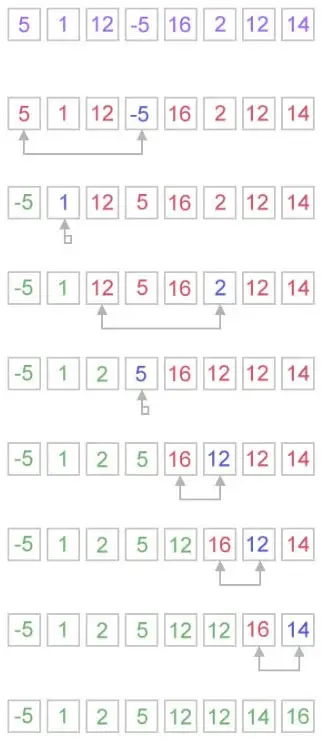
Šteina algoritms GCD atrašanai

Steina algoritms vai binārais GCD algoritms ir algoritms, kas aprēķina divu nenegatīvu veselu skaitļu lielāko kopīgo dalītāju. Steina algoritms dalīšanu aizstāj ar aritmētisko nobīdes salīdzināšanu un atņemšanu.
Piemēri:
Ievade : a = 17 b = 34
Izvade : 17
Ievade : a = 50 b = 49
Izvade : 1
Algoritms GCD atrašanai, izmantojot Steina algoritmu gcd(a b)
Algoritms galvenokārt ir optimizācija salīdzinājumā ar standartu Eiklīda algoritms GCD
- Ja gan a, gan b ir 0, gcd ir nulle gcd(0 0) = 0.
- gcd(a 0) = a un gcd(0 b) = b, jo viss dalās ar 0.
- Ja a un b ir pāra gcd(a b) = 2*gcd(a/2 b/2), jo 2 ir kopīgs dalītājs. Reizināšanu ar 2 var veikt ar bitu maiņas operatoru.
- Ja a ir pāra un b ir nepāra gcd(a b) = gcd(a/2 b). Līdzīgi, ja a ir nepāra un b ir pāra
gcd(a b) = gcd(a b/2). Tas ir tāpēc, ka 2 nav kopīgs dalītājs. - Ja gan a, gan b ir nepāra, tad gcd(a b) = gcd(|a-b|/2 b). Ņemiet vērā, ka divu nepāra skaitļu starpība ir pāra
- Atkārtojiet 3.–5. darbību, līdz a = b vai līdz a = 0. Jebkurā gadījumā GCD ir jauda (2 k) * b, kur jauda (2 k) ir 2 palielinājums līdz k pakāpei un k ir kopējo faktoru skaits 2, kas atrasti 3. darbībā.
// Iterative C++ program to // implement Stein's Algorithm #include using namespace std ; // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm int gcd ( int a int b ) { /* GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a GCD(0 0) == 0 */ if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; /*Finding K where K is the greatest power of 2 that divides both a and b. */ int k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } /* Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd */ while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; /* From here on 'a' is always odd. */ do { /* If b is even remove all factor of 2 in b */ while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; /* Now a and b are both odd. Swap if necessary so a <= b then set b = b - a (which is even).*/ if ( a > b ) swap ( a b ); // Swap u and v. b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); /* restore common factors of 2 */ return a < < k ; } // Driver code int main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; printf ( 'Gcd of given numbers is %d n ' gcd ( a b )); return 0 ; }
Java // Iterative Java program to // implement Stein's Algorithm import java.io.* ; class GFG { // Function to implement Stein's // Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // Finding K where K is the greatest // power of 2 that divides both a and b int k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } // Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; // From here on 'a' is always odd. do { // If b is even remove // all factor of 2 in b while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; // Now a and b are both odd. Swap // if necessary so a <= b then set // b = b - a (which is even) if ( a > b ) { // Swap u and v. int temp = a ; a = b ; b = temp ; } b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); // restore common factors of 2 return a < < k ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String args [] ) { int a = 34 b = 17 ; System . out . println ( 'Gcd of given ' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari
Python # Iterative Python 3 program to # implement Stein's Algorithm # Function to implement # Stein's Algorithm def gcd ( a b ): # GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a # GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ): return b if ( b == 0 ): return a # Finding K where K is the # greatest power of 2 that # divides both a and b. k = 0 while ((( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ): a = a >> 1 b = b >> 1 k = k + 1 # Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ): a = a >> 1 # From here on 'a' is always odd. while ( b != 0 ): # If b is even remove all # factor of 2 in b while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ): b = b >> 1 # Now a and b are both odd. Swap if # necessary so a <= b then set # b = b - a (which is even). if ( a > b ): # Swap u and v. temp = a a = b b = temp b = ( b - a ) # restore common factors of 2 return ( a < < k ) # Driver code a = 34 b = 17 print ( 'Gcd of given numbers is ' gcd ( a b )) # This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C# // Iterative C# program to implement // Stein's Algorithm using System ; class GFG { // Function to implement Stein's // Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // Finding K where K is the greatest // power of 2 that divides both a and b int k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } // Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; // From here on 'a' is always odd do { // If b is even remove // all factor of 2 in b while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; /* Now a and b are both odd. Swap if necessary so a <= b then set b = b - a (which is even).*/ if ( a > b ) { // Swap u and v. int temp = a ; a = b ; b = temp ; } b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); /* restore common factors of 2 */ return a < < k ; } // Driver code public static void Main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; Console . Write ( 'Gcd of given ' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal
JavaScript < script > // Iterative JavaScript program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( a b ) { /* GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a GCD(0 0) == 0 */ if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; /*Finding K where K is the greatest power of 2 that divides both a and b. */ let k ; for ( k = 0 ; (( a | b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ k ) { a >>= 1 ; b >>= 1 ; } /* Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd */ while (( a & 1 ) == 0 ) a >>= 1 ; /* From here on 'a' is always odd. */ do { /* If b is even remove all factor of 2 in b */ while (( b & 1 ) == 0 ) b >>= 1 ; /* Now a and b are both odd. Swap if necessary so a <= b then set b = b - a (which is even).*/ if ( a > b ){ let t = a ; a = b ; b = t ; } b = ( b - a ); } while ( b != 0 ); /* restore common factors of 2 */ return a < < k ; } // Driver code let a = 34 b = 17 ; document . write ( 'Gcd of given numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); // This code contributed by gauravrajput1 < /script>
PHP // Iterative php program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( $a $b ) { // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( $a == 0 ) return $b ; if ( $b == 0 ) return $a ; // Finding K where K is the greatest // power of 2 that divides both a and b. $k ; for ( $k = 0 ; (( $a | $b ) & 1 ) == 0 ; ++ $k ) { $a >>= 1 ; $b >>= 1 ; } // Dividing a by 2 until a becomes odd while (( $a & 1 ) == 0 ) $a >>= 1 ; // From here on 'a' is always odd. do { // If b is even remove // all factor of 2 in b while (( $b & 1 ) == 0 ) $b >>= 1 ; // Now a and b are both odd. Swap // if necessary so a <= b then set // b = b - a (which is even) if ( $a > $b ) swap ( $a $b ); // Swap u and v. $b = ( $b - $a ); } while ( $b != 0 ); // restore common factors of 2 return $a < < $k ; } // Driver code $a = 34 ; $b = 17 ; echo 'Gcd of given numbers is ' . gcd ( $a $b ); // This code is contributed by ajit ?>
Izvade
Gcd of given numbers is 17
Laika sarežģītība: O(N*N)
Palīgtelpa: O(1)
[Paredzamā 2. pieeja] Rekursīvā ieviešana — O(N*N) Laiks un O(N*N) Kosmoss
C++ // Recursive C++ program to // implement Stein's Algorithm #include using namespace std ; // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm int gcd ( int a int b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 if ( ~ a & 1 ) // a is even { if ( b & 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } if ( ~ b & 1 ) // a is odd b is even return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver code int main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; printf ( 'Gcd of given numbers is %d n ' gcd ( a b )); return 0 ; }
Java // Recursive Java program to // implement Stein's Algorithm import java.io.* ; class GFG { // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ) // a is even { if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } // a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String args [] ) { int a = 34 b = 17 ; System . out . println ( 'Gcd of given' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari
Python # Recursive Python 3 program to # implement Stein's Algorithm # Function to implement # Stein's Algorithm def gcd ( a b ): if ( a == b ): return a # GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a # GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ): return b if ( b == 0 ): return a # look for factors of 2 # a is even if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ): # b is odd if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ): return gcd ( a >> 1 b ) else : # both a and b are even return ( gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ) # a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ): return gcd ( a b >> 1 ) # reduce larger number if ( a > b ): return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ) return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ) # Driver code a b = 34 17 print ( 'Gcd of given numbers is ' gcd ( a b )) # This code is contributed # by Nikita Tiwari.
C# // Recursive C# program to // implement Stein's Algorithm using System ; class GFG { // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm static int gcd ( int a int b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; // GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 // a is even if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ) { // b is odd if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } // a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver code public static void Main () { int a = 34 b = 17 ; Console . Write ( 'Gcd of given' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( a b ) { if ( a == b ) return a ; // GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a // GCD(0 0) == 0 if ( a == 0 ) return b ; if ( b == 0 ) return a ; // look for factors of 2 if (( ~ a & 1 ) == 1 ) // a is even { if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( a >> 1 b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( a >> 1 b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } // a is odd b is even if (( ~ b & 1 ) == 1 ) return gcd ( a b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( a > b ) return gcd (( a - b ) >> 1 b ); return gcd (( b - a ) >> 1 a ); } // Driver Code let a = 34 b = 17 ; document . write ( 'Gcd of given ' + 'numbers is ' + gcd ( a b )); < /script>
PHP // Recursive PHP program to // implement Stein's Algorithm // Function to implement // Stein's Algorithm function gcd ( $a $b ) { if ( $a == $b ) return $a ; /* GCD(0 b) == b; GCD(a 0) == a GCD(0 0) == 0 */ if ( $a == 0 ) return $b ; if ( $b == 0 ) return $a ; // look for factors of 2 if ( ~ $a & 1 ) // a is even { if ( $b & 1 ) // b is odd return gcd ( $a >> 1 $b ); else // both a and b are even return gcd ( $a >> 1 $b >> 1 ) < < 1 ; } if ( ~ $b & 1 ) // a is odd b is even return gcd ( $a $b >> 1 ); // reduce larger number if ( $a > $b ) return gcd (( $a - $b ) >> 1 $b ); return gcd (( $b - $a ) >> 1 $a ); } // Driver code $a = 34 ; $b = 17 ; echo 'Gcd of given numbers is: ' gcd ( $a $b ); // This code is contributed by aj_36 ?>
Izvade
Gcd of given numbers is 17
Laika sarežģītība : O(N*N), kur N ir bitu skaits lielākā skaitā.
Palīgtelpa: O(N*N), kur N ir bitu skaits lielākā skaitā.
Jums var patikt arī - Pamata un paplašinātais Eiklīda algoritms
Priekšrocības salīdzinājumā ar Eiklida GCD algoritmu
- Steina algoritms ir optimizēta Eiklida GCD algoritma versija.
- tas ir efektīvāk, izmantojot bitu maiņas operatoru.