Analiza asymptotyczna i porównanie algorytmów sortowania
Powszechnie wiadomo, że sortowanie przez scalanie działa szybciej niż sortowanie przez wstawianie. Używanie analiza asymptotyczna . możemy udowodnić, że sortowanie przez scalanie trwa O(nlogn), a sortowanie przez wstawianie zajmuje O(n^2). Jest to oczywiste, ponieważ sortowanie przez scalanie wykorzystuje podejście „dziel i zwyciężaj” poprzez rekurencyjne rozwiązywanie problemów, podczas gdy sortowanie przez wstawianie opiera się na podejściu przyrostowym. Jeśli dokładniej przyjrzymy się analizie złożoności czasowej, dowiemy się, że sortowanie przez wstawianie nie jest aż tak złe. Co zaskakujące, sortowanie przez wstawianie bije od sortowania przez łączenie przy mniejszym rozmiarze wejściowym. Dzieje się tak dlatego, że istnieje niewiele stałych, które ignorujemy przy wyprowadzaniu złożoności czasowej. W przypadku większych rozmiarów wejściowych rzędu 10^4 nie ma to wpływu na zachowanie naszej funkcji. Ale gdy rozmiary wejściowe spadną poniżej, powiedzmy mniej niż 40, wówczas stałe w równaniu dominują nad rozmiarem wejściowym „n”. Na razie w porządku. Ale taka analiza matematyczna mnie nie zadowoliła. Jako student informatyki musimy wierzyć w pisanie kodu. Napisałem program w języku C, aby poznać sposób, w jaki algorytmy konkurują ze sobą o różne rozmiary danych wejściowych. A także dlaczego przeprowadza się tak rygorystyczną analizę matematyczną w celu ustalenia złożoności czasu działania tych algorytmów sortowania.
Realizacja:
CPP #include #include #include #include #define MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY 1000000001 int cmpfunc ( const void * a const void * b ) { // Compare function used by qsort return ( * ( int * ) a - * ( int * ) b ); } int * generate_random_array ( int n ) { srand ( time ( NULL )); int * a = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = rand () % MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ; return a ; } int * copy_array ( int a [] int n ) { int * arr = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) arr [ i ] = a [ i ]; return arr ; } // Code for Insertion Sort void insertion_sort_asc ( int a [] int start int end ) { int i ; for ( i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; ++ i ) { int key = a [ i ]; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; -- j ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Code for Merge Sort void merge ( int a [] int start int end int mid ) { int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; int * aux = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * ( end - start + 1 )); while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; else aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; } while ( i <= mid ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; while ( j <= end ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; j = 0 ; for ( i = start ; i <= end ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = aux [ j ++ ]; free ( aux ); } void _merge_sort ( int a [] int start int end ) { if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; _merge_sort ( a start mid ); _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void merge_sort ( int a [] int n ) { return _merge_sort ( a 0 n - 1 ); } void insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( int a [] int start int end int k ) { // Performs insertion sort if size of array is less than or equal to k // Otherwise uses mergesort if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { return insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ); } int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void test_sorting_runtimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Measuring the runtime of the sorting algorithms int number_of_times = num_of_times ; int t = number_of_times ; int n = size ; double insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 ; double merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 ; while ( t -- ) { clock_t start end ; int * a = generate_random_array ( n ); int * b = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 n - 1 ); end = clock (); insertion_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( b ); int * c = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); merge_sort ( c n ); end = clock (); merge_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( c ); int * d = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 n - 1 40 ); end = clock (); merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( d ); start = clock (); qsort ( a n sizeof ( int ) cmpfunc ); end = clock (); qsort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( a ); } insertion_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= number_of_times ; qsort_time /= number_of_times ; printf ( ' n Time taken to sort: n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f nn ' '(i)Insertion sort: ' insertion_sort_time '(ii)Merge sort: ' merge_sort_time '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time '(iv)Qsort library function: ' qsort_time ); } int main ( int argc char const * argv []) { int t ; scanf ( '%d' & t ); while ( t -- ) { int size num_of_times ; scanf ( '%d %d' & size & num_of_times ); test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ); } return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Scanner ; import java.util.Arrays ; import java.util.Random ; public class SortingAlgorithms { // Maximum element in array static final int MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; public static void main ( String [] args ) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( System . in ); int t = scanner . nextInt (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < t ; i ++ ) { int size = scanner . nextInt (); int num_of_times = scanner . nextInt (); testSortingRuntimes ( size num_of_times ); } scanner . close (); } static int [] generateRandomArray ( int n ) { // Generate an array of n random integers. int [] arr = new int [ n ] ; Random random = new Random (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { arr [ i ] = random . nextInt ( MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ); } return arr ; } static void insertionSortAsc ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for ( int i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { int key = a [ i ] ; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] ; j -- ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } static void merge ( int [] a int start int end int mid ) { // Merge two sorted sublists of a. // The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. int [] aux = new int [ end - start + 1 ] ; int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ] ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } else { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } System . arraycopy ( aux 0 a start aux . length ); } static void mergeSort ( int [] a ) { // Perform an in-place merge sort on a. mergeSortHelper ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } static void mergeSortHelper ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Recursive merge sort function. if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; mergeSortHelper ( a start mid ); mergeSortHelper ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } static void insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( int [] a int start int end int k ) { /* Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. */ if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } static void testSortingRuntimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. double insertionSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; double qsortTime = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < num_of_times ; i ++ ) { int [] a = generateRandomArray ( size ); int [] b = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); long start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); long end = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; int [] c = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSort ( c ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; int [] d = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; int [] e = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); Arrays . sort ( e ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= num_of_times ; qsortTime /= num_of_times ; System . out . println ( 'nTime taken to sort:n' + '(i) Insertion sort: ' + insertionSortTime + 'n' + '(ii) Merge sort: ' + mergeSortTime + 'n' + '(iii) Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' + mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime + 'n' + '(iv) Qsort library function: ' + qsortTime + 'n' ); } }
Python3 import time import random import copy from typing import List # Maximum element in array MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 def generate_random_array ( n : int ) -> List [ int ]: #Generate a list of n random integers. return [ random . randint ( 0 MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ) for _ in range ( n )] def insertion_sort_asc ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for i in range ( start + 1 end + 1 ): key = a [ i ] j = i - 1 while j >= start and a [ j ] > key : a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] j -= 1 a [ j + 1 ] = key def merge ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int mid : int ) -> None : #Merge two sorted sublists of a. #The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. aux = [] i = start j = mid + 1 while i <= mid and j <= end : if a [ i ] <= a [ j ]: aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 else : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 while i <= mid : aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 while j <= end : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 a [ start : end + 1 ] = aux def _merge_sort ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Recursive merge sort function. if start < end : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 _merge_sort ( a start mid ) _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ) merge ( a start end mid ) def merge_sort ( a : List [ int ]) -> None : #Perform an in-place merge sort on a. _merge_sort ( a 0 len ( a ) - 1 ) def insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int k : int ) -> None : ''' Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. ''' if start < end : size = end - start + 1 if size <= k : insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ) else : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ) insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ) merge ( a start end mid ) def test_sorting_runtimes ( size : int num_of_times : int ) -> None : #Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 for _ in range ( num_of_times ): a = generate_random_array ( size ) b = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 len ( b ) - 1 ) end = time . time () insertion_sort_time += end - start c = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () merge_sort ( c ) end = time . time () merge_sort_time += end - start d = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 len ( d ) - 1 40 ) end = time . time () merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += end - start start = time . time () a . sort () end = time . time () qsort_time += end - start insertion_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= num_of_times qsort_time /= num_of_times print ( f ' n Time taken to sort: n ' f '(i)Insertion sort: { insertion_sort_time } n ' f '(ii)Merge sort: { merge_sort_time } n ' f '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: { merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time } n ' f '(iv)Qsort library function: { qsort_time } n ' ) def main () -> None : t = int ( input ()) for _ in range ( t ): size num_of_times = map ( int input () . split ()) test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript // Importing required modules const { performance } = require ( 'perf_hooks' ); // Maximum element in array const MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; // Function to generate a list of n random integers function generateRandomArray ( n ) { return Array . from ({ length : n } () => Math . floor ( Math . random () * MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY )); } // Function to perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end function insertionSortAsc ( a start end ) { for ( let i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { let key = a [ i ]; let j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; j -= 1 ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Function to merge two sorted sublists of a function merge ( a start end mid ) { let aux = []; let i = start ; let j = mid + 1 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } else { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } for ( let i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { a [ i ] = aux [ i - start ]; } } // Recursive merge sort function function _mergeSort ( a start end ) { if ( start < end ) { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); _mergeSort ( a start mid ); _mergeSort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } // Function to perform an in-place merge sort on a function mergeSort ( a ) { _mergeSort ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } // Function to perform an in-place sort on a from start to end function insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start end k ) { if ( start < end ) { let size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } // Function to test the runtime of the sorting algorithms function testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ) { let insertionSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; let qsortTime = 0 ; for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < numOfTimes ; _ ++ ) { let a = generateRandomArray ( size ); let b = [... a ]; let start = performance . now (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); let end = performance . now (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; let c = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); mergeSort ( c ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; let d = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; start = performance . now (); a . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); end = performance . now (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= numOfTimes ; qsortTime /= numOfTimes ; console . log ( `nTime taken to sort:n(i)Insertion sort: ${ insertionSortTime } n(ii)Merge sort: ${ mergeSortTime } n(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ${ mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime } n(iv)Qsort library function: ${ qsortTime } n` ); } // Main function function main () { let t = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of test cases: ' )); for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < t ; _ ++ ) { let size = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the size of the array: ' )); let numOfTimes = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of times to run the test: ' )); testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ); } } // Call the main function main ();
Porównałem czasy działania następujących algorytmów:
- Sortowanie przez wstawianie : Tradycyjny algorytm bez modyfikacji/optymalizacji. Działa bardzo dobrze w przypadku mniejszych rozmiarów danych wejściowych. I tak, to przewyższa sortowanie przez scalanie
- Idzie los : Stosuje podejście „dziel i zwyciężaj”. Dla rozmiarów wejściowych rzędu 10^5 ten algorytm jest właściwym wyborem. To sprawia, że sortowanie przez wstawianie jest niepraktyczne w przypadku tak dużych rozmiarów danych wejściowych.
- Połączona wersja sortowania przez wstawianie i sortowania przez scalanie: Poprawiłem nieco logikę sortowania przez scalanie, aby osiągnąć znacznie lepszy czas działania w przypadku mniejszych rozmiarów danych wejściowych. Jak wiemy, sortowanie przez scalanie dzieli dane wejściowe na dwie połowy, dopóki sortowanie elementów nie stanie się wystarczająco proste. Ale tutaj, gdy rozmiar wejściowy spadnie poniżej progu, takiego jak „n” < 40 then this hybrid algorithm makes a call to traditional insertion sort procedure. From the fact that insertion sort runs faster on smaller inputs and merge sort runs faster on larger inputs this algorithm makes best use both the worlds.
- Szybkie sortowanie: Nie wdrożyłem tej procedury. To jest funkcja biblioteczna qsort(), która jest dostępna w . Rozważałem ten algorytm, aby poznać znaczenie implementacji. Aby zminimalizować liczbę kroków i maksymalnie wykorzystać podstawowe elementy języka, aby wdrożyć algorytm w najlepszy możliwy sposób, wymagana jest duża wiedza programistyczna. Jest to główny powód, dla którego zaleca się korzystanie z funkcji bibliotecznych. Są napisane tak, aby radzić sobie ze wszystkim. Optymalizują w maksymalnym możliwym stopniu. I zanim zapomnę z mojej analizy, qsort() działa niesamowicie szybko na praktycznie każdym rozmiarze wejściowym!
Analiza:
- Wejście: Użytkownik musi podać ile razy chce przetestować algorytm odpowiadającą liczbie przypadków testowych. Dla każdego przypadku testowego użytkownik musi wprowadzić dwie liczby całkowite oddzielone spacjami, oznaczające rozmiar wejściowy „n” i „liczba_razów” oznaczającą, ile razy chce przeprowadzić analizę i wziąć średnią. (Wyjaśnienie: Jeśli „liczba_razów” wynosi 10, wówczas każdy z algorytmów określonych powyżej jest uruchamiany 10 razy i pobierana jest średnia. Dzieje się tak, ponieważ tablica wejściowa jest generowana losowo zgodnie z określonym rozmiarem wejściowym. Tablica wejściowa może być w całości posortowana. Może to odpowiadać najgorszemu przypadkowi, tj. kolejności malejącej. Aby uniknąć czasu wykonywania takich tablic wejściowych. Algorytm jest uruchamiany „liczba_razów” i pobierana jest średnia.) clock() procedura i makro CLOCKS_PER_SEC służą do pomiaru czasu. Kompilacja: Powyższy kod napisałem w środowisku Linux (Ubuntu 16.04 LTS). Skopiuj powyższy fragment kodu. Skompiluj go, używając klucza gcc na wejściach zgodnie ze specyfikacją i podziwiaj moc algorytmów sortowania!
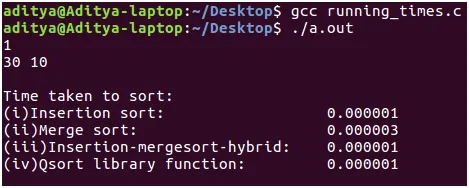
- Wyniki: Jak widać w przypadku małych rozmiarów wejściowych, sortowanie przez wstawianie uderzeń, łączenie, sortowanie według 2 * 10^-6 sek. Ale ta różnica w czasie nie jest tak znacząca. Z drugiej strony algorytm hybrydowy i funkcja biblioteczna qsort() działają równie dobrze, jak sortowanie przez wstawianie.
 Rozmiar danych wejściowych został teraz zwiększony około 100 razy do n = 1000 z n = 30. Różnica jest teraz namacalna. Sortowanie przez scalanie działa 10 razy szybciej niż sortowanie przez wstawianie. Ponownie istnieje powiązanie między wydajnością algorytmu hybrydowego a funkcją qsort(). Sugeruje to, że funkcja qsort() jest zaimplementowana w sposób mniej więcej podobny do naszego algorytmu hybrydowego, tj. przełączanie pomiędzy różnymi algorytmami, aby jak najlepiej je wykorzystać.
Rozmiar danych wejściowych został teraz zwiększony około 100 razy do n = 1000 z n = 30. Różnica jest teraz namacalna. Sortowanie przez scalanie działa 10 razy szybciej niż sortowanie przez wstawianie. Ponownie istnieje powiązanie między wydajnością algorytmu hybrydowego a funkcją qsort(). Sugeruje to, że funkcja qsort() jest zaimplementowana w sposób mniej więcej podobny do naszego algorytmu hybrydowego, tj. przełączanie pomiędzy różnymi algorytmami, aby jak najlepiej je wykorzystać.  Na koniec rozmiar danych wejściowych zostaje zwiększony do 10^5 (1 lakh!), co jest najprawdopodobniej idealnym rozmiarem stosowanym w praktycznych scenariuszach. W porównaniu do poprzedniego wejścia n = 1000, gdzie sortowanie przez scalanie pokonuje sortowanie przez wstawianie, działając 10 razy szybciej, tutaj różnica jest jeszcze bardziej znacząca. Sortowanie przez scalanie bije sortowanie przez wstawianie 100 razy! Napisany przez nas algorytm hybrydowy faktycznie przewyższa tradycyjne sortowanie przez scalanie, ponieważ działa o 0,01 sekundy szybciej. I na koniec, funkcja biblioteczna qsort() w końcu udowadnia nam, że implementacja również odgrywa kluczową rolę podczas dokładnego pomiaru czasu działania, działając o 3 milisekundy szybciej! :D
Na koniec rozmiar danych wejściowych zostaje zwiększony do 10^5 (1 lakh!), co jest najprawdopodobniej idealnym rozmiarem stosowanym w praktycznych scenariuszach. W porównaniu do poprzedniego wejścia n = 1000, gdzie sortowanie przez scalanie pokonuje sortowanie przez wstawianie, działając 10 razy szybciej, tutaj różnica jest jeszcze bardziej znacząca. Sortowanie przez scalanie bije sortowanie przez wstawianie 100 razy! Napisany przez nas algorytm hybrydowy faktycznie przewyższa tradycyjne sortowanie przez scalanie, ponieważ działa o 0,01 sekundy szybciej. I na koniec, funkcja biblioteczna qsort() w końcu udowadnia nam, że implementacja również odgrywa kluczową rolę podczas dokładnego pomiaru czasu działania, działając o 3 milisekundy szybciej! :D

Uwaga: Nie uruchamiaj powyższego programu z n >= 10^6, ponieważ będzie to wymagało dużej mocy obliczeniowej. Dziękuję i życzę miłego kodowania! :)
Utwórz quiz