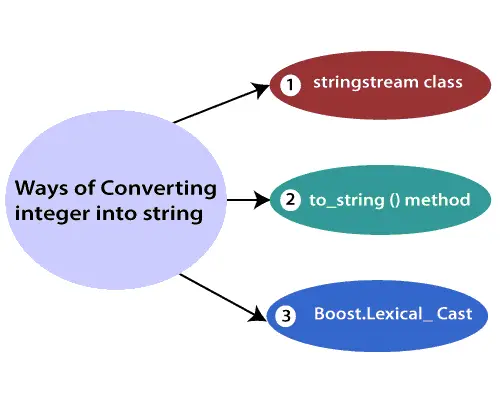
Kas yra prioritetinė eilė | Prioritetinės eilės įvadas

A pirmumo eilė yra eilės tipas, kuris sutvarko elementus pagal jų prioritetines reikšmes. Elementai su aukštesnėmis prioritetinėmis reikšmėmis paprastai nuskaitomi anksčiau nei elementai, kurių prioriteto reikšmės mažesnės.
Prioritetinėje eilėje kiekvienas elementas turi su juo susietą prioritetinę reikšmę. Kai į eilę įtraukiate elementą, jis įterpiamas į vietą, pagrįstą jo prioritetine verte. Pavyzdžiui, jei prie prioritetinės eilės pridedate elementą su aukšto prioriteto reikšme, jis gali būti įterptas šalia eilės priekio, o elementas su žemo prioriteto reikšme gali būti įterptas netoli užpakalinės dalies.
Yra keletas būdų, kaip įdiegti prioritetinę eilę, įskaitant masyvo, susieto sąrašo, krūvos arba dvejetainės paieškos medžio naudojimą. Kiekvienas metodas turi savo privalumų ir trūkumų, o geriausias pasirinkimas priklausys nuo konkrečių jūsų programos poreikių.
Prioritetinės eilės dažnai naudojamos realaus laiko sistemose, kur elementų apdorojimo tvarka gali turėti reikšmingų pasekmių. Jie taip pat naudojami algoritmuose, siekiant pagerinti jų efektyvumą, pvz Dijkstros algoritmas Norėdami rasti trumpiausią kelią grafike ir A* paieškos algoritmą kelio paieškai.
Prioritetinės eilės ypatybės
Taigi, prioritetinė eilė yra pratęsimas eilė su šiomis savybėmis.
- Kiekvienas elementas turi su juo susietą prioritetą.
- Aukšto prioriteto elementas ištraukiamas prieš elementą, kurio prioritetas žemas.
- Jei du elementai turi tą patį prioritetą, jie pateikiami pagal eilę.
Žemiau pateiktoje prioriteto eilėje elementas su didžiausia ASCII reikšme turės didžiausią prioritetą. Pirmiausia patiekiami aukštesnio prioriteto elementai.

Kaip prioritetas priskiriamas prioritetinės eilės elementams?
Prioriteto eilėje priskiriant prioritetą paprastai atsižvelgiama į elemento vertę.
Pavyzdžiui, didžiausią reikšmę turinčiam elementui priskiriamas didžiausias prioritetas, o mažiausią reikšmę turinčiam elementui – mažiausias prioritetas. Taip pat gali būti naudojamas atvirkštinis atvejis, ty mažiausią reikšmę turinčiam elementui gali būti suteiktas didžiausias prioritetas. Taip pat prioritetą galima priskirti pagal mūsų poreikius.
Prioritetinės eilės operacijos:
Įprasta prioritetinė eilė palaiko šias operacijas:
1) Įterpimas į prioritetinę eilę
Kai į prioritetinę eilę įterpiamas naujas elementas, jis perkeliamas į tuščią vietą iš viršaus į apačią ir iš kairės į dešinę. Tačiau jei elementas nėra tinkamoje vietoje, jis bus lyginamas su pirminiu mazgu. Jei elementas yra netinkama tvarka, elementai sukeičiami. Keitimo procesas tęsiasi tol, kol visi elementai yra tinkamoje padėtyje.
2) Ištrynimas prioritetinėje eilėje
Kaip žinote, didžiausioje krūvoje didžiausias elementas yra šakninis mazgas. Ir jis pašalins elementą, kuris pirmiausia turi didžiausią prioritetą. Taigi jūs pašalinate šakninį mazgą iš eilės. Šis pašalinimas sukuria tuščią angą, kuri bus toliau užpildyta nauju įterpimu. Tada jis lygina naujai įterptą elementą su visais eilėje esančiais elementais, kad išlaikytų krūvos invariantą.
3) Žvilgtelėkite į prioritetinę eilę
Ši operacija padeda grąžinti maksimalų elementą iš Max Heap arba minimalų elementą iš Min Heap neištrinant mazgo iš prioritetinės eilės.
Prioritetinių eilių tipai:
1) Didėjančios eilės prioriteto eilė
Kaip rodo pavadinimas, prioriteto eilėje didėjimo tvarka mažesnę prioriteto reikšmę turinčiam elementui prioritetų sąraše suteikiamas didesnis prioritetas. Pavyzdžiui, jei prioritetinėje eilėje turime šiuos elementus, išdėstytus didėjančia tvarka, pvz., 4,6,8,9,10. Čia 4 yra mažiausias skaičius, todėl jam bus suteiktas didžiausias prioritetas prioritetinėje eilėje, taigi, kai išeisime iš šio tipo prioritetinės eilės, 4 pašalins iš eilės ir iš eilės grąžins 4.
2) Mažėjančia tvarka Priority Queue
Kaip tikriausiai žinote, šakninis mazgas yra didžiausias elementas didžiausioje krūvoje. Taip pat pirmiausia bus pašalintas elementas, turintis aukščiausią prioritetą. Dėl to šakninis mazgas pašalinamas iš eilės. Šis ištrynimas palieka tuščią vietą, kuri ateityje bus užpildyta naujais įterpimais. Tada krūvos invariantas išlaikomas lyginant naujai įterptą elementą su visais kitais įrašais eilėje.

Prioritetinių eilių tipai
Skirtumas tarp prioritetinės ir įprastos eilės?
Elementams eilėje nėra priskirtas joks prioritetas, įgyvendinama FIFO taisyklė, o prioritetinėje eilėje elementai turi prioritetą. Pirmiausia patiekiami aukštesnio prioriteto elementai.
Kaip įdiegti prioritetinę eilę?
Prioritetinė eilė gali būti įdiegta naudojant šias duomenų struktūras:
- Masyvai
- Susietas sąrašas
- Krūvos duomenų struktūra
- Dvejetainis paieškos medis
Aptarkime visa tai išsamiai.
1) Įdiekite prioritetinę eilę naudodami masyvą:
Paprastas įgyvendinimas yra naudoti šios struktūros masyvą.
struct item {
int prekė;
int priority;
}
- enqueue(): Ši funkcija naudojama naujiems duomenims į eilę įterpti. dequeue(): Ši funkcija iš eilės pašalina didžiausio prioriteto elementą. peek()/top(): ši funkcija naudojama norint gauti aukščiausio prioriteto elementą eilėje nepašalinant jo iš eilės.
| Masyvai | eilė () | atitinkamai () | žvilgtelėti () |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laiko sudėtingumas | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
C++
// C++ program to implement Priority Queue> // using Arrays> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Structure for the elements in the> // priority queue> struct> item {> > int> value;> > int> priority;> };> // Store the element of a priority queue> item pr[100000];> // Pointer to the last index> int> size = -1;> // Function to insert a new element> // into priority queue> void> enqueue(> int> value,> int> priority)> {> > // Increase the size> > size++;> > // Insert the element> > pr[size].value = value;> > pr[size].priority = priority;> }> // Function to check the top element> int> peek()> {> > int> highestPriority = INT_MIN;> > int> ind = -1;> > // Check for the element with> > // highest priority> > for> (> int> i = 0; i <= size; i++) {> > // If priority is same choose> > // the element with the> > // highest value> > if> (highestPriority == pr[i].priority && ind>-1> > && pr[ind].value highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } else if (highestPriority highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } } // Return position of the element return ind; } // Function to remove the element with // the highest priority void dequeue() { // Find the position of the element // with highest priority int ind = peek(); // Shift the element one index before // from the position of the element // with highest priority is found for (int i = ind; i pr[i] = pr[i + 1]; } // Decrease the size of the // priority queue by one size--; } // Driver Code int main() { // Function Call to insert elements // as per the priority enqueue(10, 2); enqueue(14, 4); enqueue(16, 4); enqueue(12, 3); // Stores the top element // at the moment int ind = peek(); cout < < pr[ind].value < < endl; // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); cout < < pr[ind].value < < endl; // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); cout < < pr[ind].value < < endl; return 0; }> |
Java
// Java program to implement Priority Queue> // using Arrays> import> java.util.*;> // Structure for the elements in the> // priority queue> class> item {> > public> int> value;> > public> int> priority;> };> class> GFG {> > // Store the element of a priority queue> > static> item[] pr => new> item[> 100000> ];> > // Pointer to the last index> > static> int> size = -> 1> ;> > // Function to insert a new element> > // into priority queue> > static> void> enqueue(> int> value,> int> priority)> > {> > // Increase the size> > size++;> > // Insert the element> > pr[size] => new> item();> > pr[size].value = value;> > pr[size].priority = priority;> > }> > // Function to check the top element> > static> int> peek()> > {> > int> highestPriority = Integer.MIN_VALUE;> > int> ind = -> 1> ;> > // Check for the element with> > // highest priority> > for> (> int> i => 0> ; i <= size; i++) {> > // If priority is same choose> > // the element with the> > // highest value> > if> (highestPriority == pr[i].priority> > && ind>-> 1> > && pr[ind].value highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } else if (highestPriority highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } } // Return position of the element return ind; } // Function to remove the element with // the highest priority static void dequeue() { // Find the position of the element // with highest priority int ind = peek(); // Shift the element one index before // from the position of the element // with highest priority is found for (int i = ind; i pr[i] = pr[i + 1]; } // Decrease the size of the // priority queue by one size--; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Function Call to insert elements // as per the priority enqueue(10, 2); enqueue(14, 4); enqueue(16, 4); enqueue(12, 3); // Stores the top element // at the moment int ind = peek(); System.out.println(pr[ind].value); // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); System.out.println(pr[ind].value); // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); System.out.println(pr[ind].value); } } // this code is contributed by phasing17> |
Python3
import> sys> # Structure for the elements in the> # priority queue> class> item :> > value> => 0> > priority> => 0> class> GFG :> > > # Store the element of a priority queue> > pr> => [> None> ]> *> (> 100000> )> > > # Pointer to the last index> > size> => -> 1> > > # Function to insert a new element> > # into priority queue> > @staticmethod> > def> enqueue( value, priority) :> > > # Increase the size> > GFG.size> +> => 1> > > # Insert the element> > GFG.pr[GFG.size]> => item()> > GFG.pr[GFG.size].value> => value> > GFG.pr[GFG.size].priority> => priority> > > # Function to check the top element> > @staticmethod> > def> peek() :> > highestPriority> => -> sys.maxsize> > ind> => -> 1> > > # Check for the element with> > # highest priority> > i> => 0> > while> (i <> => GFG.size) :> > > # If priority is same choose> > # the element with the> > # highest value> > if> (highestPriority> => => GFG.pr[i].priority> and> ind>>> |
C#
// C# program to implement Priority Queue> // using Arrays> using> System;> // Structure for the elements in the> // priority queue> public> class> item {> > public> int> value;> > public> int> priority;> };> public> class> GFG> {> > > // Store the element of a priority queue> > static> item[] pr => new> item[100000];> > // Pointer to the last index> > static> int> size = -1;> > // Function to insert a new element> > // into priority queue> > static> void> enqueue(> int> value,> int> priority)> > {> > // Increase the size> > size++;> > > // Insert the element> > pr[size] => new> item();> > pr[size].value = value;> > pr[size].priority = priority;> > }> > > // Function to check the top element> > static> int> peek()> > {> > int> highestPriority => int> .MinValue;> > int> ind = -1;> > > // Check for the element with> > // highest priority> > for> (> int> i = 0; i <= size; i++) {> > > // If priority is same choose> > // the element with the> > // highest value> > if> (highestPriority == pr[i].priority && ind>-1> > && pr[ind].value highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } else if (highestPriority highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } } // Return position of the element return ind; } // Function to remove the element with // the highest priority static void dequeue() { // Find the position of the element // with highest priority int ind = peek(); // Shift the element one index before // from the position of the element // with highest priority is found for (int i = ind; i pr[i] = pr[i + 1]; } // Decrease the size of the // priority queue by one size--; } public static void Main(string[] args) { // Function Call to insert elements // as per the priority enqueue(10, 2); enqueue(14, 4); enqueue(16, 4); enqueue(12, 3); // Stores the top element // at the moment int ind = peek(); Console.WriteLine(pr[ind].value); // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); Console.WriteLine(pr[ind].value); // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); Console.WriteLine(pr[ind].value); } } //this code is contributed by phasing17> |
Javascript
// JavaScript program to implement Priority Queue> // using Arrays> // Structure for the elements in the> // priority queue> class item {> > constructor()> > {> > this> .value;> > this> .priority;> > }> };> // Store the element of a priority queue> let pr = [];> for> (> var> i = 0; i <100000; i++)> > pr.push(> new> item());> // Pointer to the last index> let size = -1;> // Function to insert a new element> // into priority queue> function> enqueue(value, priority)> {> > // Increase the size> > size++;> > // Insert the element> > pr[size] => new> item();> > pr[size].value = value;> > pr[size].priority = priority;> }> // Function to check the top element> function> peek()> {> > let highestPriority = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;> > let ind = -1;> > // Check for the element with> > // highest priority> > for> (> var> i = 0; i <= size; i++) {> > // If priority is same choose> > // the element with the> > // highest value> > if> (highestPriority == pr[i].priority && ind>-1> > && pr[ind].value highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } else if (highestPriority highestPriority = pr[i].priority; ind = i; } } // Return position of the element return ind; } // Function to remove the element with // the highest priority function dequeue() { // Find the position of the element // with highest priority let ind = peek(); // Shift the element one index before // from the position of the element // with highest priority is found for (var i = ind; i pr[i] = pr[i + 1]; } // Decrease the size of the // priority queue by one size--; } // Function Call to insert elements // as per the priority enqueue(10, 2); enqueue(14, 4); enqueue(16, 4); enqueue(12, 3); // Stores the top element // at the moment let ind = peek(); console.log(pr[ind].value); // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); console.log(pr[ind].value); // Dequeue the top element dequeue(); // Check the top element ind = peek(); console.log(pr[ind].value); // this code is contributed by phasing17> |
Išvestis
16 14 12
Pastaba: Skaityti Šis straipsnis daugiau detalių.
2) Įdiekite prioritetinę eilę naudodami susietą sąrašą:
Įgyvendinant „LinkedList“, įrašai rūšiuojami mažėjančia tvarka pagal jų prioritetą. Aukščiausio prioriteto elementas visada pridedamas prie prioritetinės eilės, kuri sudaroma naudojant susietus sąrašus, priekyje. Funkcijos kaip stumti () , pop () , ir žvilgtelėti () naudojami prioritetinei eilei įgyvendinti naudojant susietą sąrašą ir paaiškinti taip:
- push(): Ši funkcija naudojama naujiems duomenims įterpti į eilę. pop(): Ši funkcija iš eilės pašalina didžiausio prioriteto elementą. peek() / top(): ši funkcija naudojama norint gauti aukščiausio prioriteto elementą eilėje nepašalinant jo iš eilės.
| Susietas sąrašas | stumti () | pop () | žvilgtelėti () |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laiko sudėtingumas | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
C++
// C++ code to implement Priority Queue> // using Linked List> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Node> typedef> struct> node {> > int> data;> > // Lower values indicate> > // higher priority> > int> priority;> > struct> node* next;> } Node;> // Function to create a new node> Node* newNode(> int> d,> int> p)> {> > Node* temp = (Node*)> malloc> (> sizeof> (Node));> > temp->duomenys = d;> > temp->prioritetas = p;> > temp->kitas = NULL;> > return> temp;> }> // Return the value at head> int> peek(Node** head) {> return> (*head)->duomenys; }> // Removes the element with the> // highest priority form the list> void> pop(Node** head)> {> > Node* temp = *head;> > (*head) = (*head)->kitas;> > free> (temp);> }> // Function to push according to priority> void> push(Node** head,> int> d,> int> p)> {> > Node* start = (*head);> > // Create new Node> > Node* temp = newNode(d, p);> > // Special Case: The head of list has> > // lesser priority than new node> > if> ((*head)->prioritetas // Įterpti naują mazgą prieš head temp->next = *head; (*galva) = temp; } else { // Pereikite sąrašą ir raskite // vietą, kurioje norite įterpti naują mazgą, while (pradžia->kitas != NULL && start->next->priority> p) { start = start->next; } // Sąrašo pabaigoje // arba reikiamoje pozicijoje temp->next = start->ext; start->ext = temp; } } // Funkcija patikrinti, ar sąrašas tuščias int isEmpty(Node** head) { return (*head) == NULL; } // Tvarkyklės kodas int main() { // Sukurti prioritetinę eilę // 7->4->5->6 Mazgas* pq = newNode(4, 1); stumti(&pq, 5, 2); stumti(&pq, 6, 3); stumti(&pq, 7, 0); while (!isEmpty(&pq)) { cout < < ' ' < < peek(&pq); pop(&pq); } return 0; }> |
Java
// Java code to implement Priority Queue> // using Linked List> import> java.util.* ;> class> Solution> {> // Node> static> class> Node {> > int> data;> > > // Lower values indicate higher priority> > int> priority;> > Node next;> > }> static> Node node => new> Node();> > // Function to Create A New Node> static> Node newNode(> int> d,> int> p)> {> > Node temp => new> Node();> > temp.data = d;> > temp.priority = p;> > temp.next => null> ;> > > return> temp;> }> > // Return the value at head> static> int> peek(Node head)> {> > return> (head).data;> }> > // Removes the element with the> // highest priority from the list> static> Node pop(Node head)> {> > Node temp = head;> > (head) = (head).next;> > return> head;> }> > // Function to push according to priority> static> Node push(Node head,> int> d,> int> p)> {> > Node start = (head);> > > // Create new Node> > Node temp = newNode(d, p);> > > // Special Case: The head of list has lesser> > // priority than new node. So insert new> > // node before head node and change head node.> > if> ((head).priority // Insert New Node before head temp.next = head; (head) = temp; } else { // Traverse the list and find a // position to insert new node while (start.next != null && start.next.priority>p) { pradžia = pradžia.kitas; } // Sąrašo pabaigoje // arba reikiamoje pozicijoje temp.next = start.next; start.ext = temp; } grįžti galvutė; } // Funkcija patikrinti, ar sąrašas yra tuščias static int isEmpty(Node head) { return ((head) == null)?1:0; } // Tvarkyklės kodas public static void main(String args[]) { // Sukurti prioritetinę eilę // 7.4.5.6 Mazgas pq = newNode(4, 1); pq =push(pq, 5, 2); pq =push(pq, 6, 3); pq =push(pq, 7, 0); while (isEmpty(pq)==0) { System.out.printf('%d ', peek(pq)); pq=pop(pq); } } } // Šį kodą pateikė ishankhandelwals.>> |
>
# Python3 code to implement Priority Queue># using Singly Linked List># Class to create new node which includes># Node Data, and Node Priority>class>PriorityQueueNode:>>def>_init_(>self>, value, pr):>>self>.data>=>value>>self>.priority>=>pr>>self>.>next>=>None># Implementation of Priority Queue>class>PriorityQueue:>>def>_init_(>self>):>>self>.front>=>None>># Method to check Priority Queue is Empty>># or not if Empty then it will return True>># Otherwise False>>def>isEmpty(>self>):>>return>True>if>self>.front>=>=>None>else>False>># Method to add items in Priority Queue>># According to their priority value>>def>push(>self>, value, priority):>># Condition check for checking Priority>># Queue is empty or not>>if>self>.isEmpty()>=>=>True>:>># Creating a new node and assigning>># it to class variable>>self>.front>=>PriorityQueueNode(value,>>priority)>># Returning 1 for successful execution>>return>1>>else>:>># Special condition check to see that>># first node priority value>>if>self>.front.priority # Creating a new node newNode = PriorityQueueNode(value, priority) # Updating the new node next value newNode.next = self.front # Assigning it to self.front self.front = newNode # Returning 1 for successful execution return 1 else: # Traversing through Queue until it # finds the next smaller priority node temp = self.front while temp.next: # If same priority node found then current # node will come after previous node if priority>= temp.next.priority: pertrauka temp = temp.next newNode = PriorityQueueMazgas(reikšmė, prioritetas) newNode.next = temp.next temp.next = naujasMazgas # Grąžina 1 už sėkmingą vykdymą return 1 # Aukšto prioriteto elemento # pašalinimo iš Priority Queue def pop(self): # Sąlygos patikrinimas tikrinimui # Priority Queue yra tuščia arba ne, jei self.isEmpty() == Tiesa: grąžinkite kitur: # Aukšto prioriteto mazgo pašalinimas iš # Priority Queue ir priekinės # atnaujinimas su next mazgas self.front = self.front.next return 1 # Metodas grąžinti aukšto prioriteto mazgą # reikšmė Nepašalinant def peek(self): # Sąlygos tikrinimas tikrinant Priority # Eilė tuščia arba ne, jei self.isEmpty() == Tiesa: return else: return self.front.data # Metodas pereiti per prioritetą # Eilės def traverse(self): # Sąlygos tikrinimas tikrinant Priority # Eilė tuščia arba ne, jei self.isEmpty() == Tiesa: grįžti ' Eilė tuščia!' else: temp = self.front while temp: print(temp.data, end=' ') temp = temp.next # Tvarkyklės kodas if _name_ == '_main_': # Kuriamas Priority # Queue egzempliorius ir pridedant reikšmes # 7 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 pq = PriorityQueue() pq.push(4, 1) pq.push(5, 2) pq.push(6, 3) pq .push(7, 0) # Perėjimas per prioritetinę eilę pq.traverse() # Pašalinamas aukščiausio prioriteto elementas # prioritetinei eilei pq.pop()>
C#
// C# code to implement Priority Queue>// using Linked List>using>System;>class>GFG>{>>// Node>>public>class>Node>>{>>public>int>data;>>// Lower values indicate>>// higher priority>>public>int>priority;>>public>Node next;>>}>>public>static>Node node =>new>Node();>>// Function to Create A New Node>>public>static>Node newNode(>int>d,>int>p)>>{>>Node temp =>new>Node();>>temp.data = d;>>temp.priority = p;>>temp.next =>null>;>>return>temp;>>}>>// Return the value at head>>public>static>int>peek(Node head)>>{>>return>(head).data;>>}>>// Removes the element with the>>// highest priority from the list>>public>static>Node pop(Node head)>>{>>Node temp = head;>>(head) = (head).next;>>return>head;>>}>>// Function to push according to priority>>public>static>Node push(Node head,>>int>d,>int>p)>>{>>Node start = (head);>>// Create new Node>>Node temp = newNode(d, p);>>// Special Case: The head of list>>// has lesser priority than new node.>>// So insert new node before head node>>// and change head node.>>if>((head).priority { // Insert New Node before head temp.next = head; (head) = temp; } else { // Traverse the list and find a // position to insert new node while (start.next != null && start.next.priority>p) { pradžia = pradžia.kitas; } // Sąrašo pabaigoje // arba reikiamoje pozicijoje temp.next = start.next; start.ext = temp; } grįžti galvutė; } // Funkcija patikrinti, ar sąrašas yra tuščias public static int isEmpty(Node head) { return ((head) == null) ? 1:0; } // Tvarkyklės kodas public static void Main(string[] args) { // Sukurti prioritetinę eilę // 7.4.5.6 Mazgas pq = newNode(4, 1); pq = push(pq, 5, 2); pq = push(pq, 6, 3); pq = push(pq, 7, 0); while (isEmpty(pq) == 0) { Console.Write('{0:D} ', peek(pq)); pq = pop(pq); } } } // Šį kodą pateikė ishankhandelwals.>>
>
// JavaScript code to implement Priority Queue>// using Linked List>// Node>class Node {>>// Lower values indicate>>// higher priority>>constructor() {>>this>.data = 0;>>this>.priority = 0;>>this>.next =>null>;>>}>}>var>node =>new>Node();>// Function to Create A New Node>function>newNode(d, p) {>>var>temp =>new>Node();>>temp.data = d;>>temp.priority = p;>>temp.next =>null>;>>return>temp;>}>// Return the value at head>function>peek(head) {>>return>head.data;>}>// Removes the element with the>// highest priority from the list>function>pop(head) {>>var>temp = head;>>head = head.next;>>return>head;>}>// Function to push according to priority>function>push(head, d, p) {>>var>start = head;>>// Create new Node>>var>temp = newNode(d, p);>>// Special Case: The head of list>>// has lesser priority than new node.>>// So insert new node before head node>>// and change head node.>>if>(head.priority // Insert New Node before head temp.next = head; head = temp; } else { // Traverse the list and find a // position to insert new node while (start.next != null && start.next.priority>p) { pradžia = pradžia.kitas; } // Sąrašo pabaigoje // arba reikiamoje pozicijoje temp.next = start.next; start.ext = temp; } grįžti galvutė; } // Funkcija patikrinti, ar sąrašas tuščias function isEmpty(head) { return head == null ? 1:0; } // Tvarkyklės kodas // Sukurti prioritetinę eilę // 7.4.5.6 var pq = newNode(4, 1); pq = push(pq, 5, 2); pq = push(pq, 6, 3); pq = push(pq, 7, 0); while (isEmpty(pq) == 0) { console.log(peek(pq),' '); pq = pop(pq); } // Šį kodą pateikė ishankhandelwals.>>
>
Prioritetinė eilė C++ „Java“ prioritetinė eilė „Python“ prioritetinė eilė „JavaScript“ prioritetinė eilė Naujausi straipsniai apie prioritetinę eilę!

![10 galingiausių pasaulio šalių pagal karinę jėgą [2023]](https://techcodeview.com/img/current-gk/40/top-10-most-powerful-country-world-military-strength.webp)