Javaで設定する
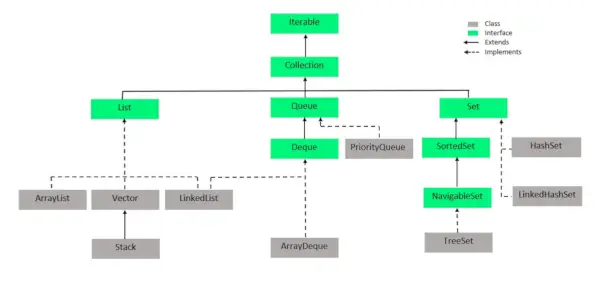
set インターフェイスは java.util パッケージに存在し、 コレクションインターフェース 。これは、重複した値を格納できない、順序付けされていないオブジェクトのコレクションです。数学的集合を実装するインターフェースです。このインターフェイスには、Collection インターフェイスから継承されたメソッドが含まれており、重複要素の挿入を制限する機能が追加されています。セットの実装を拡張する 2 つのインターフェイス、つまり SortedSet と NavigableSet があります。

上の画像では、ナビゲート可能なセットはソートされたセットのインターフェイスを拡張しています。セットは挿入順序を保持しないため、ナビゲート可能なセット インターフェイスはセット内をナビゲートするための実装を提供します。ナビゲート可能なセットを実装するクラスは、自己均衡ツリーの実装である TreeSet です。したがって、このインターフェイスは、このツリー内を移動する方法を提供します。
宣言: Set インターフェイスは次のように宣言されます。
public interface Set extends Collection
セットオブジェクトの作成
Set は インターフェース 、タイプセットからオブジェクトを作成することはできません。オブジェクトを作成するには、このリストを拡張するクラスが常に必要です。また、導入後は、 ジェネリック Java 1.5 では、Set に格納できるオブジェクトの種類を制限できるようになりました。このタイプセーフなセットは次のように定義できます。
// Obj is the type of the object to be stored in Set Set set = new HashSet ();
以下に示す Set インターフェイスに存在するメソッドを表形式で説明します。
| 方法 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 追加(要素) | このメソッドは、特定の要素をセットに追加するために使用されます。この関数は、指定された要素がセット内に存在しない場合にのみ要素を追加します。要素がセット内に既に存在する場合、関数は False を返します。 |
| すべて追加(コレクション) | このメソッドは、言及されたコレクションのすべての要素を既存のセットに追加するために使用されます。要素は特定の順序に従わずにランダムに追加されます。 |
| クリア() | このメソッドは、セットからすべての要素を削除するために使用されますが、セットは削除されません。このセットの参照はまだ存在します。 |
| 含む(要素) | このメソッドは、特定の要素が Set に存在するかどうかを確認するために使用されます。 |
| すべてを含む(コレクション) | このメソッドは、指定されたコレクションに存在するすべての要素がセットに含まれているかどうかを確認するために使用されます。このメソッドは、セットにすべての要素が含まれている場合は true を返し、要素のいずれかが欠落している場合は false を返します。 |
| ハッシュコード() | このメソッドは、Set のこのインスタンスの hashCode 値を取得するために使用されます。 Set のこのインスタンスの hashCode 値である整数値を返します。 |
| isEmpty() | このメソッドは、セットが空かどうかを確認するために使用されます。 |
| イテレータ() | このメソッドは、 イテレータ セットの。セットの要素はランダムな順序で返されます。 |
| 削除(要素) | このメソッドは、セットから指定された要素を削除するために使用されます。このメソッドは、指定された要素が Set 内に存在する場合は True を返し、それ以外の場合は False を返します。 |
| すべて削除(コレクション) | このメソッドは、セット内に存在するすべての要素をコレクションから削除するために使用されます。呼び出しの結果としてこのセットが変更された場合、このメソッドは true を返します。 |
| すべて保持(コレクション) | このメソッドは、指定されたコレクションで言及されているセットのすべての要素を保持するために使用されます。呼び出しの結果としてこのセットが変更された場合、このメソッドは true を返します。 |
| サイズ() | このメソッドはセットのサイズを取得するために使用されます。これは、要素の数を示す整数値を返します。 |
| toArray() | このメソッドは、Set と同じ要素の配列を形成するために使用されます。 |
図: Setインターフェースを説明するサンプルプログラム
ジャワ
// Java program Illustrating Set Interface> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Demonstrating Set using HashSet> > // Declaring object of type String> > Set hash_Set => new> HashSet();> > > // Adding elements to the Set> > // using add() method> > hash_Set.add(> 'Geeks'> );> > hash_Set.add(> 'For'> );> > hash_Set.add(> 'Geeks'> );> > hash_Set.add(> 'Example'> );> > hash_Set.add(> 'Set'> );> > > // Printing elements of HashSet object> > System.out.println(hash_Set);> > }> }> |
出力
[Set, Example, Geeks, For]
Set インターフェイスの操作
セット インターフェイスを使用すると、ユーザーはセットに対して基本的な数学演算を実行できます。これらの基本的な操作を理解するために 2 つの配列を取り上げてみましょう。 set1 = [1, 3, 2, 4, 8, 9, 0]、set2 = [1, 3, 7, 5, 4, 0, 7, 5] とします。この場合、セットに対して可能な操作は次のとおりです。
1. 交差点: この操作は、指定された 2 つのセットからすべての共通要素を返します。上記 2 つのセットの場合、交差は次のようになります。
Intersection = [0, 1, 3, 4]
2.結合: この操作では、一方のセット内のすべての要素がもう一方のセットに追加されます。上記 2 つのセットの場合、和集合は次のようになります。
Union = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9]
3. 違い: この操作により、一方のセットに存在するすべての値がもう一方のセットから削除されます。上記 2 つのセットの違いは次のようになります。
Difference = [2, 8, 9]
ここで、上で定義した次の操作を次のように実装してみましょう。
例:
ジャワ
// Java Program Demonstrating Operations on the Set> // such as Union, Intersection and Difference operations> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> public> class> SetExample {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String args[])> > {> > // Creating an object of Set class> > // Declaring object of Integer type> > Set a => new> HashSet();> > > // Adding all elements to List> > a.addAll(Arrays.asList(> > new> Integer[] {> 1> ,> 3> ,> 2> ,> 4> ,> 8> ,> 9> ,> 0> }));> > > // Again declaring object of Set class> > // with reference to HashSet> > Set b => new> HashSet();> > > b.addAll(Arrays.asList(> > new> Integer[] {> 1> ,> 3> ,> 7> ,> 5> ,> 4> ,> 0> ,> 7> ,> 5> }));> > > > // To find union> > Set union => new> HashSet(a);> > union.addAll(b);> > System.out.print(> 'Union of the two Set'> );> > System.out.println(union);> > > // To find intersection> > Set intersection => new> HashSet(a);> > intersection.retainAll(b);> > System.out.print(> 'Intersection of the two Set'> );> > System.out.println(intersection);> > > // To find the symmetric difference> > Set difference => new> HashSet(a);> > difference.removeAll(b);> > System.out.print(> 'Difference of the two Set'> );> > System.out.println(difference);> > }> }> |
出力
Union of the two Set[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9] Intersection of the two Set[0, 1, 3, 4] Difference of the two Set[2, 8, 9]
SortedSet でのさまざまな操作の実行
導入後 ジェネリック Java 1.5 では、Set に格納できるオブジェクトの種類を制限できるようになりました。 Set はインターフェイスであるため、このインターフェイスを実装したクラスでのみ使用できます。 HashSet は、Set インターフェイスを実装する、広く使用されているクラスの 1 つです。次に、HashSet で頻繁に使用される操作をいくつか実行する方法を見てみましょう。以下の操作を以下のように実行していきます。
- 要素の追加
- 要素へのアクセス
- 要素の削除
- 要素の反復
- セットを反復処理する
ここで、これらの操作を次のように個別に説明します。
操作 1: 要素の追加
Set に要素を追加するには、 add() メソッド 。ただし、広告掲載オーダーはセットには保持されません。内部的には、要素ごとにハッシュが生成され、生成されたハッシュに対して値が保存されます。値は比較され、昇順に並べ替えられます。重複要素は許可されておらず、重複要素はすべて無視されることに注意してください。また、セットでは Null 値も受け入れられます。
例
ジャワ
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by> // Adding elements using add() method> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating an object of Set and> > // declaring object of type String> > Set hs => new> HashSet();> > > // Adding elements to above object> > // using add() method> > hs.add(> 'B'> );> > hs.add(> 'B'> );> > hs.add(> 'C'> );> > hs.add(> 'A'> );> > > // Printing the elements inside the Set object> > System.out.println(hs);> > }> }> |
出力
[A, B, C]
操作 2: 要素へのアクセス
要素を追加した後、要素にアクセスしたい場合は、 contains() などの組み込みメソッドを使用できます。
例
ジャワ
// Java code to demonstrate Working of Set by> // Accessing the Elements of the Set object> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating an object of Set and> > // declaring object of type String> > Set hs => new> HashSet();> > > // Elements are added using add() method> > // Later onwards we will show accessing the same> > > // Custom input elements> > hs.add(> 'A'> );> > hs.add(> 'B'> );> > hs.add(> 'C'> );> > hs.add(> 'A'> );> > > // Print the Set object elements> > System.out.println(> 'Set is '> + hs);> > > // Declaring a string> > String check => 'D'> ;> > > // Check if the above string exists in> > // the SortedSet or not> > // using contains() method> > System.out.println(> 'Contains '> + check +> ' '> > + hs.contains(check));> > }> }> |
出力
Set is [A, B, C] Contains D false
操作 3: 値の削除
値は、remove() メソッドを使用して Set から削除できます。
例
ジャワ
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by> // Removing Element/s from the Set> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Declaring object of Set of type String> > Set hs => new> HashSet();> > > // Elements are added> > // using add() method> > > // Custom input elements> > hs.add(> 'A'> );> > hs.add(> 'B'> );> > hs.add(> 'C'> );> > hs.add(> 'B'> );> > hs.add(> 'D'> );> > hs.add(> 'E'> );> > > // Printing initial Set elements> > System.out.println(> 'Initial HashSet '> + hs);> > > // Removing custom element> > // using remove() method> > hs.remove(> 'B'> );> > > // Printing Set elements after removing an element> > // and printing updated Set elements> > System.out.println(> 'After removing element '> + hs);> > }> }> |
出力
Initial HashSet [A, B, C, D, E] After removing element [A, C, D, E]
操作 4: セットの反復処理
Set を反復するにはさまざまな方法があります。最も有名なのは、拡張された for ループを使用することです。
例
ジャワ
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of Set by> // Iterating through the Elements> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating object of Set and declaring String type> > Set hs => new> HashSet();> > > // Adding elements to Set> > // using add() method> > > // Custom input elements> > hs.add(> 'A'> );> > hs.add(> 'B'> );> > hs.add(> 'C'> );> > hs.add(> 'B'> );> > hs.add(> 'D'> );> > hs.add(> 'E'> );> > > // Iterating through the Set> > // via for-each loop> > for> (String value : hs)> > > // Printing all the values inside the object> > System.out.print(value +> ', '> );> > > System.out.println();> > }> }> |
出力
A, B, C, D, E,
Java コレクションの Set インターフェイスを実装するクラスは、次の図から簡単に認識でき、次のようにリストされます。
- ハッシュセット
- 列挙セット
- リンクされたハッシュセット
- ツリーセット

クラス 1: ハッシュセット
で実装される HashSet クラス コレクションフレームワーク の固有の実装です。 例
ジャワ
// Java program Demonstrating Creation of Set object> // Using the Hashset class> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating object of Set of type String> > Set h => new> HashSet();> > > // Adding elements into the HashSet> > // using add() method> > > // Custom input elements> > h.add(> 'India'> );> > h.add(> 'Australia'> );> > h.add(> 'South Africa'> );> > > // Adding the duplicate element> > h.add(> 'India'> );> > > // Displaying the HashSet> > System.out.println(h);> > > // Removing items from HashSet> > // using remove() method> > h.remove(> 'Australia'> );> > System.out.println(> 'Set after removing '> > +> 'Australia:'> + h);> > > // Iterating over hash set items> > System.out.println(> 'Iterating over set:'> );> > > // Iterating through iterators> > Iterator i = h.iterator();> > > // It holds true till there is a single element> > // remaining in the object> > while> (i.hasNext())> > > System.out.println(i.next());> > }> }> |
出力
[South Africa, Australia, India] Set after removing Australia:[South Africa, India] Iterating over set: South Africa India
クラス 2: 列挙セット
で実装される EnumSet クラス コレクションフレームワーク で使用するための Set インターフェイスの特殊な実装の 1 つです。 列挙型 。これは、HashSet よりもはるかに高速な、高性能のセット実装です。列挙セット内のすべての要素は、セットの作成時に明示的または暗黙的に指定された単一の列挙型に由来する必要があります。このクラスを使用してセットオブジェクトを作成する方法を見てみましょう。
例
ジャワ
// Java program to demonstrate the> // creation of the set object> // using the EnumSet class> import> java.util.*;> > enum> Gfg { CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ, MCQ }> ;> > public> class> GFG {> > > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating a set> > Set set1;> > > // Adding the elements> > set1 = EnumSet.of(Gfg.QUIZ, Gfg.CONTRIBUTE,> > Gfg.LEARN, Gfg.CODE);> > > System.out.println(> 'Set 1: '> + set1);> > }> }> |
出力
Set 1: [CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ]
クラス 3: リンクされたハッシュセット
で実装される LinkedHashSet クラス コレクションフレームワーク これは、すべての要素にわたって二重リンクされたリストを維持する、HashSet の順序付きバージョンです。反復順序を維持する必要がある場合、このクラスが使用されます。 HashSet を反復処理する場合、順序は予測できませんが、LinkedHashSet を使用すると、要素が挿入された順序で要素を反復処理できます。このクラスを使用してセットオブジェクトを作成する方法を見てみましょう。
例
ジャワ
// Java program to demonstrate the> // creation of Set object using> // the LinkedHashset class> import> java.util.*;> > class> GFG {> > > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > Set lh => new> LinkedHashSet();> > > // Adding elements into the LinkedHashSet> > // using add()> > lh.add(> 'India'> );> > lh.add(> 'Australia'> );> > lh.add(> 'South Africa'> );> > > // Adding the duplicate> > // element> > lh.add(> 'India'> );> > > // Displaying the LinkedHashSet> > System.out.println(lh);> > > // Removing items from LinkedHashSet> > // using remove()> > lh.remove(> 'Australia'> );> > System.out.println(> 'Set after removing '> > +> 'Australia:'> + lh);> > > // Iterating over linked hash set items> > System.out.println(> 'Iterating over set:'> );> > Iterator i = lh.iterator();> > while> (i.hasNext())> > System.out.println(i.next());> > }> }> |
出力
[India, Australia, South Africa] Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa] Iterating over set: India South Africa
クラス 4: ツリーセット
で実装される TreeSet クラス コレクションフレームワーク SortedSet インターフェイスと SortedSet の実装は Set インターフェイスを拡張します。要素をソートされた形式で保存することを除いて、単純なセットのように動作します。 TreeSet は、ストレージにツリー データ構造を使用します。オブジェクトはソートされた昇順で保存されます。ただし、TreeSet.descendingIterator() メソッドを使用して降順で反復できます。このクラスを使用してセットオブジェクトを作成する方法を見てみましょう。
例
ジャワ
// Java Program Demonstrating Creation of Set object> // Using the TreeSet class> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Creating a Set object and declaring it of String> > // type> > // with reference to TreeSet> > Set ts => new> TreeSet();> > > // Adding elements into the TreeSet> > // using add()> > ts.add(> 'India'> );> > ts.add(> 'Australia'> );> > ts.add(> 'South Africa'> );> > > // Adding the duplicate> > // element> > ts.add(> 'India'> );> > > // Displaying the TreeSet> > System.out.println(ts);> > > // Removing items from TreeSet> > // using remove()> > ts.remove(> 'Australia'> );> > System.out.println(> 'Set after removing '> > +> 'Australia:'> + ts);> > > // Iterating over Tree set items> > System.out.println(> 'Iterating over set:'> );> > Iterator i = ts.iterator();> > > while> (i.hasNext())> > System.out.println(i.next());> > }> }> |
出力
[Australia, India, South Africa] Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa] Iterating over set: India South Africa