Permutazioni dello stack


Abbiamo uno stack vuoto e possiamo eseguire operazioni push e pop. Ci vengono dati due array UN[] E B[] dove a[] rappresenta l'ordine in cui gli elementi vengono inseriti nello stack e b[] rappresenta l'ordine in cui gli elementi vengono estratti dallo stack. Scopri se le sequenze push e pop fornite sono valide.
Esempi:
Ingresso: a[] = [1 2 3] b[] = [2 1 3]
Produzione: VERO
Spiegazione: Premi 1 e 2. Poiché b[] richiede 2, prima fai 2, poi fai 1 dopo. Infine premi 3 e fallo scoppiare. La sequenza push e pop corrisponde a a[] e b[].Ingresso: a[] = [1 2 3] b[] = [3 1 2]
Produzione: falso
Spiegazione: Dopo aver premuto 1 2 e 3 possiamo farne apparire 3 come richiesto. Ma l'elemento successivo in b[] è 1 mentre la parte superiore dello stack è 2. Poiché 1 è bloccato sotto 2, questo ordine non può essere raggiunto.
Sommario
- [Approccio ingenuo] Utilizzo della coda - Tempo O(n) e spazio O(n).
- [Approccio previsto] Simulazione Push e Pop - O(n) tempo e O(n) spazio
[Approccio ingenuo] Utilizzo della coda - Tempo O(n) e spazio O(n).
L'idea è quella di simulare le operazioni sullo stack tenendo traccia degli elementi rimanenti da elaborare code .
Mettiamo gli elementi da a[] in ordine e per ogni elemento controlliamo se corrisponde alla parte anteriore di b[] (l'ordine pop previsto). Se corrisponde lo rimuoviamo da b[]; in caso contrario lo mettiamo in uno stack. Dopo ogni push controlliamo anche se la parte superiore dello stack corrisponde alla parte anteriore di b[], lo estraiamo dallo stack e lo rimuoviamo da b[]. Ripetendo ciò vediamo se tutti gli elementi in b[] possono essere abbinati. Se sì, la sequenza pop è valida; altrimenti non lo è.
C++ #include #include #include #include using namespace std ; bool checkPerm ( vector < int >& a vector < int >& b ) { queue < int > q1 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < a . size (); i ++ ) q1 . push ( a [ i ]); queue < int > q2 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b . size (); i ++ ) q2 . push ( b [ i ]); stack < int > st ; // Dequeue all items one by one while ( ! q1 . empty ()) { int ele = q1 . front (); q1 . pop (); if ( ele == q2 . front ()) { // If matches dequeue from output queue q2 . pop (); // Pop from stack while top matches q2 front while ( ! st . empty () && ! q2 . empty () && st . top () == q2 . front ()) { st . pop (); q2 . pop (); } } else { st . push ( ele ); } } return q2 . empty (); } int main () { vector < int > a = { 1 2 3 }; vector < int > b = { 3 2 1 }; if ( checkPerm ( a b )) cout < < 'true' < < endl ; else cout < < 'false' < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.LinkedList ; import java.util.Queue ; import java.util.Stack ; public class GfG { static boolean checkPerm ( int [] a int [] b ) { Queue < Integer > q1 = new LinkedList <> (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < a . length ; i ++ ) q1 . add ( a [ i ] ); Queue < Integer > q2 = new LinkedList <> (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < b . length ; i ++ ) q2 . add ( b [ i ] ); Stack < Integer > st = new Stack <> (); // Dequeue all items one by one while ( ! q1 . isEmpty ()) { int ele = q1 . poll (); if ( ele == q2 . peek ()) { // If matches dequeue from output queue q2 . poll (); // Pop from stack while top matches q2 front while ( ! st . isEmpty () && ! q2 . isEmpty () && st . peek () == q2 . peek ()) { st . pop (); q2 . poll (); } } else { st . push ( ele ); } } return q2 . isEmpty (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] a = { 1 2 3 }; int [] b = { 3 2 1 }; if ( checkPerm ( a b )) System . out . println ( 'true' ); else System . out . println ( 'false' ); } }
Python from collections import deque def checkPerm ( a b ): q1 = deque ( a ) q2 = deque ( b ) st = [] # Dequeue all items one by one while q1 : ele = q1 . popleft () if ele == q2 [ 0 ]: # If matches dequeue from output queue q2 . popleft () # Pop from stack while top matches q2 front while st and q2 and st [ - 1 ] == q2 [ 0 ]: st . pop () q2 . popleft () else : st . append ( ele ) return not q2 if __name__ == '__main__' : a = [ 1 2 3 ] b = [ 3 2 1 ] if checkPerm ( a b ): print ( 'true' ) else : print ( 'false' )
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; public class GfG { static bool checkPerm ( int [] a int [] b ) { Queue < int > q1 = new Queue < int > ( a ); Queue < int > q2 = new Queue < int > ( b ); Stack < int > st = new Stack < int > (); // Dequeue all items one by one while ( q1 . Count > 0 ) { int ele = q1 . Dequeue (); if ( ele == q2 . Peek ()) { // If matches dequeue from output queue q2 . Dequeue (); // Pop from stack while top matches q2 front while ( st . Count > 0 && q2 . Count > 0 && st . Peek () == q2 . Peek ()) { st . Pop (); q2 . Dequeue (); } } else { st . Push ( ele ); } } return q2 . Count == 0 ; } public static void Main () { int [] a = { 1 2 3 }; int [] b = { 3 2 1 }; if ( checkPerm ( a b )) Console . WriteLine ( 'true' ); else Console . WriteLine ( 'false' ); } }
JavaScript function checkPerm ( a b ) { // simulate queue with array let q1 = a ; // simulate queue with array let q2 = b ; let st = []; // pointer for front of q1 let front1 = 0 ; // pointer for front of q2 let front2 = 0 ; while ( front1 < q1 . length ) { let ele = q1 [ front1 ]; front1 ++ ; if ( ele === q2 [ front2 ]) { front2 ++ ; // Pop from stack while top matches q2 front while ( st . length > 0 && st [ st . length - 1 ] === q2 [ front2 ]) { st . pop (); front2 ++ ; } } else { st . push ( ele ); } } return front2 === q2 . length ; } // Driver Code let a = [ 1 2 3 ]; let b = [ 3 2 1 ]; console . log ( checkPerm ( a b ));
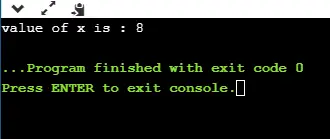
Produzione
true
[Approccio previsto] Simulazione Push e Pop - O(n) tempo e O(n) spazio
In questo approccio in realtà non creiamo code né modifichiamo gli array di input. Invece simuliamo direttamente le operazioni push e pop su uno stack.
Ogni elemento di a[] viene inserito nello stack uno per uno. Dopo ogni push controlliamo se la parte superiore dello stack corrisponde all'elemento corrente di b[]. Se lo fa, lo estraiamo dallo stack e andiamo avanti in b[]. Questo processo si ripete finché tutti gli elementi di a[] non sono stati inseriti e controllati. Se alla fine tutti gli elementi di b[] sono stati abbinati e spuntati con successo, la permutazione è valida (restituisce true); altrimenti non è valido (restituisce falso).
C++ #include #include #include using namespace std ; bool checkPerm ( vector < int >& a vector < int >& b ) { stack < int > st ; int j = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < a . size (); i ++ ) { // Push top of a[] to stack st . push ( a [ i ]); // Keep popping from stack while it // matches front of the output queue while ( ! st . empty () && st . top () == b [ j ]) { st . pop (); j ++ ; } } return ( j == b . size ()); } int main () { vector < int > a = { 1 2 3 }; vector < int > b = { 2 1 3 }; cout < < ( checkPerm ( a b ) ? 'true' : 'false' ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Stack ; public class GfG { static boolean checkPerm ( int [] a int [] b ) { Stack < Integer > st = new Stack <> (); int j = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < a . length ; i ++ ) { // Push top of a[] to stack st . push ( a [ i ] ); // Keep popping from stack while it // matches front of the output array while ( ! st . isEmpty () && st . peek (). equals ( b [ j ] )) { st . pop (); j ++ ; } } return ( j == b . length ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] a = { 1 2 3 }; int [] b = { 2 1 3 }; System . out . println ( checkPerm ( a b ) ? 'true' : 'false' ); } }
Python def checkPerm ( a b ): st = [] j = 0 for i in range ( len ( a )): # Push top of a[] to stack st . append ( a [ i ]) # Keep popping from stack while it # matches front of the output queue while st and st [ - 1 ] == b [ j ]: st . pop () j += 1 return j == len ( b ) if __name__ == '__main__' : a = [ 1 2 3 ] b = [ 2 1 3 ] print ( 'true' if checkPerm ( a b ) else 'false' )
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { static bool checkPerm ( int [] a int [] b ) { Stack < int > stack = new Stack < int > (); int j = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < a . Length ; i ++ ) { // Push top of a[] to stack stack . Push ( a [ i ]); // Keep popping from stack while it matches b[j] while ( stack . Count > 0 && stack . Peek () == b [ j ]) { stack . Pop (); j ++ ; } } return j == b . Length ; } static void Main () { int [] a = { 1 2 3 }; int [] b = { 2 1 3 }; Console . WriteLine ( checkPerm ( a b ) ? 'true' : 'false' ); } }
JavaScript function checkPerm ( a b ) { const stack = []; let j = 0 ; for ( let i = 0 ; i < a . length ; i ++ ) { // Push top of a[] to stack stack . push ( a [ i ]); // Keep popping from stack while it // matches front of the output queue while ( stack . length > 0 && stack [ stack . length - 1 ] === b [ j ]) { stack . pop (); j ++ ; } } return j === b . length ; } //Driven Code const a = [ 1 2 3 ]; const b = [ 2 1 3 ]; console . log ( checkPerm ( a b ) ? 'true' : 'false' );
Produzione
trueCrea quiz