R – duomenų rėmeliai
R programavimo kalba yra atvirojo kodo programavimo kalba, plačiai naudojama kaip statistinė programinė įranga ir duomenų analizės įrankis. Duomenų rėmeliai R kalba yra bendrieji R duomenų objektai, naudojami lentelių duomenims saugoti.
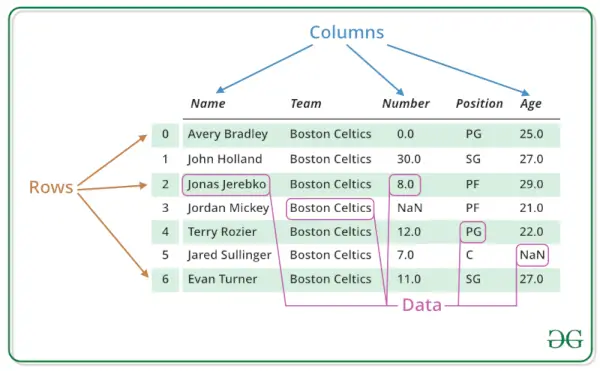
Duomenų rėmeliai taip pat gali būti interpretuojami kaip matricos, kuriose kiekvienas a stulpelis matrica gali būti skirtingų duomenų tipų. „R DataFrame“ sudaro trys pagrindiniai komponentai: duomenys, eilutės ir stulpeliai.
R duomenų rėmelių struktūra
Kaip matote toliau esančiame paveikslėlyje, duomenų rėmo struktūra yra tokia.
Duomenys pateikiami lentelių pavidalu, todėl juos lengviau valdyti ir suprasti.

R – duomenų rėmeliai
Sukurkite duomenų rėmelį R programavimo kalba
Norėdami sukurti R duomenų rėmelį, naudokite data.frame() funkciją, tada kiekvieną sukurtą vektorių perduokite kaip argumentus funkcijai.
R
# R program to create dataframe> # creating a data frame> friend.data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1:5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> > 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> > 'Dhoni'> ),> > stringsAsFactors => FALSE> )> # print the data frame> print> (friend.data)> |
Išvestis:
friend_id friend_name 1 1 Sachin 2 2 Sourav 3 3 Dravid 4 4 Sehwag 5 5 Dhoni
Gaukite R duomenų rėmelio struktūrą
R duomenų rėmo struktūrą galima gauti naudojant str() funkcija R.
Jis gali rodyti net vidinę didelių sąrašų struktūrą. Tai suteikia vieno pamušalo išvestį pagrindiniams R objektams, leidžiančius vartotojui sužinoti apie objektą ir jo sudedamąsias dalis.
R
# R program to get the> # structure of the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1:5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> > 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> > 'Dhoni'> ),> > stringsAsFactors => FALSE> )> # using str()> print> (> str> (friend.data))> |
Išvestis:
'data.frame': 5 obs. of 2 variables: $ friend_id : int 1 2 3 4 5 $ friend_name: chr 'Sachin' 'Sourav' 'Dravid' 'Sehwag' ... NULL
Duomenų santrauka R duomenų rėmelyje
R duomenų rėmelyje statistinę suvestinę ir duomenų pobūdį galima gauti taikant santrauka () funkcija.
Tai bendroji funkcija, naudojama įvairių modelių pritaikymo funkcijų rezultatų santraukoms sudaryti. Funkcija iškviečia tam tikrus metodus, kurie priklauso nuo pirmojo argumento klasės.
R
# R program to get the> # summary of the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1:5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> > 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> > 'Dhoni'> ),> > stringsAsFactors => FALSE> )> # using summary()> print> (> summary> (friend.data))> |
Išvestis:
friend_id friend_name Min. :1 Length:5 1st Qu.:2 Class :character Median :3 Mode :character Mean :3 3rd Qu.:4 Max. :5
Ištraukite duomenis iš duomenų rėmelio R
Duomenų ištraukimas iš R duomenų rėmelio reiškia, kad reikia pasiekti jo eilutes arba stulpelius. Galima išskirti konkretų stulpelį iš R duomenų rėmelio, naudojant jo stulpelio pavadinimą.
R
# R program to extract> # data from the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1:5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> > 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> > 'Dhoni'> ),> > stringsAsFactors => FALSE> )> # Extracting friend_name column> result <-> data.frame> (friend.data$friend_name)> print> (result)> |
Išvestis:
friend.data.friend_name 1 Sachin 2 Sourav 3 Dravid 4 Sehwag 5 Dhoni
Išplėskite duomenų rėmelį R kalba
Duomenų rėmelį R galima išplėsti pridedant naujų stulpelių ir eilučių prie jau esamo R duomenų rėmelio.
R
# R program to expand> # the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1:5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> > 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> > 'Dhoni'> ),> > stringsAsFactors => FALSE> )> # Expanding data frame> friend.data$location <-> c> (> 'Kolkata'> ,> 'Delhi'> ,> > 'Bangalore'> ,> 'Hyderabad'> ,> > 'Chennai'> )> resultant <- friend.data> # print the modified data frame> print> (resultant)> |
Išvestis:
friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 3 3 Dravid Bangalore 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai
R programoje galima atlikti įvairių tipų operacijas duomenų rėmelyje, pvz pasiekti eilutes ir stulpelius, pasirinkti duomenų rėmelio poaibį, redaguoti duomenų rėmelius, ištrinti eilutes ir stulpelius duomenų rėmelyje ir kt.
Prašau kreiptis į „DataFrame“ operacijos R žinoti apie visų tipų operacijas, kurias galima atlikti duomenų rėmelyje.
Pasiekite elementus R duomenų rėmelyje
Mes galime pasirinkti ir pasiekti bet kurį elementą iš duomenų rėmelio naudodami vieną $> , skliausteliuose [ ] or> dvigubi skliaustai [[]]> norėdami pasiekti stulpelius iš duomenų rėmelio.
R
# creating a data frame> friend.data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1:5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> > 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> > 'Dhoni'> ),> > stringsAsFactors => FALSE> )> # Access Items using []> friend.data[1]> # Access Items using [[]]> friend.data[[> 'friend_name'> ]]> # Access Items using $> friend.data$friend_id> |
Išvestis:
friend_id 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 Access Items using [[]] [1] 'Sachin' 'Sourav' 'Dravid' 'Sehwag' 'Dhoni' Access Items using $ [1] 1 2 3 4 5
Eilučių ir stulpelių kiekis
Naudodami dim funkciją galime sužinoti, kiek eilučių ir stulpelių yra mūsų duomenų rėmelyje.
R
# creating a data frame> friend.data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1:5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> > 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> > 'Dhoni'> ),> > stringsAsFactors => FALSE> )> # find out the number of rows and clumns> dim> (friend.data)> |
Išvestis:
[1] 5 2
Pridėkite eilutes ir stulpelius R duomenų rėmelyje
Galite lengvai pridėti eilučių ir stulpelių į R DataFrame. Įterpimas padeda išplėsti jau esamą DataFrame ir nereikia naujo.
Pažiūrėkime, kaip į DataFrame pridėti eilučių ir stulpelių? su pavyzdžiu:
Pridėkite eilutes R duomenų rėmelyje
Norėdami pridėti eilučių į duomenų rėmelį, galite naudoti įtaisytąją funkciją rbind ().
Toliau pateiktame pavyzdyje parodytas rbind() veikimas R Data Frame.
R
# Creating a dataframe representing products in a store> Products <-> data.frame> (> > Product_ID => c> (101, 102, 103),> > Product_Name => c> (> 'T-Shirt'> ,> 'Jeans'> ,> 'Shoes'> ),> > Price => c> (15.99, 29.99, 49.99),> > Stock => c> (50, 30, 25)> )> # Print the existing dataframe> cat> (> 'Existing dataframe (Products):
'> )> print> (Products)> # Adding a new row for a new product> New_Product <-> c> (104,> 'Sunglasses'> , 39.99, 40)> Products <-> rbind> (Products, New_Product)> # Print the updated dataframe after adding the new product> cat> (> '
Updated dataframe after adding a new product:
'> )> print> (Products)> |
Išvestis:
Existing dataframe (Products): Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 Updated dataframe after adding a new product: Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 4 104 Sunglasses 39.99 40
Pridėkite stulpelius R duomenų rėmelyje
Norėdami pridėti stulpelių į duomenų rėmelį, galite naudoti įtaisytąją funkciją cbind ().
Toliau pateiktame pavyzdyje parodytas cbind() veikimas R Data Frame .
R
# Existing dataframe representing products in a store> Products <-> data.frame> (> > Product_ID => c> (101, 102, 103),> > Product_Name => c> (> 'T-Shirt'> ,> 'Jeans'> ,> 'Shoes'> ),> > Price => c> (15.99, 29.99, 49.99),> > Stock => c> (50, 30, 25)> )> # Print the existing dataframe> cat> (> 'Existing dataframe (Products):
'> )> print> (Products)> # Adding a new column for 'Discount' to the dataframe> Discount <-> c> (5, 10, 8)> # New column values for discount> Products <-> cbind> (Products, Discount)> # Rename the added column> colnames> (Products)[> ncol> (Products)] <-> 'Discount'> # Renaming the last column> # Print the updated dataframe after adding the new column> cat> (> '
Updated dataframe after adding a new column 'Discount':
'> )> print> (Products)> |
Išvestis:
Existing dataframe (Products): Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 Updated dataframe after adding a new column 'Discount': Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock Discount 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 5 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 10 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 8
Pašalinti eilutes ir stulpelius
Duomenų rėmelis R pašalina stulpelius ir eilutes iš jau esamo R duomenų rėmelio.
Pašalinti R DataFrame eilutę
R
library> (dplyr)> # Create a data frame> data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> 'Dhoni'> ),> > location => c> (> 'Kolkata'> ,> 'Delhi'> ,> 'Bangalore'> ,> 'Hyderabad'> ,> 'Chennai'> )> )> data> # Remove a row with friend_id = 3> data <-> subset> (data, friend_id != 3)> data> |
Išvestis:
friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 3 3 Dravid Bangalore 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai # Remove a row with friend_id = 3 friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai
Aukščiau pateiktame kode pirmiausia sukūrėme duomenų rėmelį, vadinamą duomenis su trimis stulpeliais: draugo_id , draugo_vardas , ir vieta . Norėdami pašalinti eilutę su draugo_id lygus 3, naudojome poaibis () funkcija ir nurodė sąlygą draugo_id != 3 . Tai pašalino eilutę su draugo_id lygus 3.
Pašalinkite stulpelį R DataFrame
R
library> (dplyr)> # Create a data frame> data <-> data.frame> (> > friend_id => c> (1, 2, 3, 4, 5),> > friend_name => c> (> 'Sachin'> ,> 'Sourav'> ,> 'Dravid'> ,> 'Sehwag'> ,> 'Dhoni'> ),> > location => c> (> 'Kolkata'> ,> 'Delhi'> ,> 'Bangalore'> ,> 'Hyderabad'> ,> 'Chennai'> )> )> data> # Remove the 'location' column> data <-> select> (data, -location)> data> |
Išvestis:
friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 3 3 Dravid Bangalore 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai>Pašalinkite stulpelį „vieta“ draugo_id draugo_vardas 1 1 Sachin 2 2 Sourav 3 3 Dravid 4 4 Sehwag 5 5 Dhoni
Norėdami pašalinti vieta stulpelyje naudojome pasirinkti () funkcija ir nurodyta - vieta . The – ženklas rodo, kad norime pašalinti vieta stulpelyje. Gautas duomenų rėmelis duomenis bus tik du stulpeliai: draugo_id ir draugo_vardas .
Duomenų rėmelių sujungimas R
Yra 2 būdai, kaip sujungti duomenų rėmelius R. Galite sujungti juos vertikaliai arba horizontaliai.
Pažvelkime į abu atvejus su pavyzdžiais:
Sujunkite R duomenų rėmelį vertikaliai
Jei norite sujungti 2 duomenų rėmelius vertikaliai, galite naudoti rbind() funkcija. Ši funkcija veikia derinant du ar daugiau duomenų rėmelių.
R
# Creating two sample dataframes> df1 <-> data.frame> (> > Name => c> (> 'Alice'> ,> 'Bob'> ),> > Age => c> (25, 30),> > Score => c> (80, 75)> )> df2 <-> data.frame> (> > Name => c> (> 'Charlie'> ,> 'David'> ),> > Age => c> (28, 35),> > Score => c> (90, 85)> )> # Print the existing dataframes> cat> (> 'Dataframe 1:
'> )> print> (df1)> cat> (> '
Dataframe 2:
'> )> print> (df2)> # Combining the dataframes using rbind()> combined_df <-> rbind> (df1, df2)> # Print the combined dataframe> cat> (> '
Combined Dataframe:
'> )> print> (combined_df)> |
Išvestis:
Dataframe 1: Name Age Score 1 Alice 25 80 2 Bob 30 75 Dataframe 2: Name Age Score 1 Charlie 28 90 2 David 35 85 Combined Dataframe: Name Age Score 1 Alice 25 80 2 Bob 30 75 3 Charlie 28 90 4 David 35 85
Horizontaliai sujunkite R duomenų rėmelį:
Jei norite sujungti 2 duomenų rėmelius horizontaliai, galite naudoti cbind() funkcija. Ši funkcija veikia derinant du ar daugiau duomenų rėmelių.
R
# Creating two sample dataframes> df1 <-> data.frame> (> > Name => c> (> 'Alice'> ,> 'Bob'> ),> > Age => c> (25, 30),> > Score => c> (80, 75)> )> df2 <-> data.frame> (> > Height => c> (160, 175),> > Weight => c> (55, 70)> )> # Print the existing dataframes> cat> (> 'Dataframe 1:
'> )> print> (df1)> cat> (> '
Dataframe 2:
'> )> print> (df2)> # Combining the dataframes using cbind()> combined_df <-> cbind> (df1, df2)> # Print the combined dataframe> cat> (> '
Combined Dataframe:
'> )> print> (combined_df)> |
Išvestis:
Dataframe 1: Name Age Score 1 Alice 25 80 2 Bob 30 75 Dataframe 2: Height Weight 1 160 55 2 175 70 Combined Dataframe: Name Age Score Height Weight 1 Alice 25 80 160 55 2 Bob 30 75 175 70
Taip pat skaitykite:
- R – Objektai
- Duomenų struktūros R programavimuose
Šiame straipsnyje mes apžvelgėme R duomenų rėmeliai, ir visos pagrindinės operacijos, tokios kaip kūrimas, prieiga, suvestinė, pridėjimas ir pašalinimas. Šio straipsnio tikslas yra supažindinti jus su duomenų rėmeliais R, kad galėtumėte juos naudoti savo projektuose.
Tikimės, kad tai padės suprasti duomenų rėmelių sąvoką R ir galėsite lengvai įdiegti R duomenų rėmelį savo projektuose.