Minimālais mijmaiņas apjoms, kas nepieciešams, lai pārveidotu bināro koku par bināro meklēšanas koku

Dots masīvs arr[] kas apzīmē a Pilnīgs binārais koks i., ja indekss i ir vecāks rādītājs 2*i + 1 ir atstāts bērns un indekss 2*i + 2 ir īstais bērns. Uzdevums ir atrast minimums skaits mijmaiņas darījumi nepieciešams, lai to pārvērstu par a Binārais meklēšanas koks.
Piemēri:
Ievade: arr[] = [5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
Izvade: 3
Paskaidrojums:
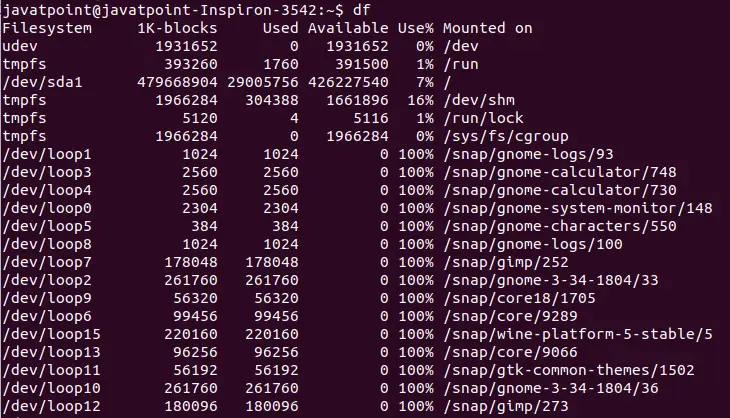
Dotā masīva binārais koks:
1. mijmaiņa: nomainiet 8. mezglu ar 5. mezglu.
2. mijmaiņa: nomainiet 9. mezglu ar 10. mezglu.
3. mijmaiņa: nomainiet mezglu 10 ar mezglu 7.Tātad, lai iegūtu tālāk redzamo bināro meklēšanas koku, ir nepieciešami vismaz 3 mijmaiņas darījumi:

Ievade: arr[] = [1 2 3]
Izvade: 1
Paskaidrojums:
Dotā masīva binārais koks:
Pēc mezgla 1 maiņas ar 2. mezglu iegūstiet tālāk redzamo bināro meklēšanas koku:

Pieeja:
C++Ideja ir izmantot faktu, ka pasūtījuma šķērsošana no Binārais meklēšanas koks ir iekšā pieaug to vērtības secībā.
Tātad atrodiet pasūtījuma šķērsošana no Binārā koka un saglabājiet to masīvā un mēģināt kārtot masīvs. The minimālais mijmaiņas darījumu skaits, kas nepieciešams, lai masīvs sakārtotu būs atbilde.
// C++ program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree #include using namespace std ; // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in vector v void inorder ( vector < int >& arr vector < int >& inorderArr int index ) { int n = arr . size (); // If index is out of bounds return if ( index >= n ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ); // Store current node value in vector inorderArr . push_back ( arr [ index ]); // Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps // to sort inorder traversal int minSwaps ( vector < int >& arr ) { int n = arr . size (); vector < int > inorderArr ; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ); // Create an array of pairs to store value // and original index vector < pair < int int >> t ( inorderArr . size ()); int ans = 0 ; // Store the value and its index for ( int i = 0 ; i < inorderArr . size (); i ++ ) t [ i ] = { inorderArr [ i ] i }; // Sort the pair array based on values // to get BST order sort ( t . begin () t . end ()); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for ( int i = 0 ; i < t . size (); i ++ ) { // If the element is already in the // correct position continue if ( i == t [ i ]. second ) continue ; // Otherwise perform swaps until the element // is in the right place else { // Swap elements to correct positions swap ( t [ i ]. first t [ t [ i ]. second ]. first ); swap ( t [ i ]. second t [ t [ i ]. second ]. second ); } // Check if the element is still not // in the correct position if ( i != t [ i ]. second ) -- i ; // Increment swap count ans ++ ; } return ans ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 }; cout < < minSwaps ( arr ) < < endl ; }
Java // Java program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree import java.util.Arrays ; class GfG { // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in an array static void inorder ( int [] arr int [] inorderArr int index int [] counter ) { int n = arr . length ; // Base case: if index is out of bounds return if ( index >= n ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 counter ); // Store current node value in the inorder array inorderArr [ counter [ 0 ]] = arr [ index ] ; counter [ 0 ]++ ; // Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 counter ); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps // to sort inorder traversal static int minSwaps ( int [] arr ) { int n = arr . length ; int [] inorderArr = new int [ n ] ; int [] counter = new int [ 1 ] ; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 counter ); // Create an array of pairs to store the value // and its original index int [][] t = new int [ n ][ 2 ] ; int ans = 0 ; // Store the value and its original index for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { t [ i ][ 0 ] = inorderArr [ i ] ; t [ i ][ 1 ] = i ; } // Sort the array based on values to get BST order Arrays . sort ( t ( a b ) -> Integer . compare ( a [ 0 ] b [ 0 ] )); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles boolean [] visited = new boolean [ n ] ; // Iterate through the array to find cycles for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { // If the element is already visited or in // the correct place continue if ( visited [ i ] || t [ i ][ 1 ] == i ) continue ; // Start a cycle and find the number of // nodes in the cycle int cycleSize = 0 ; int j = i ; while ( ! visited [ j ] ) { visited [ j ] = true ; j = t [ j ][ 1 ] ; cycleSize ++ ; } // If there is a cycle we need (cycleSize - 1) // swaps to sort the cycle if ( cycleSize > 1 ) { ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ); } } // Return the total number of swaps return ans ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 }; System . out . println ( minSwaps ( arr )); } }
Python # Python program for Minimum swap required # to convert binary tree to binary search tree # Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree # and store it in an array def inorder ( arr inorderArr index ): # If index is out of bounds return n = len ( arr ) if index >= n : return # Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ) # Store current node value in inorderArr inorderArr . append ( arr [ index ]) # Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ) # Function to calculate minimum swaps # to sort inorder traversal def minSwaps ( arr ): inorderArr = [] # Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ) # Create a list of pairs to store value and original index t = [( inorderArr [ i ] i ) for i in range ( len ( inorderArr ))] ans = 0 # Sort the list of pairs based on values # to get BST order t . sort () # Initialize visited array visited = [ False ] * len ( t ) # Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for i in range ( len ( t )): # If already visited or already in the # correct place skip if visited [ i ] or t [ i ][ 1 ] == i : continue # Start a cycle and find the number of # nodes in the cycle cycleSize = 0 j = i # Process all elements in the cycle while not visited [ j ]: visited [ j ] = True j = t [ j ][ 1 ] cycleSize += 1 # If there is a cycle of size `cycle_size` we # need `cycle_size - 1` swaps if cycleSize > 1 : ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ) # Return total number of swaps return ans if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ] print ( minSwaps ( arr ))
C# // C# program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree using System ; using System.Linq ; class GfG { // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in an array static void Inorder ( int [] arr int [] inorderArr int index ref int counter ) { int n = arr . Length ; // Base case: if index is out of bounds return if ( index >= n ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree Inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ref counter ); // Store current node value in inorderArr inorderArr [ counter ] = arr [ index ]; counter ++ ; // Recursively visit right subtree Inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ref counter ); } // Function to calculate minimum // swaps to sort inorder traversal static int MinSwaps ( int [] arr ) { int n = arr . Length ; int [] inorderArr = new int [ n ]; int counter = 0 ; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree Inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ref counter ); // Create an array of pairs to store value // and original index var t = new ( int int )[ n ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { t [ i ] = ( inorderArr [ i ] i ); } // Sort the array based on values to get BST order Array . Sort ( t ( a b ) => a . Item1 . CompareTo ( b . Item1 )); // Initialize visited array bool [] visited = new bool [ n ]; int ans = 0 ; // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { // If already visited or already in // the correct place skip if ( visited [ i ] || t [ i ]. Item2 == i ) continue ; // Start a cycle and find the number // of nodes in the cycle int cycleSize = 0 ; int j = i ; // Process all elements in the cycle while ( ! visited [ j ]) { visited [ j ] = true ; j = t [ j ]. Item2 ; cycleSize ++ ; } // If there is a cycle of size `cycle_size` we // need `cycle_size - 1` swaps if ( cycleSize > 1 ) { ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ); } } // Return total number of swaps return ans ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int [] arr = { 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 }; Console . WriteLine ( MinSwaps ( arr )); } }
JavaScript // Javascript program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree // Inorder traversal to get values in sorted order function inorder ( arr inorderArr index ) { // If index is out of bounds return if ( index >= arr . length ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ); // Store current node value in array inorderArr . push ( arr [ index ]); // Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps to sort inorder // traversal function minSwaps ( arr ) { let inorderArr = []; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ); // Create an array of pairs to store value and original // index let t = inorderArr . map (( val i ) => [ val i ]); let ans = 0 ; // Sort the pair array based on values to get BST order t . sort (( a b ) => a [ 0 ] - b [ 0 ]); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles let visited = Array ( arr . length ) . fill ( false ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < t . length ; i ++ ) { // If the element is already in the correct // position continue if ( visited [ i ] || t [ i ][ 1 ] === i ) continue ; // Otherwise perform swaps until the element is in // the right place let cycleSize = 0 ; let j = i ; while ( ! visited [ j ]) { visited [ j ] = true ; j = t [ j ][ 1 ]; cycleSize ++ ; } // If there is a cycle we need (cycleSize - 1) // swaps to sort the cycle if ( cycleSize > 1 ) { ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ); } } // Return total number of swaps return ans ; } let arr = [ 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ]; console . log ( minSwaps ( arr ));
Izvade
3
Laika sarežģītība: O(n*logn) kur n ir elementu skaits masīvā.
Palīgtelpa: O(n), jo tas izmanto papildu vietu masīvam
Vingrinājums: Vai mēs varam to attiecināt uz parastu bināro koku, t.i., bināro koku, kas attēlots, izmantojot kreiso un labo norādes un ne vienmēr ir pilnīgs?
Izveidojiet viktorīnu