Patikrinkite, ar dvigubai susietas simbolių sąrašas yra palindromas, ar ne
Atsižvelgiant į a dvigubai susietas sąrašas iš simbolių užduotis yra patikrinti, ar dvigubai susietas sąrašas yra a palindromas ar ne.
Pavyzdžiai:
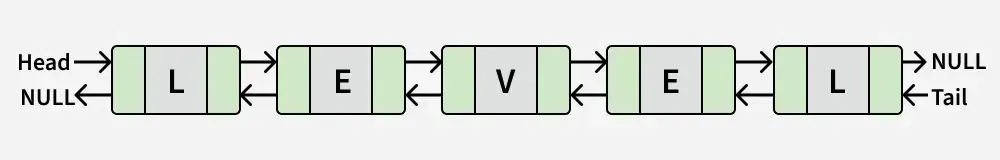
Įvestis:

Išvestis: Tiesa
Paaiškinimas: Sąrašas atitinka „LYGIS“, kuris yra palindromas.
Įvestis:
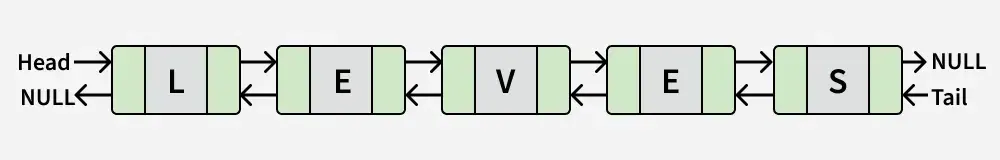
Išvestis: Netiesa
Paaiškinimas: Sąrašas atitinka „LEVES“, kuris nėra palindromas.
Prieiga:
Idėja yra inicijuoti dvi nuorodas: paliko (iš pradžių nustatyta ant galvos) ir teisingai (iš pradžių nustatyta prie uodegos). Palyginkite dviejų rodyklių reikšmes paliko nėra lygus nuliui arba paliko persikėlė į kitą teisingai. Jei dviejų rodyklių reikšmės yra lygus judėti paliko prie kito rodyklės ir teisingai į ankstesnį žymeklį. Priešingu atveju grąžinkite klaidingą.
Žemiau pateikiamas pirmiau minėto metodo įgyvendinimas:
C++ // C++ program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : char data ; Node * prev * next ; Node ( char x ) { data = x ; prev = nullptr ; next = nullptr ; } }; // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome bool isPalindrome ( Node * head ) { if ( head == nullptr ) return true ; // Find the tail ptr. Node * left = head * right = head ; while ( right -> next != nullptr ) { right = right -> next ; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while ( left != right && left -> prev != right ) { // If char mismatch return // false. if ( left -> data != right -> data ) return false ; // Move the pointers left = left -> next ; right = right -> prev ; } return true ; } int main () { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L Node * head = new Node ( 'L' ); head -> next = new Node ( 'E' ); head -> next -> prev = head ; head -> next -> next = new Node ( 'V' ); head -> next -> next -> prev = head -> next ; head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 'E' ); head -> next -> next -> next -> prev = head -> next -> next ; head -> next -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 'L' ); head -> next -> next -> next -> next -> prev = head -> next -> next -> next ; if ( isPalindrome ( head )) cout < < 'True' ; else cout < < 'False' ; return 0 ; }
C // C program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. #include #include struct Node { char data ; struct Node * prev ; struct Node * next ; }; // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome int isPalindrome ( struct Node * head ) { if ( head == NULL ) return 1 ; // Find the tail ptr. struct Node * left = head * right = head ; while ( right -> next != NULL ) { right = right -> next ; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while ( left != right && left -> prev != right ) { // If char mismatch return // false. if ( left -> data != right -> data ) return 0 ; // Move the pointers left = left -> next ; right = right -> prev ; } return 1 ; } struct Node * createNode ( char x ) { struct Node * newNode = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); newNode -> data = x ; newNode -> prev = NULL ; newNode -> next = NULL ; return newNode ; } int main () { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L struct Node * head = createNode ( 'L' ); head -> next = createNode ( 'E' ); head -> next -> prev = head ; head -> next -> next = createNode ( 'V' ); head -> next -> next -> prev = head -> next ; head -> next -> next -> next = createNode ( 'E' ); head -> next -> next -> next -> prev = head -> next -> next ; head -> next -> next -> next -> next = createNode ( 'L' ); head -> next -> next -> next -> next -> prev = head -> next -> next -> next ; if ( isPalindrome ( head )) printf ( 'True n ' ); else printf ( 'False n ' ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. class Node { char data ; Node prev next ; Node ( char x ) { data = x ; prev = null ; next = null ; } } class GfG { // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome static boolean isPalindrome ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return true ; // Find the tail ptr. Node left = head right = head ; while ( right . next != null ) { right = right . next ; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while ( left != right && left . prev != right ) { // If char mismatch return // false. if ( left . data != right . data ) return false ; // Move the pointers left = left . next ; right = right . prev ; } return true ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L Node head = new Node ( 'L' ); head . next = new Node ( 'E' ); head . next . prev = head ; head . next . next = new Node ( 'V' ); head . next . next . prev = head . next ; head . next . next . next = new Node ( 'E' ); head . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next ; head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 'L' ); head . next . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next . next ; if ( isPalindrome ( head )) System . out . println ( 'True' ); else System . out . println ( 'False' ); } }
Python # Python program to check if a doubly # linked list is palindrome. class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . prev = None self . next = None # Function that returns true if the # doubly linked list is a palindrome def isPalindrome ( head ): if head is None : return True # Find the tail ptr. left = head right = head while right . next is not None : right = right . next # Check if the doubly linked list is # a palindrome. while left != right and left . prev != right : # If char mismatch return # false. if left . data != right . data : return False # Move the pointers left = left . next right = right . prev return True if __name__ == '__main__' : # Doubly Linked list: # L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L head = Node ( 'L' ) head . next = Node ( 'E' ) head . next . prev = head head . next . next = Node ( 'V' ) head . next . next . prev = head . next head . next . next . next = Node ( 'E' ) head . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next head . next . next . next . next = Node ( 'L' ) head . next . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next . next if isPalindrome ( head ): print ( 'True' ) else : print ( 'False' )
C# // C# program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. using System ; class Node { public char data ; public Node prev next ; public Node ( char x ) { data = x ; prev = null ; next = null ; } } class GfG { // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome static bool isPalindrome ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return true ; // Find the tail ptr. Node left = head right = head ; while ( right . next != null ) { right = right . next ; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while ( left != right && left . prev != right ) { // If char mismatch return // false. if ( left . data != right . data ) return false ; // Move the pointers left = left . next ; right = right . prev ; } return true ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L Node head = new Node ( 'L' ); head . next = new Node ( 'E' ); head . next . prev = head ; head . next . next = new Node ( 'V' ); head . next . next . prev = head . next ; head . next . next . next = new Node ( 'E' ); head . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next ; head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 'L' ); head . next . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next . next ; if ( isPalindrome ( head )) Console . WriteLine ( 'True' ); else Console . WriteLine ( 'False' ); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . prev = null ; this . next = null ; } } // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome function isPalindrome ( head ) { if ( head === null ) return true ; // Find the tail ptr. let left = head right = head ; while ( right . next !== null ) { right = right . next ; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while ( left !== right && left . prev !== right ) { // If char mismatch return // false. if ( left . data !== right . data ) return false ; // Move the pointers left = left . next ; right = right . prev ; } return true ; } // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L let head = new Node ( 'L' ); head . next = new Node ( 'E' ); head . next . prev = head ; head . next . next = new Node ( 'V' ); head . next . next . prev = head . next ; head . next . next . next = new Node ( 'E' ); head . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next ; head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 'L' ); head . next . next . next . next . prev = head . next . next . next ; if ( isPalindrome ( head )) console . log ( 'True' ); else console . log ( 'False' );
Išvestis
True
Laiko sudėtingumas: O(n) kur n yra mazgų skaičius dvigubai susietame sąraše.
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(1)
Susiję straipsniai:
- Funkcija patikrinti, ar atskirai susietas sąrašas yra palindromas
- Patikrinkite, ar susietas eilučių sąrašas sudaro palindromą