Analisi asintotica e confronto di algoritmi di ordinamento
È un fatto ben noto che l'ordinamento per unione è più veloce dell'ordinamento per inserimento. Utilizzando analisi asintotica . possiamo dimostrare che il merge sort viene eseguito in tempo O(nlogn) e l'ordinamento per inserimento richiede O(n^2). È ovvio perché il merge sort utilizza un approccio divide et impera risolvendo ricorsivamente i problemi in cui l'ordinamento per inserimento segue un approccio incrementale. Se esaminiamo ulteriormente l’analisi della complessità temporale, scopriremo che l’ordinamento per inserzione non è poi così male. Sorprendentemente l'ordinamento per inserimento batte l'ordinamento per unione su dimensioni di input più piccole. Questo perché ci sono poche costanti che ignoriamo mentre deduciamo la complessità temporale. Su dimensioni di input maggiori dell'ordine 10^4 ciò non influenza il comportamento della nostra funzione. Ma quando le dimensioni dell’input scendono al di sotto, diciamo, di meno di 40, allora le costanti nell’equazione dominano la dimensione dell’input “n”. Fin qui tutto bene. Ma non ero soddisfatto di tale analisi matematica. Come studenti universitari di informatica dobbiamo credere nella scrittura del codice. Ho scritto un programma C per avere un'idea di come gli algoritmi competono tra loro per varie dimensioni di input. E anche il motivo per cui viene eseguita un'analisi matematica così rigorosa per stabilire le complessità del tempo di esecuzione di questi algoritmi di ordinamento.
Attuazione:
CPP #include #include #include #include #define MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY 1000000001 int cmpfunc ( const void * a const void * b ) { // Compare function used by qsort return ( * ( int * ) a - * ( int * ) b ); } int * generate_random_array ( int n ) { srand ( time ( NULL )); int * a = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = rand () % MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ; return a ; } int * copy_array ( int a [] int n ) { int * arr = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) arr [ i ] = a [ i ]; return arr ; } // Code for Insertion Sort void insertion_sort_asc ( int a [] int start int end ) { int i ; for ( i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; ++ i ) { int key = a [ i ]; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; -- j ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Code for Merge Sort void merge ( int a [] int start int end int mid ) { int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; int * aux = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * ( end - start + 1 )); while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; else aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; } while ( i <= mid ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; while ( j <= end ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; j = 0 ; for ( i = start ; i <= end ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = aux [ j ++ ]; free ( aux ); } void _merge_sort ( int a [] int start int end ) { if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; _merge_sort ( a start mid ); _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void merge_sort ( int a [] int n ) { return _merge_sort ( a 0 n - 1 ); } void insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( int a [] int start int end int k ) { // Performs insertion sort if size of array is less than or equal to k // Otherwise uses mergesort if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { return insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ); } int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void test_sorting_runtimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Measuring the runtime of the sorting algorithms int number_of_times = num_of_times ; int t = number_of_times ; int n = size ; double insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 ; double merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 ; while ( t -- ) { clock_t start end ; int * a = generate_random_array ( n ); int * b = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 n - 1 ); end = clock (); insertion_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( b ); int * c = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); merge_sort ( c n ); end = clock (); merge_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( c ); int * d = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 n - 1 40 ); end = clock (); merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( d ); start = clock (); qsort ( a n sizeof ( int ) cmpfunc ); end = clock (); qsort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( a ); } insertion_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= number_of_times ; qsort_time /= number_of_times ; printf ( ' n Time taken to sort: n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f nn ' '(i)Insertion sort: ' insertion_sort_time '(ii)Merge sort: ' merge_sort_time '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time '(iv)Qsort library function: ' qsort_time ); } int main ( int argc char const * argv []) { int t ; scanf ( '%d' & t ); while ( t -- ) { int size num_of_times ; scanf ( '%d %d' & size & num_of_times ); test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ); } return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Scanner ; import java.util.Arrays ; import java.util.Random ; public class SortingAlgorithms { // Maximum element in array static final int MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; public static void main ( String [] args ) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( System . in ); int t = scanner . nextInt (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < t ; i ++ ) { int size = scanner . nextInt (); int num_of_times = scanner . nextInt (); testSortingRuntimes ( size num_of_times ); } scanner . close (); } static int [] generateRandomArray ( int n ) { // Generate an array of n random integers. int [] arr = new int [ n ] ; Random random = new Random (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { arr [ i ] = random . nextInt ( MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ); } return arr ; } static void insertionSortAsc ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for ( int i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { int key = a [ i ] ; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] ; j -- ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } static void merge ( int [] a int start int end int mid ) { // Merge two sorted sublists of a. // The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. int [] aux = new int [ end - start + 1 ] ; int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ] ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } else { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } System . arraycopy ( aux 0 a start aux . length ); } static void mergeSort ( int [] a ) { // Perform an in-place merge sort on a. mergeSortHelper ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } static void mergeSortHelper ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Recursive merge sort function. if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; mergeSortHelper ( a start mid ); mergeSortHelper ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } static void insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( int [] a int start int end int k ) { /* Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. */ if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } static void testSortingRuntimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. double insertionSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; double qsortTime = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < num_of_times ; i ++ ) { int [] a = generateRandomArray ( size ); int [] b = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); long start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); long end = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; int [] c = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSort ( c ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; int [] d = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; int [] e = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); Arrays . sort ( e ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= num_of_times ; qsortTime /= num_of_times ; System . out . println ( 'nTime taken to sort:n' + '(i) Insertion sort: ' + insertionSortTime + 'n' + '(ii) Merge sort: ' + mergeSortTime + 'n' + '(iii) Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' + mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime + 'n' + '(iv) Qsort library function: ' + qsortTime + 'n' ); } }
Python3 import time import random import copy from typing import List # Maximum element in array MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 def generate_random_array ( n : int ) -> List [ int ]: #Generate a list of n random integers. return [ random . randint ( 0 MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ) for _ in range ( n )] def insertion_sort_asc ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for i in range ( start + 1 end + 1 ): key = a [ i ] j = i - 1 while j >= start and a [ j ] > key : a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] j -= 1 a [ j + 1 ] = key def merge ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int mid : int ) -> None : #Merge two sorted sublists of a. #The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. aux = [] i = start j = mid + 1 while i <= mid and j <= end : if a [ i ] <= a [ j ]: aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 else : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 while i <= mid : aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 while j <= end : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 a [ start : end + 1 ] = aux def _merge_sort ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Recursive merge sort function. if start < end : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 _merge_sort ( a start mid ) _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ) merge ( a start end mid ) def merge_sort ( a : List [ int ]) -> None : #Perform an in-place merge sort on a. _merge_sort ( a 0 len ( a ) - 1 ) def insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int k : int ) -> None : ''' Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. ''' if start < end : size = end - start + 1 if size <= k : insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ) else : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ) insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ) merge ( a start end mid ) def test_sorting_runtimes ( size : int num_of_times : int ) -> None : #Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 for _ in range ( num_of_times ): a = generate_random_array ( size ) b = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 len ( b ) - 1 ) end = time . time () insertion_sort_time += end - start c = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () merge_sort ( c ) end = time . time () merge_sort_time += end - start d = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 len ( d ) - 1 40 ) end = time . time () merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += end - start start = time . time () a . sort () end = time . time () qsort_time += end - start insertion_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= num_of_times qsort_time /= num_of_times print ( f ' n Time taken to sort: n ' f '(i)Insertion sort: { insertion_sort_time } n ' f '(ii)Merge sort: { merge_sort_time } n ' f '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: { merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time } n ' f '(iv)Qsort library function: { qsort_time } n ' ) def main () -> None : t = int ( input ()) for _ in range ( t ): size num_of_times = map ( int input () . split ()) test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript // Importing required modules const { performance } = require ( 'perf_hooks' ); // Maximum element in array const MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; // Function to generate a list of n random integers function generateRandomArray ( n ) { return Array . from ({ length : n } () => Math . floor ( Math . random () * MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY )); } // Function to perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end function insertionSortAsc ( a start end ) { for ( let i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { let key = a [ i ]; let j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; j -= 1 ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Function to merge two sorted sublists of a function merge ( a start end mid ) { let aux = []; let i = start ; let j = mid + 1 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } else { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } for ( let i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { a [ i ] = aux [ i - start ]; } } // Recursive merge sort function function _mergeSort ( a start end ) { if ( start < end ) { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); _mergeSort ( a start mid ); _mergeSort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } // Function to perform an in-place merge sort on a function mergeSort ( a ) { _mergeSort ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } // Function to perform an in-place sort on a from start to end function insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start end k ) { if ( start < end ) { let size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } // Function to test the runtime of the sorting algorithms function testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ) { let insertionSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; let qsortTime = 0 ; for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < numOfTimes ; _ ++ ) { let a = generateRandomArray ( size ); let b = [... a ]; let start = performance . now (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); let end = performance . now (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; let c = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); mergeSort ( c ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; let d = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; start = performance . now (); a . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); end = performance . now (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= numOfTimes ; qsortTime /= numOfTimes ; console . log ( `nTime taken to sort:n(i)Insertion sort: ${ insertionSortTime } n(ii)Merge sort: ${ mergeSortTime } n(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ${ mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime } n(iv)Qsort library function: ${ qsortTime } n` ); } // Main function function main () { let t = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of test cases: ' )); for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < t ; _ ++ ) { let size = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the size of the array: ' )); let numOfTimes = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of times to run the test: ' )); testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ); } } // Call the main function main ();
Ho confrontato i tempi di esecuzione dei seguenti algoritmi:
- Ordinamento di inserimento : L'algoritmo tradizionale senza modifiche/ottimizzazione. Funziona molto bene per dimensioni di input più piccole. E sì, batte l'ordinamento di unione
- Va il destino : Segue l'approccio divide et impera. Per dimensioni di input dell'ordine di 10^5 questo algoritmo è la scelta giusta. Rende l'ordinamento per inserimento poco pratico per dimensioni di input così grandi.
- Versione combinata dell'ordinamento per inserimento e dell'ordinamento per unione: Ho modificato leggermente la logica del merge sort per ottenere un tempo di esecuzione considerevolmente migliore per dimensioni di input più piccole. Come sappiamo, merge sort divide il suo input in due metà finché non diventa abbastanza banale ordinare gli elementi. Ma qui quando la dimensione dell'input scende al di sotto di una soglia come 'n' < 40 then this hybrid algorithm makes a call to traditional insertion sort procedure. From the fact that insertion sort runs faster on smaller inputs and merge sort runs faster on larger inputs this algorithm makes best use both the worlds.
- Ordinamento rapido: Non ho implementato questa procedura. Questa è la funzione di libreria qsort() disponibile in . Ho considerato questo algoritmo per conoscere il significato dell'implementazione. Richiede una grande esperienza di programmazione per ridurre al minimo il numero di passaggi e sfruttare al massimo le primitive del linguaggio sottostante per implementare un algoritmo nel miglior modo possibile. Questo è il motivo principale per cui si consiglia di utilizzare le funzioni di libreria. Sono scritti per gestire qualsiasi cosa. Ottimizzano nella massima misura possibile. E prima che mi dimentichi della mia analisi, qsort() funziona in modo incredibilmente veloce praticamente su qualsiasi dimensione di input!
L'analisi:
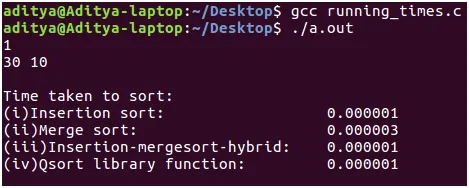
- Ingresso: L'utente deve fornire il numero di volte che desidera testare l'algoritmo corrispondente al numero di casi di test. Per ogni caso di test l'utente deve inserire due numeri interi separati da spazi che indicano la dimensione dell'input 'n' e il 'num_of_times' che indica il numero di volte in cui desidera eseguire l'analisi e calcolare la media. (Chiarimento: se 'num_of_times' è 10, ciascuno degli algoritmi specificati sopra viene eseguito 10 volte e viene presa la media. Questo viene fatto perché l'array di input viene generato in modo casuale corrispondente alla dimensione di input specificata. L'array di input potrebbe essere tutto ordinato. Potrebbe corrispondere al caso peggiore, ovvero l'ordine discendente. Per evitare tempi di esecuzione di tali array di input. L'algoritmo viene eseguito 'num_of_times' e viene presa la media.) routine clock() e la macro CLOCKS_PER_SEC viene utilizzata per misurare il tempo impiegato. Compilazione: ho scritto il codice sopra in ambiente Linux (Ubuntu 16.04 LTS). Copia lo snippet di codice sopra. Compilalo utilizzando la chiave gcc negli input come specificato e ammira la potenza degli algoritmi di ordinamento!
- Risultati: Come puoi vedere per dimensioni di input di piccole dimensioni, l'ordinamento per inserimento batte l'ordinamento per unione di 2 * 10^-6 sec. Ma questa differenza di tempo non è così significativa. D'altra parte l'algoritmo ibrido e la funzione di libreria qsort() funzionano entrambi altrettanto bene dell'ordinamento per inserzione.
 La dimensione dell'input è ora aumentata di circa 100 volte da n = 30 a n = 1000. La differenza è ora tangibile. L'ordinamento per unione viene eseguito 10 volte più velocemente dell'ordinamento per inserimento. C'è ancora un legame tra le prestazioni dell'algoritmo ibrido e la routine qsort(). Ciò suggerisce che qsort() è implementato in un modo più o meno simile al nostro algoritmo ibrido, ovvero passando da un algoritmo all'altro per trarne il meglio.
La dimensione dell'input è ora aumentata di circa 100 volte da n = 30 a n = 1000. La differenza è ora tangibile. L'ordinamento per unione viene eseguito 10 volte più velocemente dell'ordinamento per inserimento. C'è ancora un legame tra le prestazioni dell'algoritmo ibrido e la routine qsort(). Ciò suggerisce che qsort() è implementato in un modo più o meno simile al nostro algoritmo ibrido, ovvero passando da un algoritmo all'altro per trarne il meglio.  Infine la dimensione dell’input viene aumentata a 10^5 (1 Lakh!) che è molto probabilmente la dimensione ideale utilizzata negli scenari pratici. Rispetto al precedente input n = 1000 dove il merge sort batte l'insertion sort correndo 10 volte più velocemente qui la differenza è ancora più significativa. L'ordinamento per unione batte l'ordinamento per inserimento di 100 volte! L'algoritmo ibrido che abbiamo scritto infatti esegue il tradizionale merge sort eseguendo 0,01 secondi più velocemente. E infine qsort() la funzione di libreria ci dimostra finalmente che anche l'implementazione gioca un ruolo cruciale mentre misura meticolosamente i tempi di esecuzione correndo 3 millisecondi più velocemente! :D
Infine la dimensione dell’input viene aumentata a 10^5 (1 Lakh!) che è molto probabilmente la dimensione ideale utilizzata negli scenari pratici. Rispetto al precedente input n = 1000 dove il merge sort batte l'insertion sort correndo 10 volte più velocemente qui la differenza è ancora più significativa. L'ordinamento per unione batte l'ordinamento per inserimento di 100 volte! L'algoritmo ibrido che abbiamo scritto infatti esegue il tradizionale merge sort eseguendo 0,01 secondi più velocemente. E infine qsort() la funzione di libreria ci dimostra finalmente che anche l'implementazione gioca un ruolo cruciale mentre misura meticolosamente i tempi di esecuzione correndo 3 millisecondi più velocemente! :D

Nota: non eseguire il programma precedente con n >= 10^6 poiché richiederà molta potenza di calcolo. Grazie e buona programmazione! :)
Crea quiz