링크 된 목록의 중간을 삭제합니다
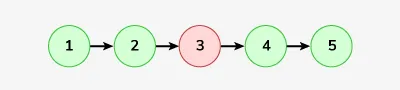
단일 연결된 목록이 주어지면 작업은 목록의 중간 노드를 삭제하는 것입니다.
- 목록에 짝수의 노드가 포함되어 있으면 두 개의 중간 노드가 있습니다. 이 경우 두 번째 중간 노드를 삭제합니다.
- 링크 된 목록이 하나의 노드로만 구성된 경우 NULL을 반환하십시오.
예:
입력: Linkedlist : 1-> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5
산출: 1-> 2-> 4-> 5
설명:

입력: Linkedlist : 2-> 4-> 6-> 7-> 5-> 1
산출: 2-> 4-> 6-> 5-> 1
설명 :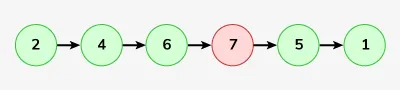
입력: Linkedlist : 7
산출:
내용 테이블
[순진한 접근] 2 패스 트래버스를 사용한 [N) 시간 및 O (1) 공간
이 접근법의 기본 아이디어는 먼저 링크 된 전체 목록을 가로 지르고 총 노드 수를 계산하는 것입니다. 총 노드 수를 알면 인덱스에있는 중간 노드의 위치를 계산할 수 있습니다. n/2 (여기서 n은 총 노드 수입니다). 그런 다음 링크 된 목록을 다시 살펴 보지만 이번에는 중간 노드 직전에 멈 춥니 다. 일단 거기에 일단 우리는 중간 노드 앞에서 노드의 다음 포인터를 수정하여 중간 노드 위로 건너 뛰고 그 다음에 노드를 직접 가리 킵니다.
아래는 위의 접근 방식의 구현입니다.
C++ // C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include using namespace std ; struct Node { int data ; Node * next ; Node ( int x ){ data = x ; next = nullptr ; } }; // Function to delete middle node from linked list. Node * deleteMid ( Node * head ) { // Edge case: return nullptr if there is only // one node. if ( head -> next == nullptr ) return nullptr ; int count = 0 ; Node * p1 = head * p2 = head ; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while ( p1 != nullptr ) { count ++ ; p1 = p1 -> next ; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2 ; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for ( int i = 0 ; i < middleIndex - 1 ; ++ i ) p2 = p2 -> next ; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2 -> next = p2 -> next -> next ; return head ; } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * temp = head ; while ( temp != nullptr ) { cout < < temp -> data < < ' -> ' ; temp = temp -> next ; } cout < < 'nullptr' < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node * head = new Node ( 1 ); head -> next = new Node ( 2 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 3 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 4 ); head -> next -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 5 ); cout < < 'Original Linked List: ' ; printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid ( head ); cout < < 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ; printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
C // C program to delete middle of a linked list #include #include struct Node { int data ; struct Node * next ; }; // Function to delete middle node from linked list. struct Node * deleteMid ( struct Node * head ) { // Edge case: return NULL if there is only // one node. if ( head -> next == NULL ) return NULL ; int count = 0 ; struct Node * p1 = head * p2 = head ; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while ( p1 != NULL ) { count ++ ; p1 = p1 -> next ; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2 ; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for ( int i = 0 ; i < middleIndex - 1 ; ++ i ) p2 = p2 -> next ; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2 -> next = p2 -> next -> next ; return head ; } void printList ( struct Node * head ) { struct Node * temp = head ; while ( temp != NULL ) { printf ( '%d -> ' temp -> data ); temp = temp -> next ; } printf ( 'NULL n ' ); } struct Node * newNode ( int x ) { struct Node * temp = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); temp -> data = x ; temp -> next = NULL ; return temp ; } int main () { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. struct Node * head = newNode ( 1 ); head -> next = newNode ( 2 ); head -> next -> next = newNode ( 3 ); head -> next -> next -> next = newNode ( 4 ); head -> next -> next -> next -> next = newNode ( 5 ); printf ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid ( head ); printf ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { int data ; Node next ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = null ; } } public class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. public static Node deleteMid ( Node head ) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if ( head . next == null ) return null ; int count = 0 ; Node p1 = head p2 = head ; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while ( p1 != null ) { count ++ ; p1 = p1 . next ; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2 ; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward predecessor // of the middle node. for ( int i = 0 ; i < middleIndex - 1 ; ++ i ) p2 = p2 . next ; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2 . next = p2 . next . next ; return head ; } public static void printList ( Node head ) { Node temp = head ; while ( temp != null ) { System . out . print ( temp . data + ' -> ' ); temp = temp . next ; } System . out . println ( 'null' ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node ( 1 ); head . next = new Node ( 2 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 3 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 5 ); System . out . print ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid ( head ); System . out . print ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # Python3 program to delete middle of a linked list class Node : def __init__ ( self data ): self . data = data self . next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list. def deleteMid ( head ): # Edge case: return None if there is only # one node. if head . next is None : return None count = 0 p1 = head p2 = head # First pass count the number of nodes # in the linked list using 'p1'. while p1 is not None : count += 1 p1 = p1 . next # Get the index of the node to be deleted. middleIndex = count // 2 # Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor # of the middle node. for i in range ( middleIndex - 1 ): p2 = p2 . next # Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2 . next = p2 . next . next return head def printList ( head ): temp = head while temp is not None : print ( temp . data end = ' -> ' ) temp = temp . next print ( 'None' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. head = Node ( 1 ) head . next = Node ( 2 ) head . next . next = Node ( 3 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 4 ) head . next . next . next . next = Node ( 5 ) print ( 'Original Linked List:' end = ' ' ) printList ( head ) # Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid ( head ) print ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node:' end = ' ' ) printList ( head )
C# // C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = null ; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. static Node deleteMid ( Node head ) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if ( head . next == null ) return null ; int count = 0 ; Node p1 = head p2 = head ; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while ( p1 != null ) { count ++ ; p1 = p1 . next ; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2 ; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for ( int i = 0 ; i < middleIndex - 1 ; ++ i ) p2 = p2 . next ; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2 . next = p2 . next . next ; return head ; } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node temp = head ; while ( temp != null ) { Console . Write ( temp . data + ' -> ' ); temp = temp . next ; } Console . WriteLine ( 'null' ); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node ( 1 ); head . next = new Node ( 2 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 3 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 5 ); Console . Write ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid ( head ); Console . Write ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head ); } }
JavaScript class Node { constructor ( data ) { this . data = data ; this . next = null ; } } // Function to delete middle node from linked list. function deleteMid ( head ) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if ( head . next === null ) return null ; let count = 0 ; let p1 = head p2 = head ; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while ( p1 !== null ) { count ++ ; p1 = p1 . next ; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. let middleIndex = Math . floor ( count / 2 ); // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for ( let i = 0 ; i < middleIndex - 1 ; ++ i ) p2 = p2 . next ; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2 . next = p2 . next . next ; return head ; } function printList ( head ) { let temp = head ; while ( temp !== null ) { console . log ( temp . data + ' -> ' ); temp = temp . next ; } console . log ( 'null' ); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. let head = new Node ( 1 ); head . next = new Node ( 2 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 3 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 5 ); console . log ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid ( head ); console . log ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head );
산출
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr
시간 복잡성 : 에). 링크 된 목록의 두 개의 횡단이 필요합니다
보조 공간 : o (1). 추가 공간이 필요하지 않습니다.
[예상 접근] 느리고 빠른 포인터가있는 1 패스 트래버스 - O (N) 시간 및 O (1) 공간
위의 솔루션은 링크 된 목록의 두 가지 횡단이 필요합니다. 하나의 트래버스를 사용하여 중간 노드를 삭제할 수 있습니다. 아이디어는 두 개의 포인터를 사용하는 것입니다 slow_ptr 그리고 FAST_PTR . 빠른 포인터는 한 번에 두 개의 노드를 움직이며 느린 포인터는 한 번에 하나의 노드를 움직입니다. 빠른 포인터가 목록의 끝에 도달하면 느린 포인터가 중간 노드에 배치됩니다. 다음으로 중간 노드 앞에 오는 노드를 연결해야합니다 ( 이전 ) 중간 노드 뒤에 오는 노드로. 이것은 중간 노드를 효과적으로 건너 며 목록에서 제거합니다.
아래는 위의 접근법의 구현입니다
C++ // C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include using namespace std ; struct Node { int data ; Node * next ; Node ( int x ){ data = x ; next = nullptr ; } }; // Function to delete middle node from linked list struct Node * deleteMid ( struct Node * head ) { // If the list is empty return NULL if ( head == NULL ) return NULL ; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return NULL if ( head -> next == NULL ) { delete head ; return NULL ; } struct Node * prev = NULL ; struct Node * slow_ptr = head ; struct Node * fast_ptr = head ; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of the list while ( fast_ptr != NULL && fast_ptr -> next != NULL ) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr -> next -> next ; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr ; slow_ptr = slow_ptr -> next ; } // At this point slow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev -> next = slow_ptr -> next ; // Delete the middle node delete slow_ptr ; // Return the head of the modified list return head ; } void printList ( struct Node * head ) { struct Node * temp = head ; while ( temp != NULL ) { cout < < temp -> data < < ' -> ' ; temp = temp -> next ; } cout < < 'NULL' < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node * head = new Node ( 1 ); head -> next = new Node ( 2 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 3 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 4 ); head -> next -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 5 ); cout < < 'Original Linked List: ' ; printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid ( head ); cout < < 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ; printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
C // C program to delete middle of a linked list #include #include struct Node { int data ; struct Node * next ; }; // Function to delete middle node from linked list struct Node * deleteMid ( struct Node * head ) { // If the list is empty return NULL if ( head == NULL ) return NULL ; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return NULL if ( head -> next == NULL ) { free ( head ); return NULL ; } struct Node * prev = NULL ; struct Node * slow_ptr = head ; struct Node * fast_ptr = head ; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of the list while ( fast_ptr != NULL && fast_ptr -> next != NULL ) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr -> next -> next ; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr ; slow_ptr = slow_ptr -> next ; } // At this point slow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev -> next = slow_ptr -> next ; // Delete the middle node free ( slow_ptr ); // Return the head of the modified list return head ; } void printList ( struct Node * head ) { struct Node * temp = head ; while ( temp != NULL ) { printf ( '%d -> ' temp -> data ); temp = temp -> next ; } printf ( 'NULL n ' ); } struct Node * newNode ( int x ) { struct Node * temp = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); temp -> data = x ; temp -> next = NULL ; return temp ; } int main () { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. struct Node * head = newNode ( 1 ); head -> next = newNode ( 2 ); head -> next -> next = newNode ( 3 ); head -> next -> next -> next = newNode ( 4 ); head -> next -> next -> next -> next = newNode ( 5 ); printf ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid ( head ); printf ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node { int data ; Node next ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = null ; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list static Node deleteMid ( Node head ) { // If the list is empty return null if ( head == null ) return null ; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if ( head . next == null ) { return null ; } Node prev = null ; Node slow_ptr = head ; Node fast_ptr = head ; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of list while ( fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr . next != null ) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr . next . next ; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr ; slow_ptr = slow_ptr . next ; } // At this pointslow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev . next = slow_ptr . next ; // Return the head of the modified list return head ; } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node temp = head ; while ( temp != null ) { System . out . print ( temp . data + ' -> ' ); temp = temp . next ; } System . out . println ( 'NULL' ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node ( 1 ); head . next = new Node ( 2 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 3 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 5 ); System . out . print ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid ( head ); System . out . print ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # Python program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node : def __init__ ( self data ): self . data = data self . next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list def deleteMid ( head ): # If the list is empty return None if head is None : return None # If the list has only one node # delete it and return None if head . next is None : return None prev = None slow_ptr = head fast_ptr = head # Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead # and the slow pointer 1 node ahead # until fast pointer reaches end of the list while fast_ptr is not None and fast_ptr . next is not None : fast_ptr = fast_ptr . next . next # Update prev to hold the previous # slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr slow_ptr = slow_ptr . next # At this point slow_ptr points to middle node # Bypass the middle node prev . next = slow_ptr . next # Return the head of the modified list return head def printList ( head ): temp = head while temp : print ( temp . data end = ' -> ' ) temp = temp . next print ( 'NULL' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node ( 1 ) head . next = Node ( 2 ) head . next . next = Node ( 3 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 4 ) head . next . next . next . next = Node ( 5 ) print ( 'Original Linked List: ' end = '' ) printList ( head ) # Delete the middle node head = deleteMid ( head ) print ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' end = '' ) printList ( head )
C# // C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = null ; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list public static Node deleteMid ( Node head ) { // If the list is empty return null if ( head == null ) return null ; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if ( head . next == null ) { return null ; } Node prev = null ; Node slow_ptr = head ; Node fast_ptr = head ; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of the list while ( fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr . next != null ) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr . next . next ; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr ; slow_ptr = slow_ptr . next ; } // At this point slow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev . next = slow_ptr . next ; // Return the head of the modified list return head ; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList ( Node head ) { Node temp = head ; while ( temp != null ) { Console . Write ( temp . data + ' -> ' ); temp = temp . next ; } Console . WriteLine ( 'NULL' ); } public static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node ( 1 ); head . next = new Node ( 2 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 3 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 5 ); Console . Write ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid ( head ); Console . Write ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // javascript program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { constructor ( data ) { this . data = data ; this . next = null ; } } // Function to delete the middle node from the linked list function deleteMid ( head ) { // If the list is empty return null if ( head === null ) { return null ; } // If the list has only one node delete it and return // null if ( head . next === null ) { return null ; } let prev = null ; let slow_ptr = head ; let fast_ptr = head ; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until the fast pointer reaches the end of the list while ( fast_ptr !== null && fast_ptr . next !== null ) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr . next . next ; // Update prev to hold the previous slow pointer // value prev = slow_ptr ; slow_ptr = slow_ptr . next ; } // At this point slow_ptr points to the middle node // Bypass the middle node prev . next = slow_ptr . next ; // Return the head of the modified list return head ; } function printList ( head ) { let temp = head ; while ( temp !== null ) { process . stdout . write ( temp . data + ' -> ' ); temp = temp . next ; } console . log ( 'null' ); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node ( 1 ); head . next = new Node ( 2 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 3 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 4 ); head . next . next . next . next = new Node ( 5 ); process . stdout . write ( 'Original Linked List: ' ); printList ( head ); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid ( head ); process . stdout . write ( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' ); printList ( head );
산출
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL
시간 복잡성 : 에). 링크 된 목록의 하나의 순회 만 필요합니다
보조 공간 : o (1). 추가 공간이 필요하지 않으므로.
관련 기사 :
- 링크 된 목록의 중간을 찾으십시오








![Java main() 메소드 – public static void main(String[] args)](https://techcodeview.com/img/java-basics/92/java-main-method-public-static-void-main.webp)