二分木を二分探索木に変換するために必要な最小スワップ

配列が与えられた場合 到着[] を表す 完全なバイナリ ツリー つまり、もし インデックス i です 親 索引 2*i + 1 です 左の子 そして インデックス 2*i + 2 は 正しい子です。 課題は、 最小 の数 スワップ に変換するために必要な 二分探索ツリー。
例:
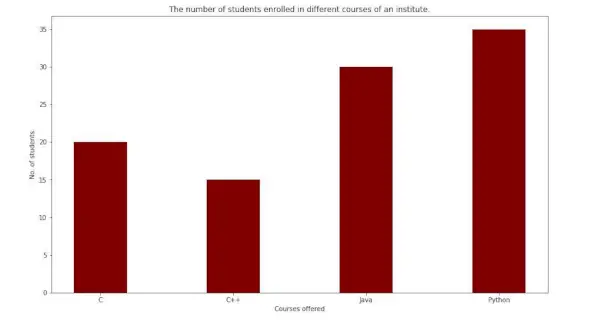
入力: arr[] = [5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
出力: 3
説明:
指定された配列のバイナリ ツリー:

スワップ 1: ノード 8 とノード 5 を交換します。
スワップ 2: ノード 9 をノード 10 と交換します。
スワップ 3: ノード 10 をノード 7 と交換します。したがって、以下の二分探索木を取得するには、少なくとも 3 つのスワップが必要です。

入力: arr[] = [1 2 3]
出力: 1
説明:
指定された配列のバイナリ ツリー:
ノード 1 をノード 2 と交換した後、以下の二分探索ツリーを取得します。

アプローチ:
C++という事実を利用するのがアイデアです。 順序トラバーサル の 二分探索木 いる 増加する 値の順序。
それで、 順序トラバーサル バイナリツリーと それを配列に格納します そして試してみてください 選別 配列。の 配列をソートするために必要なスワップの最小数 が答えになります。
// C++ program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree #include using namespace std ; // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in vector v void inorder ( vector < int >& arr vector < int >& inorderArr int index ) { int n = arr . size (); // If index is out of bounds return if ( index >= n ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ); // Store current node value in vector inorderArr . push_back ( arr [ index ]); // Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps // to sort inorder traversal int minSwaps ( vector < int >& arr ) { int n = arr . size (); vector < int > inorderArr ; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ); // Create an array of pairs to store value // and original index vector < pair < int int >> t ( inorderArr . size ()); int ans = 0 ; // Store the value and its index for ( int i = 0 ; i < inorderArr . size (); i ++ ) t [ i ] = { inorderArr [ i ] i }; // Sort the pair array based on values // to get BST order sort ( t . begin () t . end ()); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for ( int i = 0 ; i < t . size (); i ++ ) { // If the element is already in the // correct position continue if ( i == t [ i ]. second ) continue ; // Otherwise perform swaps until the element // is in the right place else { // Swap elements to correct positions swap ( t [ i ]. first t [ t [ i ]. second ]. first ); swap ( t [ i ]. second t [ t [ i ]. second ]. second ); } // Check if the element is still not // in the correct position if ( i != t [ i ]. second ) -- i ; // Increment swap count ans ++ ; } return ans ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 }; cout < < minSwaps ( arr ) < < endl ; }
Java // Java program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree import java.util.Arrays ; class GfG { // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in an array static void inorder ( int [] arr int [] inorderArr int index int [] counter ) { int n = arr . length ; // Base case: if index is out of bounds return if ( index >= n ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 counter ); // Store current node value in the inorder array inorderArr [ counter [ 0 ]] = arr [ index ] ; counter [ 0 ]++ ; // Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 counter ); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps // to sort inorder traversal static int minSwaps ( int [] arr ) { int n = arr . length ; int [] inorderArr = new int [ n ] ; int [] counter = new int [ 1 ] ; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 counter ); // Create an array of pairs to store the value // and its original index int [][] t = new int [ n ][ 2 ] ; int ans = 0 ; // Store the value and its original index for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { t [ i ][ 0 ] = inorderArr [ i ] ; t [ i ][ 1 ] = i ; } // Sort the array based on values to get BST order Arrays . sort ( t ( a b ) -> Integer . compare ( a [ 0 ] b [ 0 ] )); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles boolean [] visited = new boolean [ n ] ; // Iterate through the array to find cycles for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { // If the element is already visited or in // the correct place continue if ( visited [ i ] || t [ i ][ 1 ] == i ) continue ; // Start a cycle and find the number of // nodes in the cycle int cycleSize = 0 ; int j = i ; while ( ! visited [ j ] ) { visited [ j ] = true ; j = t [ j ][ 1 ] ; cycleSize ++ ; } // If there is a cycle we need (cycleSize - 1) // swaps to sort the cycle if ( cycleSize > 1 ) { ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ); } } // Return the total number of swaps return ans ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 }; System . out . println ( minSwaps ( arr )); } }
Python # Python program for Minimum swap required # to convert binary tree to binary search tree # Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree # and store it in an array def inorder ( arr inorderArr index ): # If index is out of bounds return n = len ( arr ) if index >= n : return # Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ) # Store current node value in inorderArr inorderArr . append ( arr [ index ]) # Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ) # Function to calculate minimum swaps # to sort inorder traversal def minSwaps ( arr ): inorderArr = [] # Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ) # Create a list of pairs to store value and original index t = [( inorderArr [ i ] i ) for i in range ( len ( inorderArr ))] ans = 0 # Sort the list of pairs based on values # to get BST order t . sort () # Initialize visited array visited = [ False ] * len ( t ) # Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for i in range ( len ( t )): # If already visited or already in the # correct place skip if visited [ i ] or t [ i ][ 1 ] == i : continue # Start a cycle and find the number of # nodes in the cycle cycleSize = 0 j = i # Process all elements in the cycle while not visited [ j ]: visited [ j ] = True j = t [ j ][ 1 ] cycleSize += 1 # If there is a cycle of size `cycle_size` we # need `cycle_size - 1` swaps if cycleSize > 1 : ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ) # Return total number of swaps return ans if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ] print ( minSwaps ( arr ))
C# // C# program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree using System ; using System.Linq ; class GfG { // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in an array static void Inorder ( int [] arr int [] inorderArr int index ref int counter ) { int n = arr . Length ; // Base case: if index is out of bounds return if ( index >= n ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree Inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ref counter ); // Store current node value in inorderArr inorderArr [ counter ] = arr [ index ]; counter ++ ; // Recursively visit right subtree Inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ref counter ); } // Function to calculate minimum // swaps to sort inorder traversal static int MinSwaps ( int [] arr ) { int n = arr . Length ; int [] inorderArr = new int [ n ]; int counter = 0 ; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree Inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ref counter ); // Create an array of pairs to store value // and original index var t = new ( int int )[ n ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { t [ i ] = ( inorderArr [ i ] i ); } // Sort the array based on values to get BST order Array . Sort ( t ( a b ) => a . Item1 . CompareTo ( b . Item1 )); // Initialize visited array bool [] visited = new bool [ n ]; int ans = 0 ; // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { // If already visited or already in // the correct place skip if ( visited [ i ] || t [ i ]. Item2 == i ) continue ; // Start a cycle and find the number // of nodes in the cycle int cycleSize = 0 ; int j = i ; // Process all elements in the cycle while ( ! visited [ j ]) { visited [ j ] = true ; j = t [ j ]. Item2 ; cycleSize ++ ; } // If there is a cycle of size `cycle_size` we // need `cycle_size - 1` swaps if ( cycleSize > 1 ) { ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ); } } // Return total number of swaps return ans ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int [] arr = { 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 }; Console . WriteLine ( MinSwaps ( arr )); } }
JavaScript // Javascript program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree // Inorder traversal to get values in sorted order function inorder ( arr inorderArr index ) { // If index is out of bounds return if ( index >= arr . length ) return ; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 1 ); // Store current node value in array inorderArr . push ( arr [ index ]); // Recursively visit right subtree inorder ( arr inorderArr 2 * index + 2 ); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps to sort inorder // traversal function minSwaps ( arr ) { let inorderArr = []; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder ( arr inorderArr 0 ); // Create an array of pairs to store value and original // index let t = inorderArr . map (( val i ) => [ val i ]); let ans = 0 ; // Sort the pair array based on values to get BST order t . sort (( a b ) => a [ 0 ] - b [ 0 ]); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles let visited = Array ( arr . length ) . fill ( false ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < t . length ; i ++ ) { // If the element is already in the correct // position continue if ( visited [ i ] || t [ i ][ 1 ] === i ) continue ; // Otherwise perform swaps until the element is in // the right place let cycleSize = 0 ; let j = i ; while ( ! visited [ j ]) { visited [ j ] = true ; j = t [ j ][ 1 ]; cycleSize ++ ; } // If there is a cycle we need (cycleSize - 1) // swaps to sort the cycle if ( cycleSize > 1 ) { ans += ( cycleSize - 1 ); } } // Return total number of swaps return ans ; } let arr = [ 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ]; console . log ( minSwaps ( arr ));
出力
3
時間計算量: O(n*logn) ここで n 配列内の要素の数です。
補助スペース: O(n) 配列に余分なスペースを使用しているため
エクササイズ: これを通常のバイナリ ツリー、つまり左右のポインタを使用して表現され、必ずしも完全ではないバイナリ ツリーに拡張できますか?
クイズの作成