Classe Java.io.FilterOutputStream en Java
Classe java.io.FilterInputStream en Java

Java.io.FilterOutputStream class est la superclasse de toutes ces classes qui filtrent les flux de sortie. La méthode write() de la classe FilterOutputStream filtre les données et les écrit dans le filtrage de flux sous-jacent qui est effectué en fonction des flux.
Déclaration :
public class FilterOutputStream extends OutputStream
Constructeurs :
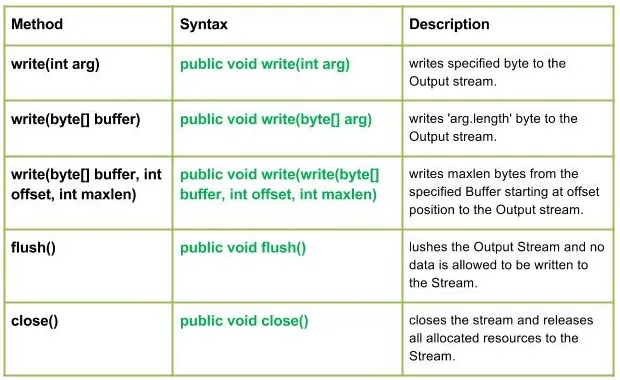
Méthodes :
Syntaxe :
public void write(int arg) Parameters : arg : Source Bytes Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
// Java program illustrating the working of work(int arg) // method import java.io.* ; import java.lang.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // OutputStream FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream // initially null OutputStream geek_out = null ; FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null ; // FileInputStream used here FileInputStream geekinput = null ; char c ; int a ; try { // create output streams geek_out = new FileOutputStream ( 'GEEKS.txt' ); geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream ( geek_out ); // write(int arg) : Used to write 'M' in the file // - 'ABC.txt' geek_filter . write ( 77 ); // Flushes the Output Stream geek_filter . flush (); // Creating Input Stream geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'GEEKS.txt' ); // read() method of FileInputStream : // reading the bytes and converting next bytes to int a = geekinput . read (); /* Since read() converts bytes to int so we convert int to char for our program output*/ c = ( char ) a ; // print character System . out . println ( 'Character written by' + ' FilterOutputStream : ' + c ); } catch ( IOException except ) { // if any I/O error occurs System . out . print ( 'Write Not working properly' ); } finally { // releases any system resources associated with // the stream if ( geek_out != null ) geek_out . close (); if ( geek_filter != null ) geek_filter . close (); } } }
Dans le programme que j'ai utilisé GEEKS.txt fichier, le programme créera un nouveau fichier du nom donné dans le code et y écrira.
Sortir :
Character written by FilterOutputStream : M
Syntaxe :
public void write(byte[] arg) Parameters : buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
// Java program illustrating the working of work(byte // buffer) method import java.io.* ; import java.lang.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // OutputStream FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream // initially null OutputStream geek_out = null ; FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null ; // FileInputStream used here FileInputStream geekinput = null ; byte [] buffer = { 77 79 72 73 84 }; char c ; int a ; try { // create output streams geek_out = new FileOutputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream ( geek_out ); // writes buffer to the output stream geek_filter . write ( buffer ); // forces byte contents to written out to the stream geek_filter . flush (); // create input streams geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); while (( a = geekinput . read ()) !=- 1 ) { // converts integer to the character c = ( char ) a ; // prints System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( IOException except ) { // if any I/O error occurs System . out . print ( 'Write Not working properly' ); } finally { // releases any system resources associated // with the stream if ( geek_out != null ) geek_out . close (); if ( geek_filter != null ) geek_filter . close (); } } }
Dans le programme que j'utilise GEEKS.txt fichier, le programme créera un nouveau fichier du nom donné dans le code et y écrira.
Sortir :
MOHIT
Syntaxe :
public void write(write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream Return : buffer : Source Buffer to be written offset : Starting offset maxlen : max no. of bytes to be written to the Output Stream Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
Syntaxe :
public void flush() Parameters : ------ Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
Syntaxe :
public void close() Parameters : ------ Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
Programme Java illustrant : les méthodes write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) flush() close()
// Java program illustrating the working of // write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) // flush() close() method import java.io.* ; import java.lang.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // OutputStream FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream // initially null OutputStream geek_out = null ; FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null ; // FileInputStream used here FileInputStream geekinput = null ; byte [] buffer = { 65 66 77 79 72 73 84 }; char c ; int a ; try { // create output streams geek_out = new FileOutputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream ( geek_out ); // write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) : // writes buffer to the output stream // Here offset = 2 so it won't read first two bytes // then maxlen = 5 so it will print max of 5 characters geek_filter . write ( buffer 2 5 ); // forces byte contents to written out to the stream geek_filter . flush (); // create input streams geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); while (( a = geekinput . read ()) !=- 1 ) { // converts integer to the character c = ( char ) a ; // prints System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( IOException except ) { // if any I/O error occurs System . out . print ( 'Write Not working properly' ); } finally { // releases any system resources associated // with the stream if ( geek_out != null ) geek_out . close (); if ( geek_filter != null ) geek_filter . close (); } } }
Note :
Dans le programme que j'utilise GEEKS.txt fichier, le programme créera un nouveau fichier du nom donné dans le code et y écrira.
Sortir :
MOHIT
Vous Pourriez Aimer
Top Articles
Catégorie
Des Articles Intéressants