Dvejetainės paieškos medžio (BST) traversals – užsakymas, išankstinis užsakymas, post orderis
Atsižvelgiant į a
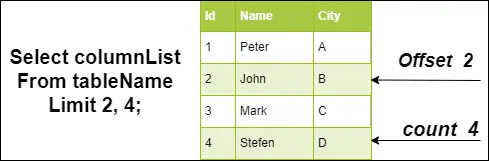
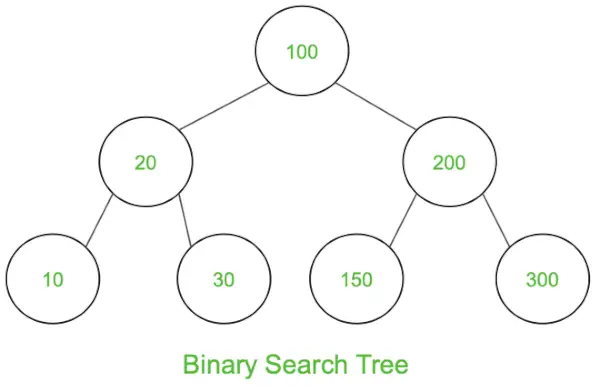
Dvejetainis paieškos medis
Išvestis:
Užsakymo perėjimas: 10 20 30 100 150 200 300
Išankstinis užsakymas: 100 20 10 30 200 150 300
Pašto siuntų pervežimas: 10 30 20 150 300 200 100
Įvestis:
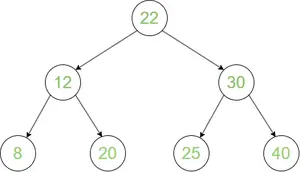
Dvejetainis paieškos medis
Išvestis:
Užsakymo perėjimas: 8 12 20 22 25 30 40
Išankstinis užsakymas: 22 12 8 20 30 25 40
Užsakymo paštu pervežimas: 8 20 12 25 40 30 22
Inorder Traversal :
Žemiau yra idėja, kaip išspręsti problemą:
Iš pradžių traversas kairysis pomedis tada apsilankykite šaknis ir tada pervažiuokite dešinysis pomedis .
Norėdami įgyvendinti idėją, atlikite šiuos veiksmus:
- Pereikite į kairįjį pomedį
- Apsilankykite šaknyje ir atsispausdinkite duomenis.
- Pereikite dešinįjį pomedį
The įsakymo perėjimas BST pateikia mazgų reikšmes surūšiuota tvarka. Norėdami gauti mažėjančią tvarką, apsilankykite dešiniajame, šakniniame ir kairiajame pomedyje.
Žemiau pateikiamas inorder traversal įgyvendinimas.
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> public> :> > int> data;> > Node* left;> > Node* right;> > Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> ->duomenys = v;> > this> ->kairėje => this> ->dešinė = NULL;> > }> };> // Inorder Traversal> void> printInorder(Node* node)> {> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> ;> > // Traverse left subtree> > printInorder(node->kairėje);> > // Visit node> > cout ' '; // Traverse right subtree printInorder(node->teisė); } // Tvarkyklės kodas int main() { // Sukurti medį Node* root = new Node(100); root->left = naujas mazgas(20); root->right = naujas mazgas (200); šaknis->kairė->kairė = naujas mazgas(10); šaknis->kairė->dešinė = naujas mazgas(30); šaknis->dešinė->kairė = naujas mazgas(150); root->right->right = naujas mazgas (300); // Funkcijos iškvietimas < < 'Inorder Traversal: '; printInorder(root); return 0; }> |
Java
// Java code to implement the approach> import> java.io.*;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node left;> > Node right;> > Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> class> GFG {> > // Inorder Traversal> > public> static> void> printInorder(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> ;> > // Traverse left subtree> > printInorder(node.left);> > // Visit node> > System.out.print(node.data +> ' '> );> > // Traverse right subtree> > printInorder(node.right);> > }> > // Driver Code> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Build the tree> > Node root => new> Node(> 100> );> > root.left => new> Node(> 20> );> > root.right => new> Node(> 200> );> > root.left.left => new> Node(> 10> );> > root.left.right => new> Node(> 30> );> > root.right.left => new> Node(> 150> );> > root.right.right => new> Node(> 300> );> > // Function call> > System.out.print(> 'Inorder Traversal: '> );> > printInorder(root);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan> |
Python3
# Python3 code to implement the approach> # Class describing a node of tree> class> Node:> > def> __init__(> self> , v):> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> > self> .data> => v> # Inorder Traversal> def> printInorder(root):> > if> root:> > # Traverse left subtree> > printInorder(root.left)> > > # Visit node> > print> (root.data,end> => ' '> )> > > # Traverse right subtree> > printInorder(root.right)> # Driver code> if> __name__> => => '__main__'> :> > # Build the tree> > root> => Node(> 100> )> > root.left> => Node(> 20> )> > root.right> => Node(> 200> )> > root.left.left> => Node(> 10> )> > root.left.right> => Node(> 30> )> > root.right.left> => Node(> 150> )> > root.right.right> => Node(> 300> )> > # Function call> > print> (> 'Inorder Traversal:'> ,end> => ' '> )> > printInorder(root)> > # This code is contributed by ajaymakvana.> |
C#
// Include namespace system> using> System;> // Class describing a node of tree> public> class> Node> {> > public> int> data;> > public> Node left;> > public> Node right;> > public> Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> public> class> GFG> {> > // Inorder Traversal> > public> static> void> printInorder(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > {> > return> ;> > }> > // Traverse left subtree> > GFG.printInorder(node.left);> > // Visit node> > Console.Write(node.data.ToString() +> ' '> );> > // Traverse right subtree> > GFG.printInorder(node.right);> > }> > // Driver Code> > public> static> void> Main(String[] args)> > {> > // Build the tree> > var> root => new> Node(100);> > root.left => new> Node(20);> > root.right => new> Node(200);> > root.left.left => new> Node(10);> > root.left.right => new> Node(30);> > root.right.left => new> Node(150);> > root.right.right => new> Node(300);> > // Function call> > Console.Write(> 'Inorder Traversal: '> );> > GFG.printInorder(root);> > }> }> |
Javascript
// JavaScript code to implement the approach> class Node {> constructor(v) {> this> .left => null> ;> this> .right => null> ;> this> .data = v;> }> }> // Inorder Traversal> function> printInorder(root)> {> if> (root)> {> // Traverse left subtree> printInorder(root.left);> // Visit node> console.log(root.data);> // Traverse right subtree> printInorder(root.right);> }> }> // Driver code> if> (> true> )> {> // Build the tree> let root => new> Node(100);> root.left => new> Node(20);> root.right => new> Node(200);> root.left.left => new> Node(10);> root.left.right => new> Node(30);> root.right.left => new> Node(150);> root.right.right => new> Node(300);> // Function call> console.log(> 'Inorder Traversal:'> );> printInorder(root);> }> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
Išvestis
Inorder Traversal: 10 20 30 100 150 200 300
Laiko sudėtingumas: O(N), kur N yra mazgų skaičius.
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(h), kur h yra medžio aukštis
Išankstinis užsakymas:
Žemiau yra idėja, kaip išspręsti problemą:
Iš pradžių apsilankykite šaknis tada skersai kairysis pomedis ir tada pervažiuokite dešinysis pomedis .
Norėdami įgyvendinti idėją, atlikite šiuos veiksmus:
- Apsilankykite šaknyje ir atsispausdinkite duomenis.
- Pereikite į kairįjį pomedį
- Pereikite dešinįjį pomedį
Toliau pateikiamas išankstinio užsakymo judėjimo įgyvendinimas.
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> public> :> > int> data;> > Node* left;> > Node* right;> > Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> ->duomenys = v;> > this> ->kairėje => this> ->dešinė = NULL;> > }> };> // Preorder Traversal> void> printPreOrder(Node* node)> {> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> ;> > // Visit Node> > cout ' '; // Traverse left subtree printPreOrder(node->kairėje); // Eiti į dešinę pomedį printPreOrder(node->right); } // Tvarkyklės kodas int main() { // Sukurti medį Node* root = new Node(100); root->left = naujas mazgas(20); root->right = naujas mazgas (200); šaknis->kairė->kairė = naujas mazgas(10); šaknis->kairė->dešinė = naujas mazgas(30); šaknis->dešinė->kairė = naujas mazgas(150); root->right->right = naujas mazgas (300); // Funkcijos iškvietimas < < 'Preorder Traversal: '; printPreOrder(root); return 0; }> |
Java
// Java code to implement the approach> import> java.io.*;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node left;> > Node right;> > Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> class> GFG {> > // Preorder Traversal> > public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> ;> > // Visit node> > System.out.print(node.data +> ' '> );> > // Traverse left subtree> > printPreorder(node.left);> > // Traverse right subtree> > printPreorder(node.right);> > }> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Build the tree> > Node root => new> Node(> 100> );> > root.left => new> Node(> 20> );> > root.right => new> Node(> 200> );> > root.left.left => new> Node(> 10> );> > root.left.right => new> Node(> 30> );> > root.right.left => new> Node(> 150> );> > root.right.right => new> Node(> 300> );> > // Function call> > System.out.print(> 'Preorder Traversal: '> );> > printPreorder(root);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by lokeshmvs21.> |
Python3
class> Node:> > def> __init__(> self> , v):> > self> .data> => v> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # Preorder Traversal> def> printPreOrder(node):> > if> node> is> None> :> > return> > # Visit Node> > print> (node.data, end> => ' '> )> > # Traverse left subtree> > printPreOrder(node.left)> > # Traverse right subtree> > printPreOrder(node.right)> # Driver code> if> __name__> => => '__main__'> :> > # Build the tree> > root> => Node(> 100> )> > root.left> => Node(> 20> )> > root.right> => Node(> 200> )> > root.left.left> => Node(> 10> )> > root.left.right> => Node(> 30> )> > root.right.left> => Node(> 150> )> > root.right.right> => Node(> 300> )> > # Function call> > print> (> 'Preorder Traversal: '> , end> => '')> > printPreOrder(root)> |
C#
// Include namespace system> using> System;> // Class describing a node of tree> public> class> Node> {> > public> int> data;> > public> Node left;> > public> Node right;> > public> Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> public> class> GFG> {> > // Preorder Traversal> > public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > {> > return> ;> > }> > // Visit node> > Console.Write(node.data.ToString() +> ' '> );> > // Traverse left subtree> > GFG.printPreorder(node.left);> > // Traverse right subtree> > GFG.printPreorder(node.right);> > }> > public> static> void> Main(String[] args)> > {> > // Build the tree> > var> root => new> Node(100);> > root.left => new> Node(20);> > root.right => new> Node(200);> > root.left.left => new> Node(10);> > root.left.right => new> Node(30);> > root.right.left => new> Node(150);> > root.right.right => new> Node(300);> > // Function call> > Console.Write(> 'Preorder Traversal: '> );> > GFG.printPreorder(root);> > }> }> |
Javascript
class Node {> > constructor(v) {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> function> printPreOrder(node) {> > if> (node ==> null> )> return> ;> > console.log(node.data +> ' '> );> > printPreOrder(node.left);> > printPreOrder(node.right);> }> // Build the tree> let root => new> Node(100);> root.left => new> Node(20);> root.right => new> Node(200);> root.left.left => new> Node(10);> root.left.right => new> Node(30);> root.right.left => new> Node(150);> root.right.right => new> Node(300);> console.log(> 'Preorder Traversal: '> );> printPreOrder(root);> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
Išvestis
Preorder Traversal: 100 20 10 30 200 150 300
Laiko sudėtingumas: O(N), kur N yra mazgų skaičius.
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(H), kur H yra medžio aukštis
Pašto užsakymo pervežimas:
Žemiau yra idėja, kaip išspręsti problemą:
Iš pradžių traversas kairysis pomedis tada pervažiuokite dešinysis pomedis ir tada apsilankykite šaknis .
Norėdami įgyvendinti idėją, atlikite šiuos veiksmus:
- Pereikite į kairįjį pomedį
- Pereikite dešinįjį pomedį
- Apsilankykite šaknyje ir atsispausdinkite duomenis.
Žemiau pateikiamas postorder traversal įgyvendinimas:
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Class to define structure of a node> class> Node {> public> :> > int> data;> > Node* left;> > Node* right;> > Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> ->duomenys = v;> > this> ->kairėje => this> ->dešinė = NULL;> > }> };> // PostOrder Traversal> void> printPostOrder(Node* node)> {> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> ;> > // Traverse left subtree> > printPostOrder(node->kairėje);> > // Traverse right subtree> > printPostOrder(node->dešinėje);> > // Visit node> > cout ' '; } // Driver code int main() { Node* root = new Node(100); root->kairysis = naujas mazgas(20); root->right = naujas mazgas (200); šaknis->kairė->kairė = naujas mazgas(10); šaknis->kairė->dešinė = naujas mazgas(30); šaknis->dešinė->kairė = naujas mazgas(150); root->right->right = naujas mazgas (300); // Funkcijos iškvietimas < < 'PostOrder Traversal: '; printPostOrder(root); cout < < '
'; return 0; }> |
Java
// Java code to implement the approach> import> java.io.*;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> GFG {> > > static> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node left;> > Node right;> > Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> > // Preorder Traversal> > public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> ;> > // Traverse left subtree> > printPreorder(node.left);> > // Traverse right subtree> > printPreorder(node.right);> > > // Visit node> > System.out.print(node.data +> ' '> );> > }> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Build the tree> > Node root => new> Node(> 100> );> > root.left => new> Node(> 20> );> > root.right => new> Node(> 200> );> > root.left.left => new> Node(> 10> );> > root.left.right => new> Node(> 30> );> > root.right.left => new> Node(> 150> );> > root.right.right => new> Node(> 300> );> > // Function call> > System.out.print(> 'Preorder Traversal: '> );> > printPreorder(root);> > }> }> |
C#
// Include namespace system> using> System;> // Class describing a node of tree> public> class> Node> {> > public> int> data;> > public> Node left;> > public> Node right;> > public> Node(> int> v)> > {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> public> class> GFG> {> > // Preorder Traversal> > public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > {> > return> ;> > }> > // Traverse left subtree> > GFG.printPreorder(node.left);> > // Traverse right subtree> > GFG.printPreorder(node.right);> > // Visit node> > Console.Write(node.data.ToString() +> ' '> );> > }> > public> static> void> Main(String[] args)> > {> > // Build the tree> > var> root => new> Node(100);> > root.left => new> Node(20);> > root.right => new> Node(200);> > root.left.left => new> Node(10);> > root.left.right => new> Node(30);> > root.right.left => new> Node(150);> > root.right.right => new> Node(300);> > // Function call> > Console.Write(> 'Preorder Traversal: '> );> > GFG.printPreorder(root);> > }> }> |
Python3
class> Node:> > def> __init__(> self> , v):> > self> .data> => v> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # Preorder Traversal> def> printPostOrder(node):> > if> node> is> None> :> > return> > # Traverse left subtree> > printPostOrder(node.left)> > # Traverse right subtree> > printPostOrder(node.right)> > > # Visit Node> > print> (node.data, end> => ' '> )> # Driver code> if> __name__> => => '__main__'> :> > # Build the tree> > root> => Node(> 100> )> > root.left> => Node(> 20> )> > root.right> => Node(> 200> )> > root.left.left> => Node(> 10> )> > root.left.right> => Node(> 30> )> > root.right.left> => Node(> 150> )> > root.right.right> => Node(> 300> )> > # Function call> > print> (> 'Postorder Traversal: '> , end> => '')> > printPostOrder(root)> |
Javascript
class Node {> > constructor(v) {> > this> .data = v;> > this> .left => null> ;> > this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> // Preorder Traversal> function> printPostOrder(node) {> > if> (node ===> null> ) {> > return> ;> > }> > // Traverse left subtree> > printPostOrder(node.left);> > // Traverse right subtree> > printPostOrder(node.right);> > // Visit Node> > console.log(node.data, end => ' '> );> }> // Driver code> // Build the tree> let root => new> Node(100);> root.left => new> Node(20);> root.right => new> Node(200);> root.left.left => new> Node(10);> root.left.right => new> Node(30);> root.right.left => new> Node(150);> root.right.right => new> Node(300);> // Function call> console.log(> 'Postorder Traversal: '> , end => ''> );> printPostOrder(root);> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
Išvestis
PostOrder Traversal: 10 30 20 150 300 200 100
Laiko sudėtingumas: O(N), kur N yra mazgų skaičius.
Pagalbinė erdvė: O(H), kur H yra medžio aukštis