Ricerca nell'albero di ricerca binario (BST)
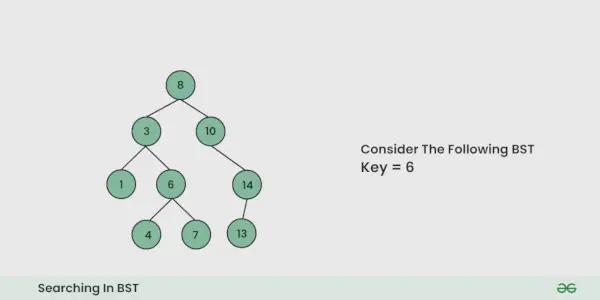
Dato un BST , il compito è cercare un nodo in questo BST .
Per cercare un valore in BST, consideralo come un array ordinato. Ora possiamo eseguire facilmente operazioni di ricerca in BST utilizzando Algoritmo di ricerca binaria .
Algoritmo per cercare una chiave in un dato albero di ricerca binario:
Diciamo che vogliamo cercare il numero X, Iniziamo dalla radice. Poi:
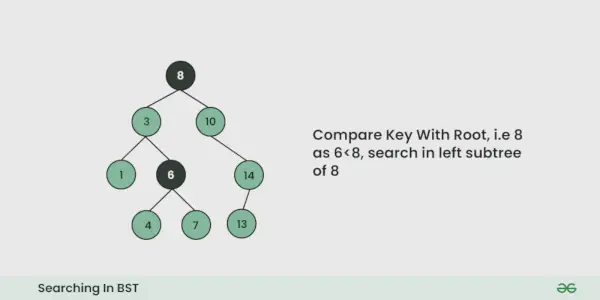
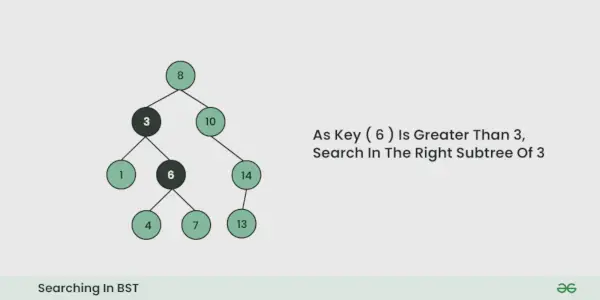
- Confrontiamo il valore da cercare con il valore della radice.
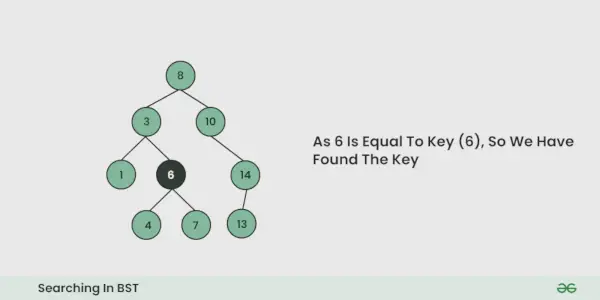
- Se è uguale abbiamo finito con la ricerca, se è più piccolo sappiamo che dobbiamo andare al sottoalbero di sinistra perché in un albero di ricerca binario tutti gli elementi nel sottoalbero di sinistra sono più piccoli e tutti gli elementi nel sottoalbero di destra sono più grandi.
- Ripetere il passaggio precedente fino a quando non sarà più possibile attraversare
- Se ad ogni iterazione viene trovata la chiave, restituisce True. Altrimenti falso.
Illustrazione della ricerca in un BST:
Vedere l'illustrazione qui sotto per una migliore comprensione:
Pratica consigliataCerca un nodo in BSTTry It!

Programma per implementare la ricerca in BST:
C++
// C++ function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> using> namespace> std;> struct> node {> > int> key;> > struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(> int> item)> {> > struct> node* temp> > => new> struct> node;> > temp->chiave = oggetto;> > temp->sinistra = temp->destra = NULL;> > return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(> struct> node* node,> int> key)> {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> newNode(key);> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key key)> > node->sinistra = inserisci(nodo->sinistra, chiave);> > else> if> (key>nodo->chiave)> > node->destra = inserisci(nodo->destra, chiave);> > // Return the (unchanged) node pointer> > return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(> struct> node* root,> int> key)> > > // Base Cases: root is null or key is present at root> > if> (root == NULL> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> > struct> node* root = NULL;> > root = insert(root, 50);> > insert(root, 30);> > insert(root, 20);> > insert(root, 40);> > insert(root, 70);> > insert(root, 60);> > insert(root, 80);> > // Key to be found> > int> key = 6;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > cout < < key < <> ' not found'> < < endl;> > else> > cout < < key < <> ' found'> < < endl;> > key = 60;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > cout < < key < <> ' not found'> < < endl;> > else> > cout < < key < <> ' found'> < < endl;> > return> 0;> }> |
C
// C function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> #include> struct> node {> > int> key;> > struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(> int> item)> {> > struct> node* temp> > = (> struct> node*)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> struct> node));> > temp->chiave = oggetto;> > temp->sinistra = temp->destra = NULL;> > return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(> struct> node* node,> int> key)> {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> newNode(key);> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key key)> > node->sinistra = inserisci(nodo->sinistra, chiave);> > else> if> (key>nodo->chiave)> > node->destra = inserisci(nodo->destra, chiave);> > // Return the (unchanged) node pointer> > return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(> struct> node* root,> int> key)> > // Driver Code> int> main()> {> > struct> node* root = NULL;> > root = insert(root, 50);> > insert(root, 30);> > insert(root, 20);> > insert(root, 40);> > insert(root, 70);> > insert(root, 60);> > insert(root, 80);> > // Key to be found> > int> key = 6;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > printf> (> '%d not found
'> , key);> > else> > printf> (> '%d found
'> , key);> > key = 60;> > // Searching in a BST> > if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> > printf> (> '%d not found
'> , key);> > else> > printf> (> '%d found
'> , key);> > return> 0;> }> |
Giava
// Java program to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node {> > int> key;> > Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item) {> > key = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> class> BinarySearchTree {> > Node root;> > // Constructor> > BinarySearchTree() {> > root => null> ;> > }> > // A utility function to insert> > // a new node with given key in BST> > Node insert(Node node,> int> key) {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node ==> null> ) {> > node => new> Node(key);> > return> node;> > }> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>nodo.chiave) nodo.destra = insert(nodo.destra, chiave); // Restituisce il puntatore del nodo (invariato) return node; } // Funzione di utilità per cercare una chiave in una ricerca nodo BST (Node root, int key) // Codice driver public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree(); // Inserimento dei nodi tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); albero.insert(albero.root, 30); albero.insert(albero.root, 20); albero.insert(albero.root, 40); albero.insert(albero.root, 70); albero.insert(albero.root, 60); albero.insert(albero.root, 80); // Chiave da trovare int key = 6; // Ricerca in un BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' notfound'); altrimenti System.out.println(chiave + ' trovato'); chiave = 60; // Ricerca in un BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' notfound'); altrimenti System.out.println(tasto + ' trovato'); } }> |
Python3
# Python3 function to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node:> > # Constructor to create a new node> > def> __init__(> self> , key):> > self> .key> => key> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # A utility function to insert> # a new node with the given key in BST> def> insert(node, key):> > # If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> node> is> None> :> > return> Node(key)> > # Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> key node.left = insert(node.left, key) elif key>node.key: node.right = insert(node.right, key) # Restituisce il puntatore del nodo (invariato) return node # Funzione di utilità per cercare una chiave in un BST def search(root, key): # Base Cases: root is null o chiave è presente su root se root è None o root.key == key: return root # La chiave è maggiore della chiave di root se root.key return search(root.right, key) # La chiave è più piccola di root 's key return search(root.left, key) # Codice driver if __name__ == '__main__': root = Nessuno root = insert(root, 50) insert(root, 30) insert(root, 20) insert (root, 40) insert(root, 70) insert(root, 60) insert(root, 80) # Chiave da trovare key = 6 # Ricerca in un BST se search(root, key) è None: print(key, 'non trovato') else: print(chiave, 'trovato') key = 60 # Ricerca in un BST se search(root, chiave) è None: print(chiave, 'non trovato') else: print(chiave, 'trovato')> |
C#
// C# function to search a given key in a given BST> using> System;> public> class> Node {> > public> int> key;> > public> Node left, right;> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> > // A utility function to create a new BST node> > public> Node NewNode(> int> item)> > {> > Node temp => new> Node();> > temp.key = item;> > temp.left = temp.right => null> ;> > return> temp;> > }> > // A utility function to insert> > // a new node with given key in BST> > public> Node Insert(Node node,> int> key)> > {> > // If the tree is empty, return a new node> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> NewNode(key);> > // Otherwise, recur down the tree> > if> (key node.left = Insert(node.left, key); else if (key>nodo.chiave) nodo.destra = Inserisci(nodo.destra, chiave); // Restituisce il puntatore del nodo (invariato) return node; } // Funzione di utilità per cercare una chiave in un BST public Node Search(Node root, int key) // Casi base: root è null o la chiave è presente alla root se (root == null // Codice driver public static void Main () { Radice del nodo = null; BinaryTree bt = nuovo BinaryTree(); root = bt.Insert(root, 30); , 40); bt.Insert(root, 70); bt.Insert(root, 60); bt.Insert(root, 80); bt.Search(root, chiave) == null) Console.WriteLine(chiave + ' non trovato'); else Console.WriteLine(chiave + ' trovato' chiave = 60; if (bt.Search(root, chiave) == null) Console.WriteLine(chiave + ' non trovato'); else Console.WriteLine(chiave + ' trovato'); |
>
// Javascript function to search a given key in a given BST>class Node {>>constructor(key) {>>this>.key = key;>>this>.left =>null>;>>this>.right =>null>;>>}>}>// A utility function to insert>// a new node with given key in BST>function>insert(node, key) {>>// If the tree is empty, return a new node>>if>(node ===>null>) {>>return>new>Node(key);>>}>>// Otherwise, recur down the tree>>if>(key node.left = insert(node.left, key); } else if (key>nodo.chiave) { nodo.destra = insert(nodo.destra, chiave); } // Restituisce il puntatore del nodo (invariato) return node; } // Funzione di utilità per cercare una chiave in una funzione BST search(root, key) { // Casi base: root è null o la chiave è presente alla root se (root === null || root.key === key ) { restituisce radice; } // La chiave è maggiore della chiave di root if (root.key return search(root.right, key); } // La chiave è più piccola della chiave di root return search(root.left, key); } // Codice driver let root = null; insert(root, 50); insert(root, 20); insert(root, 70); 60); insert(root, 80); // Chiave da trovare let key = 6; // Ricerca in un BST if (search(root, key) === null) { console.log(key + ' not find'); } else { console.log(key + 'found'); } key = 60; // Ricerca in un BST if (search(root, key) === null) { console.log( chiave + ' non trovato'); } else { console.log(chiave + ' trovato');
>
Complessità temporale: O(h), dove h è l'altezza della BST.
Spazio ausiliario: O(h), dove h è l'altezza della BST. Questo perché la quantità massima di spazio necessaria per archiviare lo stack di ricorsione sarebbe H .Link correlati:
- Operazione di inserimento dell'albero di ricerca binario
- Operazione di eliminazione dell'albero di ricerca binaria