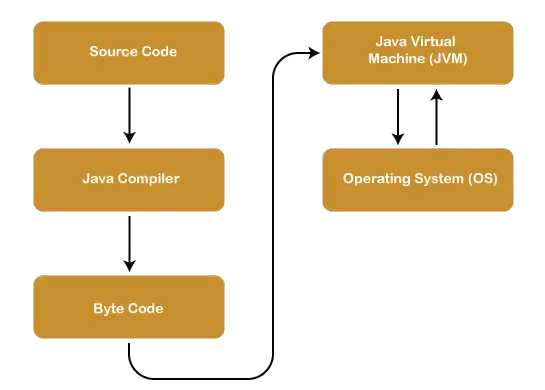
C++ でのファイル処理

ファイル処理とは、C++ 標準ライブラリによって提供されるクラスを使用して、ファイル (.txt .csv など) の読み取りと書き込みを意味します。
- プログラムは RAM で実行されます。つまり、データはプログラムの実行中にのみ存在し、プログラムが終了すると、RAM 内のすべてのデータが自動的に失われます。
- ファイル処理により、データを二次メモリ (HDD や SSD など) に保存できるため、データを永続的に保存でき、プログラム終了後でも保存してアクセスできます。
- ファイル操作のために、C++ はファイル ストリーム クラスを提供します。
ofstream ifstream fstream などのヘッダー。
ファイルを開く
ファイルの読み取りまたは書き込みを行う前に、まずファイルを開く必要があります。ファイルを開くと、そのファイルが RAM にロードされます。 C++ では、ファイルへのストリームを作成することでファイルを開きます。 fストリーム ファイルストリーム、つまりファイルへの入出力のストリームを表すクラス。
C++ fstream str ( 'filename.ext' mode );
どこ
- 文字列: ストリームに付けられた名前
- ファイル名: ファイルの名前
- モード : ファイルを操作する方法を表します。
ファイルを開くモード
ファイルオープンモードは、ファイルが読み取り書き込みまたは追加のために開かれていることを示します。以下は、C++ のすべてのファイル モードのリストです。
| モード | 説明 |
|---|---|
| ios::で | ファイルを読み取りのために開いています。ファイルが存在しない場合、開く操作は失敗します。 |
| ios::out | 書き込み用にファイルが開かれています: 内部ストリーム バッファは出力操作をサポートします。 |
| ios::バイナリ | 操作はテキストではなくバイナリ モードで実行されます。 |
| ios::食べた | 出力位置はファイルの末尾から始まります。 |
| ios::アプリ | すべての出力操作は、ファイルの最後に行われ、既存のコンテンツに追加されます。 |
| ios::トランク | ファイルを開く前にファイルに存在していた内容はすべて破棄されます。 |
例えば ファイルを読み取り用に開きたい場合は、次の開くモードを使用します。
C++ fstream filein ( 'file.txt' ios :: in );
同様に、書き込み用にファイルを開く場合は、次を使用します。
C++ fstream fileout ( 'file.txt' ios :: out );
これらのモードは、OR 演算子 (|) を使用して組み合わせることができます。たとえば、次のようにファイル ストリームを読み取りモードと書き込みモードの両方で開くことができます。
C++ fstream str ( 'file.txt' ios :: in | ios :: out );
書き込みモードで開かれたファイルが存在しない場合は、新しいファイルが作成されます。ただし、読み取りモードで開かれたファイルが存在しない場合、新しいファイルは作成されず、例外がスローされます。
その他のファイル ストリーム
fストリーム C++ が提供するファイル ストリームはこれだけではありません。さらに 2 つの特殊なストリームがあります。
- イフストリーム : 入力ファイルストリームを表します。これは fstream を開くのと同等です。 ios::で モード。
- 川下 : 出力ファイルストリームを表します。これは fstream を開くのと同等です。 ios::out モード。
上記のモードは、これらのストリームのデフォルト モードです。これらのモードは変更できませんが、他のモードと一緒にクラブ化することができます。次に、入力として、次のように ifstream を使用することもできます。
C++ ifstream filein ( 'file.txt' );
出力についても同様に:
C++ ofstream fileout ( 'file.txt' );
データをファイルに書き込む
いずれかの方法を使用してファイルが書き込みモードで開かれると、 fストリーム または 川下 cout と同様の方法で書き込み操作を実行できます。 < < operator.
C++ #include using namespace std ; int main () { // Open a file ofstream file ( 'GFG.txt' ); // Write the string to the file file < < 'Welcome to GeeksforGeeks.' ; return 0 ; }
 GFG.テキスト
GFG.テキスト ファイルからデータを読み取る
fstream または ifstream を使用してファイルが読み取りモードで開かれると、cin を使用した場合と同様の方法で書き込み操作を実行できます。 >> オペレーター。
C++ #include using namespace std ; int main () { // Open a file in read mode ifstream file ( 'GFG.txt' ); string s ; // Read string from the file file >> s ; cout < < 'Read String: ' < < s ; return 0 ; }
出力
Read String: Welcomeこれには cin と同じ問題があります。入力は最初の空白文字までのみ取得されます。これを回避するには、 getline() 図に示すように機能します。
C++using namespace std ; int main () { // Open a file in read mode ifstream file ( 'GFG.txt' ); string s ; // Read string from the file getline ( file s ); cout < < 'Read String: ' < < s ; return 0 ; }
出力Read String: Welcome to GeeksforGeeks.ファイルを閉じる
ファイルを閉じるということは、関連するストリームを閉じて、使用されているリソースを解放することを意味します。特に長時間実行されるプログラムでは、メモリ リークやデータ損失などを避けるために、ファイルの使用が終了したらファイルを閉じることが重要です。
C++ では、ファイルは次のコマンドを使用して閉じられます。 近い() すべてのファイル ストリームに存在するメンバー関数。
C++using namespace std ; int main () { // Open a file in read mode ifstream file ( 'GFG.txt' ); string s ; // Read string from the file getline ( file s ); cout < < 'Read String: ' < < s ; // Close the file file . close (); return 0 ; }
出力Read String: Welcome to GeeksforGeeks.ファイル処理のエラー
ファイルが見つからない、ディスクがいっぱいであるなど、ファイル処理ではさまざまな種類のエラーが発生する可能性があります。プログラムは一般的なエラーを予期し、それらを適切に処理できる必要があります。ファイル処理中に発生する可能性のある一般的なエラーを次に示します。
ファイルオープンの失敗
ファイルが存在しない、プログラムにファイルを開く権限がないなど、さまざまな理由でファイルが開かない場合があります。この場合、 is_open() ファイルストリームクラスのメンバー関数を使用して、ファイルが正常に開かれたかどうかを確認します。
C++using namespace std ; int main () { fstream file ( 'nonexistent_file.txt' ios :: in ); // Check if the file is opened if ( ! file . is_open ()) { cerr < < 'Error: Unable to open file!' < < endl ; return 1 ; } file . close (); return 0 ; }
出力Error: Unable to open file!データの読み取り/書き込みの失敗
もう 1 つの一般的なエラーは、不正なモードなどの理由でデータの読み取りまたは書き込みに失敗することです。この場合、読み取り/書き込みを試行するたびに操作を検証できます。たとえば、 getline() を使用した読み取りは次のように検証できます。
C++using namespace std ; int main () { fstream file ( 'GFG.txt' ios :: out ); if ( ! file . is_open ()) { cerr < < 'Error: Unable to open file!' < < endl ; return 1 ; } string line ; // Checking if getline() read successfully or not if ( ! getline ( file line )) cerr < < 'Error: Failed to read data' < < endl ; file . close (); return 0 ; }
出力Error: Failed to read dataファイルの終わり (EOF) エラー
ファイルの終わりを超えて読み取ろうとすると、EOF エラーが発生する可能性があります。これは、読み取る前にファイルの終わりを確認しない場合に発生する可能性があります。次を使用して EOF を確認できます eof() メンバー関数。
C++using namespace std ; int main () { ifstream file ( 'GFG.txt' ); if ( ! file . is_open ()) { cerr < < 'Error: Unable to open file!' < < endl ; return 1 ; } string line ; while ( getline ( file line )) cout < < line < < endl ; // Check for eof if ( file . eof ()) cout < < 'Reached end of file.' < < endl ; else cerr < < 'Error: File reading failed!' < < endl ; file . close (); return 0 ; }
出力Reached end of file.EOF をチェックする前に読み取り操作も検証していることに注意してください。 getline() 戻るだけです nullptr 何らかの理由で読み取りが失敗した場合でも。
バイナリファイルの処理
C++でも扱えます バイナリファイル データを生の形式で保存します。バイナリ データの読み取りと書き込みには、 ios::バイナリ バイナリ ファイルを作成または開くときにフラグを設定します。
バイナリファイルへの書き込み
バイナリ ファイルにデータを書き込むには、まずファイルを開くか作成する必要があります。 ios::バイナリ モード。
C++#include #include using namespace std ; int main () { string str = 'Welcome to GeeksForGeeks' ; // Open a binary file for writing ofstream file ( 'fileBin.bin' ios :: binary ); // Check if the file is open if ( ! file ) { cerr < < 'Error opening the file for writing.' ; return 1 ; } // Write the length of the string (size) to file first size_t strLength = str . length (); file . write ( reinterpret_cast < const char *> ( & strLength ) sizeof ( strLength )); // Write the string to the binary file file . write ( str . c_str () strLength ); // Close the file file . close (); return 0 ; }
出力バイナリファイル
バイナリファイルからの読み取り
バイナリ モードでファイルを開いてデータを書き込み、バイナリ ファイルからデータを読み取るのと同じように、次を使用してファイルを読み取りモードで開く必要があります。 ios::で 。
構文:
C++C++fstream fileInstance ( 'fileName.bin' ios :: in | ios :: binary );#include #include using namespace std ; int main () { string str ; // Open the binary file for reading fstream file ( 'fileBin.bin' ios :: in | ios :: binary ); // Check if the file is open if ( ! file ) { cerr < < 'Error opening the file for reading.' ; return 1 ; } // Read the length of the string (size) from the file size_t strLength ; file . read ( reinterpret_cast < char *> ( & strLength ) sizeof ( strLength )); // Allocate memory for the string and read the data char * buffer = new char [ strLength + 1 ]; // +1 for the null-terminator file . read ( buffer strLength ); // Null-terminate the string buffer [ strLength ] = '�' ; // Convert the buffer to a string str = buffer ; // Print file data cout < < 'File Data: ' < < str ; delete [] buffer ; file . close (); return 0 ; }
出力File Data: Welcome to GeeksForGeeksその他のファイル操作
C++ プログラムからファイルを操作するための追加の操作を実行することもできます。一般的なファイル操作には次のようなものがあります。
クイズの作成
- ファイルを削除する C++ プログラム
- 既存のファイルに文字列を追加する
- あるファイルを別のファイルにコピーする
 バイナリファイル
バイナリファイル