Java의 메소드 오버로딩
Java에서 메소드 오버로딩을 사용하면 서로 다른 메소드가 동일한 이름을 가질 수 있지만 서명이 입력 매개변수 수나 입력 매개변수 유형 또는 둘의 혼합에 따라 다를 수 있는 서로 다른 서명을 가질 수 있습니다.
Java의 메소드 오버로딩은 다음과 같이 알려져 있습니다. 컴파일 타임 다형성 , 정적 다형성 또는 초기 제본 . 상위 인수와 비교하여 메소드 오버로딩에서는 하위 인수가 가장 높은 우선순위를 갖습니다.
메소드 오버로딩의 예
자바
// Java program to demonstrate working of method> // overloading in Java> > public> class> Sum {> > // Overloaded sum(). This sum takes two int parameters> > public> int> sum(> int> x,> int> y) {> return> (x + y); }> > > // Overloaded sum(). This sum takes three int parameters> > public> int> sum(> int> x,> int> y,> int> z)> > {> > return> (x + y + z);> > }> > > // Overloaded sum(). This sum takes two double> > // parameters> > public> double> sum(> double> x,> double> y)> > {> > return> (x + y);> > }> > > // Driver code> > public> static> void> main(String args[])> > {> > Sum s => new> Sum();> > System.out.println(s.sum(> 10> ,> 20> ));> > System.out.println(s.sum(> 10> ,> 20> ,> 30> ));> > System.out.println(s.sum(> 10.5> ,> 20.5> ));> > }> }> |
산출
30 60 31.0
Java에서 메소드 오버로딩의 다양한 방법
- 매개변수 수 변경.
- 인수의 데이터 유형 변경.
- 메소드 매개변수의 순서 변경
1. 매개변수 개수 변경
메소드 오버로딩은 다른 메소드에 전달하는 동안 매개변수 수를 변경하여 달성할 수 있습니다.
위 메소드를 구현하면 다음과 같습니다.
자바
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading> // By Changing the Number of Parameters> > // Importing required classes> import> java.io.*;> > // Class 1> // Helper class> class> Product {> > // Method 1> > // Multiplying two integer values> > public> int> multiply(> int> a,> int> b)> > {> > int> prod = a * b;> > return> prod;> > }> > > // Method 2> > // Multiplying three integer values> > public> int> multiply(> int> a,> int> b,> int> c)> > {> > int> prod = a * b * c;> > return> prod;> > }> }> > // Class 2> // Main class> class> GFG {> > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating object of above class inside main()> > // method> > Product ob => new> Product();> > > // Calling method to Multiply 2 numbers> > int> prod1 = ob.multiply(> 1> ,> 2> );> > > // Printing Product of 2 numbers> > System.out.println(> > 'Product of the two integer value :'> + prod1);> > > // Calling method to multiply 3 numbers> > int> prod2 = ob.multiply(> 1> ,> 2> ,> 3> );> > > // Printing product of 3 numbers> > System.out.println(> > 'Product of the three integer value :'> + prod2);> > }> }> |
산출
Product of the two integer value :2 Product of the three integer value :6
2. 인수의 데이터 유형 변경
대부분의 경우 메서드 이름은 같지만 매개 변수 유형이 다르면 메서드가 오버로드된 것으로 간주될 수 있으며 메서드는 오버로드된 것으로 간주됩니다.
위 메소드를 구현하면 다음과 같습니다.
자바
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading> // By Changing Data Types of the Parameters> > // Importing required classes> import> java.io.*;> > // Class 1> // Helper class> class> Product {> > // Multiplying three integer values> > public> int> Prod(> int> a,> int> b,> int> c)> > {> > int> prod1 = a * b * c;> > return> prod1;> > }> > > // Multiplying three double values.> > public> double> Prod(> double> a,> double> b,> double> c)> > {> > double> prod2 = a * b * c;> > return> prod2;> > }> }> > class> GFG {> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > Product obj => new> Product();> > > int> prod1 = obj.Prod(> 1> ,> 2> ,> 3> );> > System.out.println(> > 'Product of the three integer value :'> + prod1);> > > double> prod2 = obj.Prod(> 1.0> ,> 2.0> ,> 3.0> );> > System.out.println(> > 'Product of the three double value :'> + prod2);> > }> }> |
산출
Product of the three integer value :6 Product of the three double value :6.0
3. 분석법 매개변수의 순서 변경
메소드 오버로딩은 둘 이상의 오버로드된 메소드의 매개변수를 재배열하여 구현할 수도 있습니다. 예를 들어, 메소드 1의 매개변수가 (문자열 이름, int Roll_no)이고 다른 메소드가 (int Roll_no, 문자열 이름)이지만 둘 다 동일한 이름을 갖는 경우 이 두 메소드는 서로 다른 매개변수 시퀀스로 오버로드된 것으로 간주됩니다. .
위 메소드를 구현하면 다음과 같습니다.
자바
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Overloading> // By changing the Order of the Parameters> > // Importing required classes> import> java.io.*;> > // Class 1> // Helper class> class> Student {> > // Method 1> > public> void> StudentId(String name,> int> roll_no)> > {> > System.out.println(> 'Name :'> + name +> ' '> > +> 'Roll-No :'> + roll_no);> > }> > > // Method 2> > public> void> StudentId(> int> roll_no, String name)> > {> > // Again printing name and id of person> > System.out.println(> 'Roll-No :'> + roll_no +> ' '> > +> 'Name :'> + name);> > }> }> > // Class 2> // Main class> class> GFG {> > // Main function> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating object of above class> > Student obj => new> Student();> > > // Passing name and id> > // Note: Reversing order> > obj.StudentId(> 'Spyd3r'> ,> 1> );> > obj.StudentId(> 2> ,> 'Kamlesh'> );> > }> }> |
산출
Name :Spyd3r Roll-No :1 Roll-No :2 Name :Kamlesh
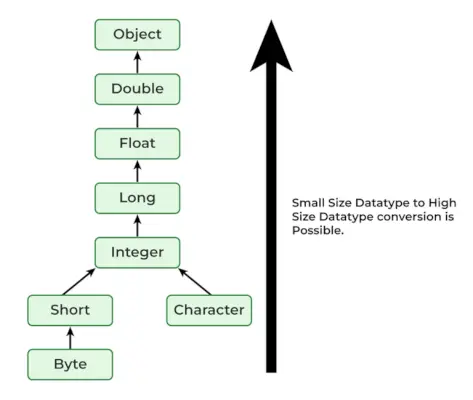
정확한 프로토타입이 인수와 일치하지 않으면 어떻게 되나요?
우선순위에 따라 컴파일러는 다음 단계를 수행합니다.
- 유형 변환이 가능하지만 동일한 제품군에서 더 높은 유형(범위 측면에서)으로 변환됩니다.
- 다음 상위 계열로의 변환을 입력합니다(int 데이터 유형에 사용할 수 있는 long 데이터 유형이 없으면 float 데이터 유형을 검색한다고 가정합니다).

개념을 명확히 하기 위해 예를 들어보겠습니다.
자바
// Demo Class> class> Demo {> > public> void> show(> int> x)> > {> > System.out.println(> 'In int'> + x);> > }> > public> void> show(String s)> > {> > System.out.println(> 'In String'> + s);> > }> > public> void> show(> byte> b)> > {> > System.out.println(> 'In byte'> + b);> > }> }> > class> UseDemo {> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > byte> a => 25> ;> > Demo obj => new> Demo();> > > // it will go to> > // byte argument> > obj.show(a);> > > // String> > obj.show(> 'hello'> );> > > // Int> > obj.show(> 250> );> > > // Since char is> > // not available, so the datatype> > // higher than char in terms of> > // range is int.> > obj.show(> 'A'> );> > > // String> > obj.show(> 'A'> );> > > // since float datatype> > // is not available and so it's higher> > // datatype, so at this step their> > // will be an error.> > obj.show(> 7.5> );> > }> }> |
산출
./UseDemo.java:46: error: no suitable method found for show(double) obj.show(7.5); ^ method Demo.show(int) is not applicable (argument mismatch; possible lossy conversion from double to int) method Demo.show(String) is not applicable (argument mismatch; double cannot be converted to String) method Demo.show(byte) is not applicable (argument mismatch; possible lossy conversion from double to byte) 1 error
메소드 오버로딩의 장점
- 메소드 오버로딩은 프로그램의 가독성과 재사용성을 향상시킵니다.
- 메소드 오버로딩은 프로그램의 복잡성을 줄여줍니다.
- 메소드 오버로딩을 사용하면 프로그래머는 효율적이고 효과적으로 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 메소드 오버로딩을 사용하면 약간 다른 인수와 유형을 사용하여 관련 기능을 수행하는 메소드에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
- 클래스의 객체는 생성자를 사용하여 다양한 방법으로 초기화할 수도 있습니다.
Java의 중요한 질문
Q1. 정적 메소드를 오버로드할 수 있나요?
답변:
정답은 ' 예 '. 이름은 같지만 입력 매개변수에 차이가 있는 정적 메서드가 두 개 이상 있을 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 다음 Java 프로그램을 고려하십시오. 이에 대한 자세한 내용은 다음 기사를 참조하세요. Java에서 정적 메서드를 오버로드하거나 재정의할 수 있나요?
Q2. 정적 키워드만 다른 메서드를 오버로드할 수 있나요?
답변:
우리 할 수 없다 정적 키워드만 다른 경우(매개변수 수와 매개변수 유형이 동일함) Java에서 두 메소드를 오버로드합니다. 예를 들어 다음 Java 프로그램을 참조하세요. 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요.
Q3. Java에서 main()을 오버로드할 수 있나요?
답변:
다른 정적 메서드와 마찬가지로 우리는 ~할 수 있다 Java에서 main()을 오버로드합니다.
자바
// Java program with overloaded main()>import>java.io.*;>>public>class>Test {>>// Normal main()>>public>static>void>main(String[] args)>>{>>System.out.println(>'Hi Geek (from main)'>);>>Test.main(>'Geek'>);>>}>>>// Overloaded main methods>>public>static>void>main(String arg1)>>{>>System.out.println(>'Hi, '>+ arg1);>>Test.main(>'Dear Geek'>,>'My Geek'>);>>}>>>public>static>void>main(String arg1, String arg2)>>{>>System.out.println(>'Hi, '>+ arg1 +>', '>+ arg2);>>}>}>
산출
Hi Geek (from main) Hi, Geek Hi, Dear Geek, My Geek
Q4. Java는 연산자 오버로딩을 지원합니까?
답변:
C++와 달리 Java는 사용자 정의 오버로드된 연산자를 허용하지 않습니다. 내부적으로 Java는 연산자를 오버로드합니다. 예를 들어 +는 연결을 위해 오버로드됩니다.
Q5. 반환 유형에 메서드를 오버로드할 수 있나요?
답변:
반환 유형에 따라 오버로드할 수 없습니다. 이 동작은 C++에서도 동일합니다. 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요.
자바
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */>>import>java.io.*;>>public>class>Main {>>public>int>foo() {>return>10>; }>>>// compiler error: foo() is already defined>>public>char>foo() {>return>'a'>; }>>>public>static>void>main(String args[]) {}>}>
오류
./Main.java:8: error: method foo() is already defined in class Main public char foo() { return 'a'; } ^ 1 error그러나 호출되는 함수의 데이터 유형이 명시적으로 지정된 경우에는 반환 유형에 대한 오버로딩 메서드가 가능합니다. 아래 예를 살펴보십시오.
자바
// Java program to demonstrate the working of method>// overloading in static methods>>import>java.io.*;>>public>class>Main {>>>public>static>int>foo(>int>a) {>return>10>; }>>public>static>char>foo(>int>a,>int>b) {>return>'a'>; }>>>public>static>void>main(String args[])>>{>>System.out.println(foo(>1>));>>System.out.println(foo(>1>,>2>));>>}>}>
산출
10 a자바
// Java program to demonstrate working of method>// overloading in methods>class>A {>>public>int>foo(>int>a) {>return>10>; }>>>public>char>foo(>int>a,>int>b) {>return>'a'>; }>}>>public>class>Main {>>>public>static>void>main(String args[])>>{>>A a =>new>A();>>System.out.println(a.foo(>1>));>>System.out.println(a.foo(>1>,>2>));>>}>}>
산출
10 a
Q6. 오버로딩과 오버라이딩의 차이점은 무엇입니까?
답변:
오버로딩은 서로 다른 시그니처를 갖는 동일한 함수에 관한 것입니다. 재정의 동일한 기능과 동일한 서명에 관한 것이지만 상속을 통해 연결된 다른 클래스입니다.
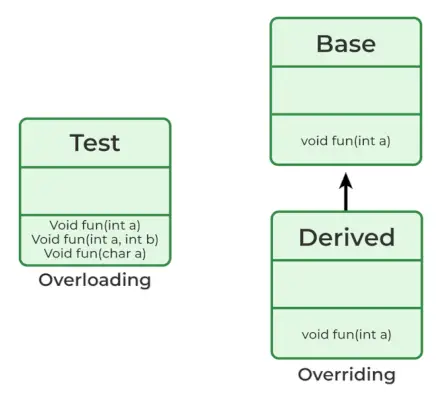
오버로딩은 컴파일러 시간 다형성의 예이고 재정의는 런타임 다형성의 예입니다.
관련 기사
- Java에서 메소드 오버로딩의 다양한 방법
- Java의 메소드 오버로딩 및 Null 오류
- Java에서 정적 메서드를 오버로드하거나 재정의할 수 있나요?