiuje wszystkie elementy do nowo utworzonej tablicy. Stosujemy następujące podejście:

Usuń element z tablicy dynamicznej
Jeśli chcemy usunąć element z tablicy o określonym indeksie, używamy metody usuńAt(i) metoda. Metoda analizuje numer indeksu elementu, który chcemy usunąć. Po usunięciu elementu przesuwa pozostałe elementy (elementy znajdujące się na prawo od usuwanego elementu) w lewo od podanego numeru indeksu. Używamy również metody usuwania(), która usuwa element z końca tablicy. Po przesunięciu elementów zapisuje 0 w pałacu ostatniego żywiołu. Rozumiemy to na przykładzie, jak pokazano na poniższym rysunku.

Zmiana rozmiaru tablicy dynamicznej w Javie
Musimy zmienić rozmiar tablicy w dwóch scenariuszach, jeśli:
- Tablica wykorzystuje dodatkową pamięć niż jest to wymagane.
- Tablica zajmuje całą pamięć i musimy dodać elementy.
W pierwszym przypadku korzystamy z rozmiar zlewu() metoda zmiany rozmiaru szyk . Zmniejsza rozmiar tablicy. Zwalnia dodatkową lub nieużywaną pamięć. W drugim przypadku korzystamy z rosnąćRozmiar() metoda zmiany rozmiaru tablicy. Zwiększa rozmiar tablicy.
Jest to kosztowna operacja, ponieważ wymaga większej tablicy i kopiuje wszystkie elementy z poprzedniej tablicy, a następnie zwraca nową tablicę.

Załóżmy, że w powyższej tablicy trzeba dodać sześć kolejnych elementów, a w tablicy nie ma już pamięci do przechowywania elementów. W takich przypadkach powiększamy tablicę za pomocą metody rosnąćRozmiar() metoda.

Zainicjuj tablicę dynamiczną
Inicjalizacja tablicy dynamicznej jest taka sama jak tablicy statycznej. Rozważmy następujący program Java, który inicjuje tablicę dynamiczną.
ZainicjujDynamicArray.java
public class InitializeDynamicArray { public static void main(String[] args) { //declaring array int array[]; //initialize an array array= new int[6]; //adding elements to the array array[0] = 34; array[1] = 90; array[2] = 12; array[3] = 22; array[4] = 9; array[5] = 27; System.out.print('Elements of Array are: '); //iteraton over the array for(int i=0; i <array.length ; i++) { system.out.print(array[i] +' '); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Elements of Array are: 34 90 12 22 9 27 </pre> <p>Let's implement the operations in a Java program that we have discussed above.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample1.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + ' '); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println('
elements after adding 5:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println('elements of array:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] ' '); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print('
elements element: system.out.print('no. da.count+'
'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;></pre></array.length> Zaimplementujmy operacje w programie Java, które omówiliśmy powyżej.
DynamicArrayExample1.java
public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + \' \'); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println(\'
elements after adding 5:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println(\'elements of array:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] \' \'); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print(\'
elements element: system.out.print(\'no. da.count+\'
\'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;>