별도의 연결을 사용하여 C/C++에서 해시 테이블 구현
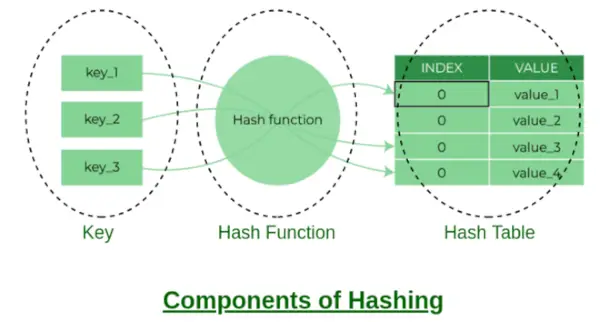
소개:
URL 단축기는 큰 크기의 URL을 작은 크기로 매핑하는 해싱의 예입니다.
해시 함수의 몇 가지 예:
- 키 % 버킷 수
- 문자의 ASCII 값 * PrimeNumber 엑스 . 여기서 x = 1, 2, 3….n
- 자신만의 해시 함수를 만들 수 있지만 충돌 횟수를 줄이는 좋은 해시 함수여야 합니다.

해싱의 구성 요소
버킷 인덱스:
해시 함수에서 반환되는 값은 별도의 연결 방법에 있는 키의 버킷 인덱스입니다. 배열의 각 인덱스는 연결 목록의 버킷이므로 버킷이라고 합니다.
재해싱:
리해싱(Rehashing)은 현재 해시 테이블에서 요소가 증가할 때 충돌을 줄이는 개념이다. 두 배 크기의 새 배열을 만들고 이전 배열 요소를 여기에 복사하며 이는 C++에서 벡터의 내부 작업과 같습니다. 분명히 해시 함수는 용량이 증가할 때 일부 변경 사항을 반영해야 하므로 동적이어야 합니다. 해시 함수에는 해시 테이블의 용량이 포함되므로 이전 배열 해시 함수에서 키 값을 복사하면 해시 테이블의 용량(버킷)에 따라 다른 버킷 인덱스가 제공됩니다. 일반적으로 로드 팩터 값이 0.5보다 크면 재해싱이 수행됩니다.
- 배열 크기를 두 배로 늘립니다.
- 이전 배열의 요소를 새 배열에 복사합니다. 각 노드를 새로운 배열에 다시 복사하는 동안 해시 함수를 사용하므로 충돌이 줄어듭니다.
- 메모리에서 이전 배열을 삭제하고 해시 맵의 내부 배열 포인터가 이 새 배열을 가리키도록 합니다.
- 일반적으로 로드 팩터 = 해시 맵의 요소 수 / 총 버킷 수(용량)입니다.
충돌:
충돌은 버킷 인덱스가 비어 있지 않은 상황입니다. 이는 해당 버킷 인덱스에 연결 목록 헤드가 있음을 의미합니다. 동일한 버킷 인덱스에 매핑되는 값이 두 개 이상 있습니다.
프로그램의 주요 기능
- 삽입
- 찾다
- 해시 함수
- 삭제
- 재해싱
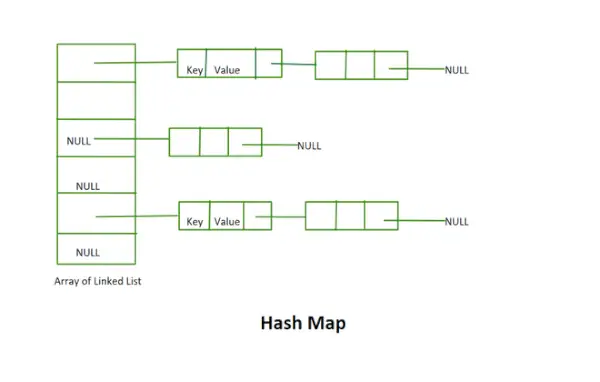
해시 맵
재해싱 없이 구현:
씨
#include> #include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> > // key is string> > char> * key;> > // value is also string> > char> * value;> > struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(> struct> node* node,> char> * key,> char> * value)> {> > node->키 = 키;> > node->값 = 값;> > node->다음 = NULL;> > return> ;> };> struct> hashMap {> > // Current number of elements in hashMap> > // and capacity of hashMap> > int> numOfElements, capacity;> > // hold base address array of linked list> > struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(> struct> hashMap* mp)> {> > // Default capacity in this case> > mp->용량 = 100;> > mp->요소 수 = 0;> > // array of size = 1> > mp->arr = (> struct> node**)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> struct> node*)> > * mp->용량);> > return> ;> }> int> hashFunction(> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key)> {> > int> bucketIndex;> > int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> > for> (> int> i = 0; i <> strlen> (key); i++) {> > // sum = sum + (ascii value of> > // char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> > // where x = 1, 2, 3....n> > sum = ((sum % mp->용량)> > + (((> int> )key[i]) * factor) % mp->용량)> > % mp->용량;> > // factor = factor * prime> > // number....(prime> > // number) ^ x> > factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__)> > * (31 % __INT16_MAX__))> > % __INT16_MAX__;> > }> > bucketIndex = sum;> > return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key,> char> * value)> {> > // Getting bucket index for the given> > // key - value pair> > int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> > struct> node* newNode = (> struct> node*)> malloc> (> > // Creating a new node> > sizeof> (> struct> node));> > // Setting value of node> > setNode(newNode, key, value);> > // Bucket index is empty....no collision> > if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> > mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> > }> > // Collision> > else> {> > // Adding newNode at the head of> > // linked list which is present> > // at bucket index....insertion at> > // head in linked list> > newNode->다음 = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> > mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> > }> > return> ;> }> void> delete> (> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key)> {> > // Getting bucket index for the> > // given key> > int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> > struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> > // Points to the head of> > // linked list present at> > // bucket index> > struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> > while> (currNode != NULL) {> > // Key is matched at delete this> > // node from linked list> > if> (> strcmp> (key, currNode->키) == 0) {> > // Head node> > // deletion> > if> (currNode == mp->arr[bucketIndex]) {> > mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->next;> > }> > // Last node or middle node> > else> {> > prevNode->다음 = currNode->다음;> > }> > free> (currNode);> > break> ;> > }> > prevNode = currNode;> > currNode = currNode->다음;> > }> > return> ;> }> char> * search(> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key)> {> > // Getting the bucket index> > // for the given key> > int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> > // Head of the linked list> > // present at bucket index> > struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> > while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> > // Key is found in the hashMap> > if> (bucketHead->키 == 키) {> > return> bucketHead->값;> > }> > bucketHead = bucketHead->다음;> > }> > // If no key found in the hashMap> > // equal to the given key> > char> * errorMssg = (> char> *)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> char> ) * 25);> > errorMssg => 'Oops! No data found.
'> ;> > return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> > // Initialize the value of mp> > struct> hashMap* mp> > = (> struct> hashMap*)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> struct> hashMap));> > initializeHashMap(mp);> > insert(mp,> 'Yogaholic'> ,> 'Anjali'> );> > insert(mp,> 'pluto14'> ,> 'Vartika'> );> > insert(mp,> 'elite_Programmer'> ,> 'Manish'> );> > insert(mp,> 'GFG'> ,> 'techcodeview.com'> );> > insert(mp,> 'decentBoy'> ,> 'Mayank'> );> > printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'elite_Programmer'> ));> > printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'Yogaholic'> ));> > printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'pluto14'> ));> > printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'decentBoy'> ));> > printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'GFG'> ));> > // Key is not inserted> > printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'randomKey'> ));> > printf> (> '
After deletion :
'> );> > // Deletion of key> > delete> (mp,> 'decentBoy'> );> > printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'decentBoy'> ));> > return> 0;> }> |
C++
#include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> > // key is string> > char> * key;> > // value is also string> > char> * value;> > struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(> struct> node* node,> char> * key,> char> * value) {> > node->키 = 키;> > node->값 = 값;> > node->다음 = NULL;> > return> ;> }> struct> hashMap {> > // Current number of elements in hashMap> > // and capacity of hashMap> > int> numOfElements, capacity;> > // hold base address array of linked list> > struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(> struct> hashMap* mp) {> > // Default capacity in this case> > mp->용량 = 100;> > mp->요소 수 = 0;> > // array of size = 1> > mp->arr = (> struct> node**)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> struct> node*) * mp->용량);> > return> ;> }> int> hashFunction(> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key) {> > int> bucketIndex;> > int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> > for> (> int> i = 0; i <> strlen> (key); i++) {> > // sum = sum + (ascii value of> > // char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> > // where x = 1, 2, 3....n> > sum = ((sum % mp->용량) + (((> int> )key[i]) * factor) % mp->용량) % mp->용량;> > // factor = factor * prime> > // number....(prime> > // number) ^ x> > factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__) * (31 % __INT16_MAX__)) % __INT16_MAX__;> > }> > bucketIndex = sum;> > return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key,> char> * value) {> > // Getting bucket index for the given> > // key - value pair> > int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> > struct> node* newNode = (> struct> node*)> malloc> (> > // Creating a new node> > sizeof> (> struct> node));> > // Setting value of node> > setNode(newNode, key, value);> > // Bucket index is empty....no collision> > if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> > mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> > }> > // Collision> > else> {> > // Adding newNode at the head of> > // linked list which is present> > // at bucket index....insertion at> > // head in linked list> > newNode->다음 = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> > mp->arr[bucketIndex] = newNode;> > }> > return> ;> }> void> deleteKey(> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key) {> > // Getting bucket index for the> > // given key> > int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> > struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> > // Points to the head of> > // linked list present at> > // bucket index> > struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> > while> (currNode != NULL) {> > // Key is matched at delete this> > // node from linked list> > if> (> strcmp> (key, currNode->키) == 0) {> > // Head node> > // deletion> > if> (currNode == mp->arr[bucketIndex]) {> > mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->next;> > }> > // Last node or middle node> > else> {> > prevNode->다음 = currNode->다음;> }> free> (currNode);> break> ;> }> prevNode = currNode;> > currNode = currNode->다음;> > }> return> ;> }> char> * search(> struct> hashMap* mp,> char> * key) {> // Getting the bucket index for the given key> int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> // Head of the linked list present at bucket index> struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> > > // Key is found in the hashMap> > if> (> strcmp> (bucketHead->키, 키) == 0) {> > return> bucketHead->값;> > }> > > bucketHead = bucketHead->다음;> }> // If no key found in the hashMap equal to the given key> char> * errorMssg = (> char> *)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> char> ) * 25);> strcpy> (errorMssg,> 'Oops! No data found.
'> );> return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> // Initialize the value of mp> struct> hashMap* mp = (> struct> hashMap*)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> struct> hashMap));> initializeHashMap(mp);> insert(mp,> 'Yogaholic'> ,> 'Anjali'> );> insert(mp,> 'pluto14'> ,> 'Vartika'> );> insert(mp,> 'elite_Programmer'> ,> 'Manish'> );> insert(mp,> 'GFG'> ,> 'techcodeview.com'> );> insert(mp,> 'decentBoy'> ,> 'Mayank'> );> printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'elite_Programmer'> ));> printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'Yogaholic'> ));> printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'pluto14'> ));> printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'decentBoy'> ));> printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'GFG'> ));> // Key is not inserted> printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'randomKey'> ));> printf> (> '
After deletion :
'> );> // Deletion of key> deleteKey(mp,> 'decentBoy'> );> // Searching the deleted key> printf> (> '%s
'> , search(mp,> 'decentBoy'> ));> return> 0;> }> |
산출
Manish Anjali Vartika Mayank techcodeview.com Oops! No data found. After deletion : Oops! No data found.
설명:
- 삽입: 주어진 버킷 인덱스에 존재하는 연결 목록의 헤드에 키-값 쌍을 삽입합니다. hashFunction: 주어진 키에 대한 버킷 인덱스를 제공합니다. 우리의 해시 함수 = 문자의 ASCII 값 * primeNumber 엑스 . 우리의 경우 소수는 31이고 키의 연속 문자에 대해 x 값은 1에서 n으로 증가합니다. 삭제: 지정된 키에 대한 해시 테이블에서 키-값 쌍을 삭제합니다. 키-값 쌍을 보유하는 연결 목록에서 노드를 삭제합니다. 검색: 주어진 키의 값을 검색합니다.
- 이 구현에서는 재해싱 개념을 사용하지 않습니다. 고정된 크기의 연결 리스트 배열입니다.
- 주어진 예에서는 키와 값이 모두 문자열입니다.
시간 복잡도와 공간 복잡도:
해시 테이블 삽입 및 삭제 작업의 시간 복잡도는 평균 O(1)입니다. 이를 증명하는 수학적 계산이 있습니다.
- 삽입의 시간 복잡도: 평균적인 경우에는 일정합니다. 최악의 경우 선형입니다. 검색의 시간 복잡도: 평균적인 경우에는 일정합니다. 최악의 경우 선형입니다. 삭제 시간 복잡도: 일반적인 경우에는 일정합니다. 최악의 경우 선형입니다. 공간 복잡도: n개의 요소를 가지므로 O(n)입니다.
관련 기사:
- 해싱에서 별도의 체인 충돌 처리 기술.