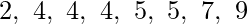Elenco di inoltro in C++ | Set 2 (funzioni di manipolazione)
Elenco di inoltro in C++ | Set 1 (Introduzione e funzioni importanti) Altre funzioni sono discusse in questo articolo. Alcune delle operazioni diverse dagli inserimenti e dalle eliminazioni che possono essere utilizzate negli elenchi di inoltro sono le seguenti:
1. unisci() :- Questa funzione viene utilizzata per unire una lista di inoltro con un'altra. Se entrambi gli elenchi vengono ordinati, viene ordinato anche l'elenco risultante restituito.
2. operatore '=' :- Questo operatore copia una lista di inoltro in un'altra. La copia effettuata in questo caso è una copia profonda.
CPP // C++ code to demonstrate the working of // merge() and operator= #include #include using namespace std ; int main () { // Initializing 1st forward list forward_list < int > flist1 = { 1 2 3 }; // Declaring 2nd forward list forward_list < int > flist2 ; // Creating deep copy using '=' flist2 = flist1 ; // Displaying flist2 cout < < 'The contents of 2nd forward list' ' after copy are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist2 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; // Using merge() to merge both list in 1 flist1 . merge ( flist2 ); // Displaying merged forward list // Prints sorted list cout < < 'The contents of forward list ' 'after merge are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Produzione:
The contents of 2nd forward list after copy are : 1 2 3 The contents of forward list after merge are : 1 1 2 2 3 3
Complessità temporale: O(1)
Spazio ausiliario: O(1)
3. ordinare() :- Questa funzione viene utilizzata per ordinare l'elenco di inoltro.
4. unico() :- Questa funzione elimina le occorrenze multiple di un numero e restituisce un elenco in avanti con elementi univoci. L'elenco di inoltro deve essere ordinato affinché questa funzione venga eseguita correttamente.
CPP // C++ code to demonstrate the working of // sort() and unique() #include #include // for sort() and unique() using namespace std ; int main () { // Initializing 1st forward list forward_list < int > flist1 = { 1 2 3 2 3 3 1 }; // Sorting the forward list using sort() flist1 . sort (); // Displaying sorted forward list cout < < 'The contents of forward list after ' 'sorting are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; // Use of unique() to remove repeated occurrences flist1 . unique (); // Displaying forward list after using unique() cout < < 'The contents of forward list after ' 'unique operation are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Produzione:
The contents of forward list after sorting are : 1 1 2 2 3 3 3 The contents of forward list after unique operation are : 1 2 3
Complessità temporale: O(1)
Spazio ausiliario: O(1)
5. inversione() :- Questa funzione viene utilizzata per invertire l'elenco di inoltro.
6. scambio() :- Questa funzione scambia il contenuto di una lista di inoltro con un'altra.
CPP // C++ code to demonstrate the working of // reverse() and swap() #include #include // for reverse() and swap() using namespace std ; int main () { // Initializing 1st forward list forward_list < int > flist1 = { 1 2 3 }; // Initializing 2nd forward list forward_list < int > flist2 = { 4 5 6 }; // Using reverse() to reverse 1st forward list flist1 . reverse (); // Displaying reversed forward list cout < < 'The contents of forward list after' ' reversing are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl < < endl ; // Displaying forward list before swapping cout < < 'The contents of 1st forward list ' 'before swapping are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; cout < < 'The contents of 2nd forward list ' 'before swapping are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist2 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; // Use of swap() to swap the list flist1 . swap ( flist2 ); // Displaying forward list after swapping cout < < 'The contents of 1st forward list ' 'after swapping are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; cout < < 'The contents of 2nd forward list ' 'after swapping are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist2 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Produzione:
The contents of forward list after reversing are : 3 2 1 The contents of 1st forward list before swapping are : 3 2 1 The contents of 2nd forward list before swapping are : 4 5 6 The contents of 1st forward list after swapping are : 4 5 6 The contents of 2nd forward list after swapping are : 3 2 1
Complessità temporale: O(1)
Spazio ausiliario: O(1)
7. chiaro() :- Questa funzione cancella il contenuto dell'elenco di inoltro. Dopo questa funzione l'elenco di inoltro diventa vuoto.
8. vuoto() :- Questa funzione restituisce vero se la lista è vuota altrimenti falso.
CPP // C++ code to demonstrate the working of // clear() and empty() #include #include // for clear() and empty() using namespace std ; int main () { // Initializing forward list forward_list < int > flist1 = { 1 2 3 }; // Displaying forward list before clearing cout < < 'The contents of forward list are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; // Using clear() to clear the forward list flist1 . clear (); // Displaying list after clear() performed cout < < 'The contents of forward list after ' < < 'clearing are : ' ; for ( int & x : flist1 ) cout < < x < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; // Checking if list is empty flist1 . empty () ? cout < < 'Forward list is empty' : cout < < 'Forward list is not empty' ; return 0 ; }
Produzione:
The contents of forward list are : 1 2 3 The contents of forward list after clearing are : Forward list is empty
Complessità temporale: O(1)
Spazio ausiliario: O(1)
Articoli recenti su forward_list