Teoria dei giochi combinatori | Set 4 (Teorema di Sprague - Grundy)
Prerequisiti: Numeri Grundy/Numeri e Mex
Abbiamo già visto nel Set 2 (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/combinatorial-game-theory-set-2-game-nim/) che possiamo scoprire chi vince in una partita di Nim senza effettivamente giocare.
Supponiamo di cambiare un po' il classico gioco Nim. Questa volta ogni giocatore può rimuovere solo 1, 2 o 3 pietre (e non un numero qualsiasi di pietre come nel classico gioco di Nim). Possiamo prevedere chi vincerà?
Sì, possiamo prevedere il vincitore usando il teorema di Sprague-Grundy.
Cos'è il teorema di Sprague-Grundy?
Supponiamo che esista un gioco composito (più di un sottogioco) composto da N sottogiochi e due giocatori A e B. Allora il Teorema di Sprague-Grundy dice che se sia A che B giocano in modo ottimale (cioè non commettono errori), allora il giocatore che inizia per primo ha la certezza di vincere se lo XOR dei numeri grossolani di posizione in ciascun sottogioco all'inizio del gioco è diverso da zero. Altrimenti, se lo XOR vale zero, il giocatore A perderà definitivamente, qualunque cosa accada.
Come applicare il teorema di Sprague Grundy?
Possiamo applicare il teorema di Sprague-Grundy a qualsiasi gioco imparziale e risolverlo. I passaggi fondamentali sono elencati come segue:
- Suddividi il gioco composito in sottogiochi.
- Quindi per ogni sottogioco calcola il numero Grundy in quella posizione.
- Quindi calcola lo XOR di tutti i numeri Grundy calcolati.
- Se il valore XOR è diverso da zero, allora il giocatore che effettuerà il turno (il primo giocatore) vincerà, altrimenti sarà destinato a perdere, qualunque cosa accada.
Gioco di esempio: Il gioco inizia con 3 pile contenenti 3, 4 e 5 pietre e il giocatore che effettua la mossa può prendere qualsiasi numero positivo di pietre fino a 3 solo da qualsiasi pila [a condizione che la pila contenga quella quantità di pietre]. Vince l'ultimo giocatore che si muove. Quale giocatore vince la partita supponendo che entrambi i giocatori giochino in modo ottimale?
Come sapere chi vincerà applicando il teorema di Sprague-Grundy?
Come possiamo vedere, questo gioco è esso stesso composto da diversi sottogiochi.
Primo passo: I sottogiochi possono essere considerati come pile ciascuna.
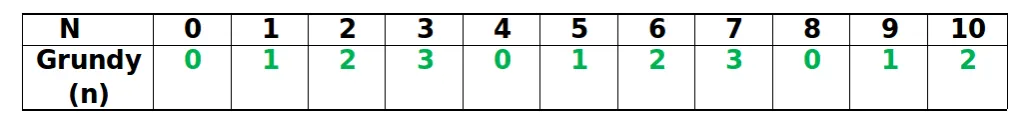
Secondo passo: Lo vediamo dalla tabella seguente
Grundy(3) = 3 Grundy(4) = 0 Grundy(5) = 1

Abbiamo già visto come calcolare i Numeri Grundy di questo gioco nel precedente articolo.
Terzo passo: Lo XOR di 3 0 1 = 2
Quarto passo: Poiché XOR è un numero diverso da zero, possiamo dire che vincerà il primo giocatore.
Di seguito è riportato il programma che implementa i 4 passaggi precedenti.
C++ /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ #include using namespace std ; /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ #define PLAYER1 1 #define PLAYER2 2 // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set int calculateMex ( unordered_set < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . find ( Mex ) != Set . end ()) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy []) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != -1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); unordered_set < int > Set ; // A Hash Table for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . insert ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) printf ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else printf ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); } return ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main () { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = sizeof ( piles ) / sizeof ( piles [ 0 ]); // Find the maximum element int maximum = * max_element ( piles piles + n ); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [ maximum + 1 ]; memset ( Grundy -1 sizeof ( Grundy )); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n -1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ return ( 0 ); }
Java import java.util.* ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; static int PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < Integer > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int Grundy [] ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ] ); // A Hash Table HashSet < Integer > Set = new HashSet < Integer > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ] ); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int piles [] int Grundy [] int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]] ; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]] ; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) System . out . printf ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else System . out . printf ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Test Case 1 int piles [] = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = Arrays . stream ( piles ). max (). getAsInt (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [] = new int [ maximum + 1 ] ; Arrays . fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3 ''' Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing''' PLAYER1 = 1 PLAYER2 = 2 # A Function to calculate Mex of all # the values in that set def calculateMex ( Set ): Mex = 0 ; while ( Mex in Set ): Mex += 1 return ( Mex ) # A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' def calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ): Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ): return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A Hash Table Set = set () for i in range ( 1 4 ): Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )) # Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ) return ( Grundy [ n ]) # A function to declare the winner of the game def declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ): xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for i in range ( 1 n ): xorValue = ( xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]) if ( xorValue != 0 ): if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ): print ( 'Player 2 will win n ' ); else : print ( 'Player 1 will win n ' ); # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : # Test Case 1 piles = [ 3 4 5 ] n = len ( piles ) # Find the maximum element maximum = max ( piles ) # An array to cache the sub-problems so that # re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided Grundy = [ - 1 for i in range ( maximum + 1 )]; # Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for i in range ( n ): calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); ''' Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); ''' # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# using System ; using System.Linq ; using System.Collections.Generic ; /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ class GFG { /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ static int PLAYER1 = 1 ; //static int PLAYER2 = 2; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set static int calculateMex ( HashSet < int > Set ) { int Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . Contains ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' static int calculateGrundy ( int n int [] Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table HashSet < int > Set = new HashSet < int > (); for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . Add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game static void declareWinner ( int whoseTurn int [] piles int [] Grundy int n ) { int xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) Console . Write ( 'Player 2 will winn' ); else Console . Write ( 'Player 1 will winn' ); } return ; } // Driver code static void Main () { // Test Case 1 int [] piles = { 3 4 5 }; int n = piles . Length ; // Find the maximum element int maximum = piles . Max (); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int [] Grundy = new int [ maximum + 1 ]; Array . Fill ( Grundy - 1 ); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( int i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ } } // This code is contributed by mits
JavaScript < script > /* Game Description- 'A game is played between two players and there are N piles of stones such that each pile has certain number of stones. On his/her turn a player selects a pile and can take any non-zero number of stones upto 3 (i.e- 123) The player who cannot move is considered to lose the game (i.e. one who take the last stone is the winner). Can you find which player wins the game if both players play optimally (they don't make any mistake)? ' A Dynamic Programming approach to calculate Grundy Number and Mex and find the Winner using Sprague - Grundy Theorem. */ /* piles[] -> Array having the initial count of stones/coins in each piles before the game has started. n -> Number of piles Grundy[] -> Array having the Grundy Number corresponding to the initial position of each piles in the game The piles[] and Grundy[] are having 0-based indexing*/ let PLAYER1 = 1 ; let PLAYER2 = 2 ; // A Function to calculate Mex of all the values in that set function calculateMex ( Set ) { let Mex = 0 ; while ( Set . has ( Mex )) Mex ++ ; return ( Mex ); } // A function to Compute Grundy Number of 'n' function calculateGrundy ( n Grundy ) { Grundy [ 0 ] = 0 ; Grundy [ 1 ] = 1 ; Grundy [ 2 ] = 2 ; Grundy [ 3 ] = 3 ; if ( Grundy [ n ] != - 1 ) return ( Grundy [ n ]); // A Hash Table let Set = new Set (); for ( let i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i ++ ) Set . add ( calculateGrundy ( n - i Grundy )); // Store the result Grundy [ n ] = calculateMex ( Set ); return ( Grundy [ n ]); } // A function to declare the winner of the game function declareWinner ( whoseTurn piles Grundy n ) { let xorValue = Grundy [ piles [ 0 ]]; for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) xorValue = xorValue ^ Grundy [ piles [ i ]]; if ( xorValue != 0 ) { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); } else { if ( whoseTurn == PLAYER1 ) document . write ( 'Player 2 will win
' ); else document . write ( 'Player 1 will win
' ); } return ; } // Driver code // Test Case 1 let piles = [ 3 4 5 ]; let n = piles . length ; // Find the maximum element let maximum = Math . max (... piles ) // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided let Grundy = new Array ( maximum + 1 ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < maximum + 1 ; i ++ ) Grundy [ i ] = 0 ; // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for ( let i = 0 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++ ) calculateGrundy ( piles [ i ] Grundy ); declareWinner ( PLAYER1 piles Grundy n ); /* Test Case 2 int piles[] = {3 8 2}; int n = sizeof(piles)/sizeof(piles[0]); int maximum = *max_element (piles piles + n); // An array to cache the sub-problems so that // re-computation of same sub-problems is avoided int Grundy [maximum + 1]; memset(Grundy -1 sizeof (Grundy)); // Calculate Grundy Value of piles[i] and store it for (int i=0; i <=n-1; i++) calculateGrundy(piles[i] Grundy); declareWinner(PLAYER2 piles Grundy n); */ // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 < /script>
Produzione :
Player 1 will win
Complessità temporale: O(n^2) dove n è il numero massimo di pietre in una pila.
Complessità spaziale: O(n) poiché l'array Grundy viene utilizzato per memorizzare i risultati dei sottoproblemi per evitare calcoli ridondanti e occupa lo spazio O(n).
Riferimenti:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sprague%E2%80%93Grundy_theorem
Esercizio per i lettori: Considera il gioco qui sotto.
Una partita è giocata da due giocatori con N numeri interi A1 A2 .. AN. Al proprio turno il giocatore sceglie un numero intero lo divide per 2 3 o 6 e poi prende la parola. Se il numero intero diventa 0 viene rimosso. Vince l'ultimo giocatore che si muove. Quale giocatore vince la partita se entrambi i giocatori giocano in modo ottimale?
Suggerimento: vedere l'esempio 3 di precedente articolo.