Finn høyden på et spesielt binært tre hvis bladnoder er koblet sammen

Gitt en spesielt binært tre hvems bladnoder er koblet til form a sirkulær dobbeltlenket liste oppgaven er å finne høyde av treet.
Eksempler:
Inndata:

Produksjon: 2
Forklaring: Høyden på binærtreet etter gjenkjenning av bladnodene er 2. I det ovennevnte binære treet er 6 5 og 4 bladnoder og de danner en sirkulær dobbeltlenket liste. Her vil venstre peker til bladnoden fungere som en tidligere peker på sirkulær dobbeltlenket liste og høyre peker vil fungere som neste peker på sirkulær dobbeltlenket liste.Inndata:
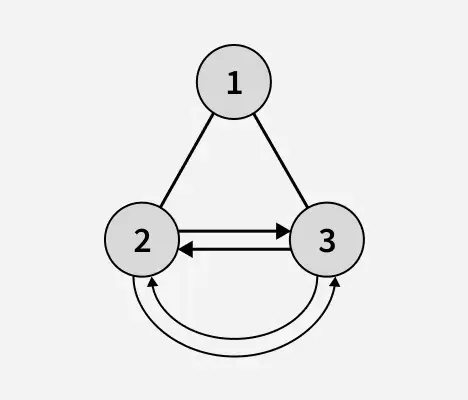
Produksjon: 1
Forklaring: Høyden på det binære treet etter gjenkjennelse av bladnodene er 1. I det ovenstående er binærtreet 2 og 3 bladnoder og de danner en sirkulær dobbeltlenket liste.
Nærme :
C++Tanken er å følge med lignende tilnærming som vi gjør for finne høyden til et normalt binært tre . Vi rekursivt kalkulere høyde av venstre og høyre undertrær til en node og tilordne høyde til noden som maks av høyden til to barn pluss 1. Men venstre og høyre barn av en bladnode er null for vanlige binære trær. Men her er bladnode en sirkulær dobbeltlenket listenode. Så for at en node skal være en bladnode sjekker vi om nodens venstre til høyre peker på node og dens høyre er venstre peker også på node seg selv.
// C++ program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * left * right ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = nullptr ; right = nullptr ; } }; // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node bool isLeaf ( Node * node ) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other consition is also true. return node -> left && node -> left -> right == node && node -> right && node -> right -> left == node ; } // Compute the height of a tree int findTreeHeight ( Node * node ) { // if node is NULL return -1. if ( node == nullptr ) return -1 ; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if ( isLeaf ( node )) return 0 ; // compute the depth of each subtree // and take maximum return 1 + max ( findTreeHeight ( node -> left ) findTreeHeight ( node -> right )); } int main () { Node * root = new Node ( 1 ); root -> left = new Node ( 2 ); root -> right = new Node ( 3 ); root -> left -> left = new Node ( 4 ); root -> left -> right = new Node ( 5 ); root -> left -> left -> left = new Node ( 6 ); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node * l1 = root -> left -> left -> left ; Node * l2 = root -> left -> right ; Node * l3 = root -> right ; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1 -> right = l2 l2 -> right = l3 l3 -> right = l1 ; // set prev pointer of linked list l3 -> left = l2 l2 -> left = l1 l1 -> left = l3 ; cout < < findTreeHeight ( root ); return 0 ; }
C // C program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include #include struct Node { int data ; struct Node * left * right ; }; // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node int isLeaf ( struct Node * node ) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node -> left && node -> left -> right == node && node -> right && node -> right -> left == node ; } // Compute the height of a tree int findTreeHeight ( struct Node * node ) { // if node is NULL return -1. if ( node == NULL ) return -1 ; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if ( isLeaf ( node )) return 0 ; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum int leftDepth = findTreeHeight ( node -> left ); int rightDepth = findTreeHeight ( node -> right ); return 1 + ( leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth : rightDepth ); } struct Node * createNode ( int data ) { struct Node * newNode = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); newNode -> data = data ; newNode -> left = NULL ; newNode -> right = NULL ; return newNode ; } int main () { struct Node * root = createNode ( 1 ); root -> left = createNode ( 2 ); root -> right = createNode ( 3 ); root -> left -> left = createNode ( 4 ); root -> left -> right = createNode ( 5 ); root -> left -> left -> left = createNode ( 6 ); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes struct Node * l1 = root -> left -> left -> left ; struct Node * l2 = root -> left -> right ; struct Node * l3 = root -> right ; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1 -> right = l2 l2 -> right = l3 l3 -> right = l1 ; // set prev pointer of linked list l3 -> left = l2 l2 -> left = l1 l1 -> left = l3 ; printf ( '%d' findTreeHeight ( root )); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { int data ; Node left right ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = null ; right = null ; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static boolean isLeaf ( Node node ) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node . left != null && node . left . right == node && node . right != null && node . right . left == node ; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight ( Node node ) { // if node is NULL return -1. if ( node == null ) return - 1 ; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if ( isLeaf ( node )) return 0 ; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math . max ( findTreeHeight ( node . left ) findTreeHeight ( node . right )); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 5 ); root . left . left . left = new Node ( 6 ); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root . left . left . left ; Node l2 = root . left . right ; Node l3 = root . right ; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1 . right = l2 ; l2 . right = l3 ; l3 . right = l1 ; // set prev pointer of linked list l3 . left = l2 ; l2 . left = l1 ; l1 . left = l3 ; System . out . println ( findTreeHeight ( root )); } }
Python # Python program to calculate height of a special tree # whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node : def __init__ ( self data ): self . data = data self . left = None self . right = None # function to check if given # node is a leaf node or node def isLeaf ( node ): # For a node to be a leaf node it should # satisfy the following two conditions: # 1. Node's left's right pointer should be # current node. # 2. Node's right's left pointer should be # current node. # If one condition is met it is guaranteed # that the other condition is also true. return ( node . left and node . left . right == node and node . right and node . right . left == node ) # Compute the height of a tree def findTreeHeight ( node ): # if node is NULL return -1. if node is None : return - 1 # if node is a leaf node return 0 if isLeaf ( node ): return 0 # compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + max ( findTreeHeight ( node . left ) findTreeHeight ( node . right )) if __name__ == '__main__' : root = Node ( 1 ) root . left = Node ( 2 ) root . right = Node ( 3 ) root . left . left = Node ( 4 ) root . left . right = Node ( 5 ) root . left . left . left = Node ( 6 ) # Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes l1 = root . left . left . left l2 = root . left . right l3 = root . right # create circular doubly linked list out of # leaf nodes of the tree # set next pointer of linked list l1 . right = l2 l2 . right = l3 l3 . right = l1 # set prev pointer of linked list l3 . left = l2 l2 . left = l1 l1 . left = l3 print ( findTreeHeight ( root ))
C# // C# program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node left right ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = null ; right = null ; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static bool isLeaf ( Node node ) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node . left != null && node . left . right == node && node . right != null && node . right . left == node ; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight ( Node node ) { // if node is NULL return -1. if ( node == null ) return - 1 ; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if ( isLeaf ( node )) return 0 ; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math . Max ( findTreeHeight ( node . left ) findTreeHeight ( node . right )); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { Node root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 5 ); root . left . left . left = new Node ( 6 ); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root . left . left . left ; Node l2 = root . left . right ; Node l3 = root . right ; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1 . right = l2 ; l2 . right = l3 ; l3 . right = l1 ; // set prev pointer of linked list l3 . left = l2 ; l2 . left = l1 ; l1 . left = l3 ; Console . WriteLine ( findTreeHeight ( root )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { constructor ( data ) { this . data = data ; this . left = null ; this . right = null ; } } // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node function isLeaf ( node ) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node . left && node . left . right === node && node . right && node . right . left === node ; } // Compute the height of a tree function findTreeHeight ( node ) { // if node is NULL return -1. if ( node === null ) return - 1 ; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if ( isLeaf ( node )) return 0 ; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math . max ( findTreeHeight ( node . left ) findTreeHeight ( node . right )); } const root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 5 ); root . left . left . left = new Node ( 6 ); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes const l1 = root . left . left . left ; const l2 = root . left . right ; const l3 = root . right ; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1 . right = l2 ; l2 . right = l3 ; l3 . right = l1 ; // set prev pointer of linked list l3 . left = l2 ; l2 . left = l1 ; l1 . left = l3 ; console . log ( findTreeHeight ( root ));
Produksjon
3
Tidskompleksitet: O(n) hvor n er antall noder.
Ekstra plass: O(h)