ניתוח נתונים ויזואליזציה עם Python

Python נמצא בשימוש נרחב כשפת ניתוח נתונים בשל הספריות והכלים החזקים שלה לניהול נתונים. בין הספריות אלה נמצאת Pandas שמקלה על חקירת נתונים מניפולציה וניתוח יותר יותר. נשתמש פנדות לנתח מערך נתונים שנקרא Country-data.csv מקאגל. תוך כדי עבודה עם נתונים אלה אנו מציגים גם כמה מושגים חשובים בפנדות.
1. התקנה
הדרך הקלה ביותר להתקין פנדות היא להשתמש ב-pip:
Python pip install pandas
או הורד אותו מ כָּאן .
2. יצירת DataFrame ב-Pandas
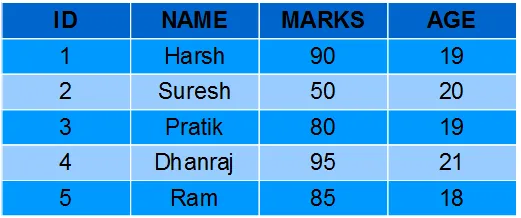
א DataFrame הוא מבנה נתונים דמוי טבלה ב-Pandas שיש בו נתונים המאוחסנים בשורות ובעמודות. ניתן ליצור DataFrame על ידי העברת אובייקטים מרובים מסדרת python לתוך DataFrame כיתה ( pd.DataFrame() ) באמצעות ה pd.Series שִׁיטָה. בדוגמה זו נעשה שימוש בשני אובייקטים מסדרה: s1 בתור השורה הראשונה ו s2 בתור השורה השנייה.
דוגמה 1: יצירת DataFrame מסדרה:
Python
import pandas as pd # Creating two Series: s1 (numbers) and s2 (names) s1 = pd . Series ([ 1 2 ]) s2 = pd . Series ([ 'Ashish' 'Sid' ]) # Creating DataFrame by combining Series as rows dataframe = pd . DataFrame ([ s1 s2 ]) # Displaying the DataFrame print ( dataframe )
תְפוּקָה:

דוגמה 2: DataFrame מרשימה עם אינדקס ושמות עמודות מותאמים אישית:
Python dataframe1 = pd . DataFrame ([[ 1 2 ] [ 'Ashish' 'Sid' ]] index = [ 'r1' 'r2' ] columns = [ 'c1' 'c2' ]) print ( dataframe1 )
תְפוּקָה:

דוגמה 3: DataFrame מתוך מילון:
Python dataframe2 = pd . DataFrame ({ 'c1' : [ 1 'Ashish' ] 'c2' : [ 2 'Sid' ] }) print ( dataframe2 )
תְפוּקָה:

3. ייבוא נתונים עם פנדות
השלב הראשון הוא לקרוא את הנתונים. במקרה שלנו הנתונים מאוחסנים כקובץ CSV (Comma-Separated Values) כאשר כל שורה מופרדת בשורה חדשה וכל עמודה בפסיק. על מנת להיות מסוגל לעבוד עם הנתונים ב- Python יש צורך לקרוא את ה-csv קוֹבֶץ לתוך Pandas DataFrame.
Python import pandas as pd # Read Country-data.csv into a DataFrame df = pd . read_csv ( 'Country-data.csv' ) # Prints the first 5 rows of a DataFrame as default df . head () # Prints no. of rows and columns of a DataFrame df . shape
תְפוּקָה:

(167 10)4. אינדקס DataFrames עם Pandas
Pandas מספקת יכולות אינדקס חזקות. אתה יכול לאינדקס DataFrames באמצעות שניהם מבוסס עמדה ו מבוסס תווית שיטות.
אינדקס מבוסס מיקום (באמצעות
Pythoniloc):תְפוּקָה:



אינדקס מבוסס תוויות (באמצעות
loc):ניתן לעבוד באינדקס עם תוויות באמצעות ה pandas.DataFrame.loc שיטה המאפשרת אינדקס באמצעות תוויות במקום מיקומים.
דוגמאות:
Pythonתְפוּקָה:


האמור לעיל למעשה לא נראה שונה בהרבה מ-df.iloc[0:5:]. הסיבה לכך היא שאמנם תוויות שורות יכולות לקבל כל ערך שתוויות השורות שלנו תואמות את המיקומים בדיוק. אבל תוויות עמודות יכולות להקל הרבה יותר בעבודה עם נתונים.דוּגמָה:
Pythonתְפוּקָה:

5. DataFrame Math עם פנדות
Pandas מקלה על ביצוע פעולות מתמטיות על הנתונים המאוחסנים במסגרות נתונים. הפעולות שניתן לבצע על פנדות הן וקטוריות כלומר הן מהירות ומוחלות אוטומטית על כל האלמנטים מבלי להשתמש בלולאות.
דוגמה - מתמטיקה לפי עמודה:
Pythonתְפוּקָה:

פונקציות סטטיסטיות בפנדות:
חישוב מסגרות נתונים יכול להיעשות באמצעות שימוש בפונקציות סטטיסטיות של כלי פנדה. נוכל להשתמש בפונקציות כמו:
-
df.sum()→ סכום ערכים -
df.mean()→ ממוצע -
df.max()/df.min()→ ערכי מקסימום ומינימום -
df.describe()← סיכום סטטיסטיקה מהיר
# computes various summary statistics excluding NaN values df . describe () # Provides sum of all the values for each column df . sum ()
תְפוּקָה:


6. הדמיית נתונים עם Pandas ו-Matplotlib
פנדה קל מאוד לשימוש Matplotlib ספרייה רבת עוצמה המשמשת ליצירת עלילות ותרשימים בסיסיים. עם מספר שורות קוד בלבד נוכל לדמיין את הנתונים שלנו ולהבין אותם טוב יותר. להלן כמה דוגמאות פשוטות שיעזרו לך להתחיל בתכנון באמצעות Pandas ו-Matplotlib:
Python # Import the library first import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
היסטוגרמה
היסטוגרמה מציגה את התפלגות הערכים בעמודה.
Python df [ 'income' ] . hist ( bins = 10 ) plt . title ( 'Histogram of Income' ) plt . xlabel ( 'Income Value' ) plt . ylabel ( 'Frequency' ) plt . show ()
תְפוּקָה:

עלילת קופסה
א עלילת קופסה שימושי כדי לזהות חריגים ולהבין את התפשטות הנתונים.
Python df = df . head ( 10 ) plt . figure ( figsize = ( 20 6 )) # Increase width to make x-axis labels clearer df . boxplot ( column = 'imports' by = 'country' ) plt . title ( 'Boxplot by Country' ) plt . suptitle ( '' ) # Removes default title plt . xlabel ( 'Country' ) plt . ylabel ( 'Imports' ) plt . xticks ( rotation = 45 ) # Optional: Rotate x-axis labels for better visibility plt . tight_layout () # Adjust layout to avoid clipping plt . show ()
תְפוּקָה:

עלילת פיזור
א עלילת פיזור מראה את הקשר בין שני משתנים.
Python x = df [ 'health' ] y = df [ 'life_expec' ] plt . scatter ( x y label = 'Data Points' color = 'm' marker = '*' s = 30 ) plt . xlabel ( 'Health' ) plt . ylabel ( 'Life Expectancy' ) plt . title ( 'Scatter Plot of Health vs Life Expectancy' ) plt . legend () plt . show ()
תְפוּקָה:

מאמר קשור:
- מבוא לפנדות
- שרטוט גרפים בפייתון
- עבודה עם קבצי csv ב-Python
- Pandas DataFrame
- מבוא ל-Matplotlib
- היסטוגרמה - סוגי הגדרה גרף ודוגמאות
- עלילת קופסה
- עלילת פיזור