Salva il file json in Python
Python consente la manipolazione dei file (crea, salva, leggi, scrivi, elimina file e molto altro). Python semplifica il salvataggio di numerosi formati di file e salva diversi formati di file.
JSON lo è Notazione oggetto JavaScript . I dati vengono archiviati e inviati tramite un file di script (eseguibile) in linguaggio informatico basato su testo.
Il modulo json di Python supporta JSON. JSON utilizza una stringa tra virgolette con mappatura del valore-chiave all'interno della parentesi graffa { }.
Passaggi per salvare il file json
Esistono i seguenti passaggi per creare e salvare file json:
1. Importa il pacchetto json
import json
2. Scrivi i dati json in formato hash
Json_value ={ 'best_student': { 'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2' }, } 3. Crea un file json e utilizza la modalità 'w' (scrittura) per salvare dati e file.
save_file = open('filename', 'w')
4. Utilizzare il metodo json.dump per connettere file e dati json.
5. Chiudere il file.
save_file.close()
Esempi
L'esempio seguente mostra il salvataggio del file json in Python.
Esempio 1
L'esempio Python fornito salva i dati dell'oggetto nel file json. Sono dati di base per convertire il file in json e salvarlo in un file. L'esempio mostra dati a variabile singola da salvare nel file json.
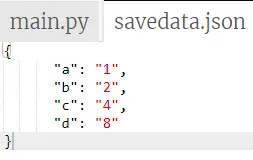
import json # python objects can store in json format value ={ 'a': '1', 'b': '2', 'c': '4', 'd': '8' } # the json file to save the output data save_file = open('savedata.json', 'w') json.dump(value, save_file, indent = 6) save_file.close() Produzione:
L'immagine seguente mostra il file json e il valore dell'oggetto in formato json.

Esempio n.2
L'esempio Python fornito salva i dati dell'oggetto nel file json. In questo esempio, possiamo utilizzare il valore intero e quello stringa in un singolo oggetto e visualizzarli nel file json.
import json # python objects can store in json format value ={ 'best_student': { 'name': 'Ram', 'subject': 'python', 'age': '24', 'marks': '98' }, } # the json file to save the output data save_file = open('savedata.json', 'w') json.dump(value, save_file, indent = 6) save_file.close() Produzione
L'immagine seguente mostra il file json e il valore dell'oggetto in formato json.

Esempio n.3
L'esempio Python fornito salva i dati dell'oggetto nel file json. Qui possiamo utilizzare più oggetti e i relativi dati per convertirli in file json e salvarli utilizzando Python.
import json # python objects can store in json format Topper_student ={ 'student1': { 'name': 'Ram', 'subject': 'python', 'age': '24', 'marks': '98' }, 'student2': { 'name': 'sam', 'subject': 'Java', 'age': '24', 'marks': '92' }, 'student3': { 'name': 'Radha', 'subject': 'Html', 'age': '24', 'marks': '96' }, } # the json file to save the output data save_file = open('savedata.json', 'w') json.dump(Topper_student, save_file, indent = 6) save_file.close() Produzione
L'immagine seguente mostra il file json e il valore dell'oggetto in formato json.

Esempio n.4
L'esempio Python fornito salva i dati dell'oggetto nel file json. Qui possiamo vedere il valore dell'oggetto senza nome e utilizzando il formato array per i valori.
import json # python objects can store in json format value =[{ 'a': '1', 'b': '2', 'c': '4', 'd': '8' }, { 'a1': '11', 'b1': '21', 'c1': '41', 'd1': '18' }, { 'a2': '21', 'b2': '22', 'c2': '42', 'd2': '28' }] # the json file to save the output data save_file = open('savedata.json', 'w') json.dump(value, save_file, indent = 6) save_file.close() produzione
l'immagine seguente mostra il file json e il valore dell'oggetto in formato json.

Esempio n.5
L'esempio Python fornito salva i dati dell'oggetto nel file json. Possiamo utilizzare diversi oggetti e il loro nome come dati in formato hash. In questo esempio, possiamo creare due file Json per oggetti diversi.
import json # python objects can store in json format Topper_student =[{ 'a': '1', 'b': '2', 'c': '4', 'd': '8' }, { 'a1': '11', 'b1': '21', 'c1': '41', 'd1': '18' }] value = { 'a2': '21', 'b2': '22', 'c2': '42', 'd2': '28' } # the json file to save the output data save_file = open('savedata.json', 'w') save_file1 = open('save.json', 'w') json.dump(Topper_student, save_file, indent = 6) json.dump(value, save_file1, indent = 6) save_file.close() save_file1.close()# the json file to save the output data save_file = open('savedata.json', 'w') save_file1 = open('save.json', 'w') json.dump(Topper_student, save_file, indent = 6) json.dump(Topper_student, save_file1, indent = 6) save_file.close() save_file1.close() Produzione
L'immagine seguente mostra il file json e il valore dell'oggetto in formato json.

Conclusione
Possiamo salvare file json utilizzando il linguaggio Python con dati oggetto. Python memorizza i dati degli oggetti nel file json dopo averli convertiti in un formato hash. Questi dati sono contenuti nel file e archiviati sul desktop dell'utente.