Kombinatoryczna teoria gier | Zbiór 4 (Twierdzenie Sprague’a – Grundy’ego)
Warunki wstępne: Grundy Numbers/Numbers i Mex
Widzieliśmy już w zestawie 2 (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/combinatorial-game-theory-set-2-game-nim/), że możemy dowiedzieć się, kto wygrywa w grze Nim, bez faktycznego grania w tę grę.
Załóżmy, że zmienimy nieco klasyczną grę Nim. Tym razem każdy gracz może usunąć tylko 1 2 lub 3 kamienie (a nie dowolną liczbę kamieni, jak w klasycznej grze Nim). Czy możemy przewidzieć, kto wygra?
Tak, możemy przewidzieć zwycięzcę, korzystając z twierdzenia Sprague'a-Grundy'ego.
Co to jest twierdzenie Sprague'a-Grundy'ego?
Załóżmy, że istnieje gra złożona (więcej niż jedna gra podrzędna) składająca się z N gier podrzędnych oraz dwóch graczy A i B. Następnie twierdzenie Sprague'a-Grundy'ego mówi, że jeśli zarówno A, jak i B grają optymalnie (tj. nie popełniają żadnych błędów), to gracz rozpoczynający jako pierwszy ma gwarancję wygranej, jeśli XOR grundy liczb pozycji w każdej podgrze na początku gry jest niezerowy. W przeciwnym razie, jeśli XOR wyniesie zero, gracz A zdecydowanie przegra bez względu na wszystko.
Jak zastosować twierdzenie Sprague'a Grundy'ego?
Twierdzenie Sprague’a-Grundy’ego możemy zastosować w dowolnym przypadku bezstronna gra i rozwiązać to. Podstawowe kroki są wymienione w następujący sposób:
- Podziel grę złożoną na podgry.
- Następnie dla każdej podgry oblicz liczbę Grundy'ego w tej pozycji.
- Następnie oblicz XOR wszystkich obliczonych liczb Grundy'ego.
- Jeśli wartość XOR jest różna od zera, gracz, który wykona turę (pierwszy gracz), wygra, w przeciwnym razie jego przeznaczeniem będzie przegrać bez względu na wszystko.
Przykładowa gra: Gra rozpoczyna się od 3 stosów zawierających 3 4 i 5 kamieni, a gracz wykonujący ruch może pobrać dowolną dodatnią liczbę kamieni do 3 tylko z dowolnego stosu [pod warunkiem, że na stosie znajduje się odpowiednia ilość kamieni]. Ostatni gracz, który się poruszy, wygrywa. Który gracz wygrywa grę, zakładając, że obaj gracze grają optymalnie?
Jak stwierdzić, kto wygra, stosując twierdzenie Sprague'a-Grundy'ego?
Jak widzimy, ta gra sama w sobie składa się z kilku podgier.
Pierwszy krok: Pod-gry można traktować jako każdy stos.
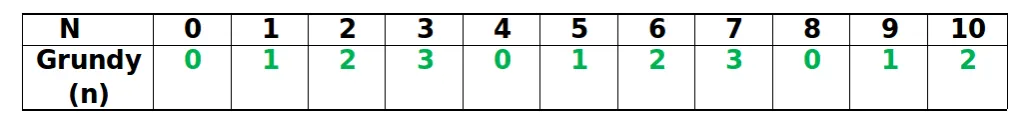
Drugi krok: Widzimy to z poniższej tabeli
Grundy(3) = 3 Grundy(4) = 0 Grundy(5) = 1

Widzieliśmy już, jak obliczyć liczby Grundy'ego w tej grze w poprzedni artykuł.
Trzeci krok: XOR liczby 3 0 1 = 2
Czwarty krok: Ponieważ XOR jest liczbą różną od zera, możemy więc powiedzieć, że wygra pierwszy gracz.
Poniżej znajduje się program realizujący powyższe 4 kroki.
C++ /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ #include using namespace std ; /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ #define PLAYER1 1 #define PLAYER2 2 // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set int calculateMex ( unordered_set < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . find ( Mex ) != Set . end ()) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy []) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != -1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); unordered_set < int > Set ; // A Hash Table for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . insert ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); } return ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main () { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = sizeof ( piles ) / sizeof ( piles [ 0 ]); // Find the maximum element int maximum = * max_element ( piles piles + n ); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [ maximum + 1 ]; memset ( Grundy -1 sizeof ( Grundy )); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ return ( 0 ); }
Java import java.util.* ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; static int PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < Integer > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy [] ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ] ); // A Hash Table HashSet < Integer > Set = new HashSet < Integer > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ] ); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]] ; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]] ; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = Arrays . stream ( piles ). max (). getAsInt (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [] = new int [ maximum + 1 ] ; Arrays . fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3 ''' Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing''' PLAYER1 = 1 PLAYER2 = 2 # A Function to calculate Mex of all # the values in that set def calculateMex ( Set ): Mex = 0 ; while ( Mex in Set ): Mex += 1 return ( Mex ) # A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' def calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ): Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ): return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A Hash Table Set = set () for i in range ( 1 4 ): Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )) # Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ) return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A function to declare the winner of the game def declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ): xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for i in range ( 1 n ): xorValue = ( xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]) if ( xorValue != 0 ): if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : # Test Case 1 piles = [ 3 4 5 ] n = len ( piles ) # Find the maximum element maximum = max ( piles ) # An array to cache the sub-problems so that # re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided Grundy = [ - 1 for i in range ( maximum + 1 )]; # Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for i in range ( n ): calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); ''' Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); ''' # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# using System ; using System.Linq ; using System.Collections.Generic ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; //static int PLAYER2 = 2; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . Contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int [] Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table HashSet < int > Set = new HashSet < int > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . Add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int [] piles int [] Grundy int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code static void Main () { // Test Case 1 int [] piles = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . Length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = piles . Max (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int [] Grundy = new int [ maximum + 1 ]; Array . Fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by mits
JavaScript < script > /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ let PLAYER1 = 1 ; let PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set function calculateMex ( Set ) { let Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . has ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' function calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table let Set = new Set (); for ( let i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game function declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ) { let xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); } return ; } // Driver code // Test Case 1 let piles = [ 3 4 5 ]; let n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element let maximum = Math . max (... piles ) // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided let Grundy = new Array ( maximum + 1 ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < maximum + 1 ; i ++ ) Grundy [ i ] = 0 ; // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( let i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 < /script>
Wyjście :
Player 1 will win
Złożoność czasowa: O(n^2) gdzie n to maksymalna liczba kamieni w stosie.
Złożoność przestrzeni: O(n), ponieważ tablica Grundy'ego jest używana do przechowywania wyników podproblemów, aby uniknąć zbędnych obliczeń i zajmuje przestrzeń O(n).
Referencje:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sprague%E2%80%93Grundy_theorem
Ćwiczenie dla czytelników: Rozważ poniższą grę.
W grze bierze udział dwóch graczy z N liczbami całkowitymi A1 A2 .. AN. W swojej turze gracz wybiera liczbę całkowitą, dzieli ją przez 2, 3 lub 6, a następnie zabiera głos. Jeśli liczba całkowita osiągnie 0, jest usuwana. Ostatni gracz, który się poruszy, wygrywa. Który gracz wygrywa grę, jeśli obaj gracze grają optymalnie?
Wskazówka: spójrz na przykład 3 z poprzedni artykuł.