Menetes bináris fa | Beillesztés

Már megbeszéltük a Bináris szálú bináris fa .
A bináris menetes fába történő beillesztés hasonló a bináris fába történő beszúráshoz, de minden elem beillesztése után módosítanunk kell a szálakat.
A bináris szálas csomópont C ábrázolása:
struct Node { struct Node *left *right; int info; // false if left pointer points to predecessor // in Inorder Traversal boolean lthread; // false if right pointer points to successor // in Inorder Traversal boolean rthread; }; A következő magyarázatban figyelembe vettük Bináris keresőfa (BST) a beszúráshoz, mivel a beillesztést bizonyos szabályok határozzák meg a BST-ben.
Hadd tmp legyen az újonnan beillesztett csomópont . A beillesztés során három eset lehet:
1. eset: Beszúrás üres fába
A tmp bal és jobb oldali mutatói NULL-ra lesznek állítva, és az új csomópont lesz a gyökér.
root = tmp; tmp -> left = NULL; tmp -> right = NULL;
2. eset: Amikor új csomópont került be a bal oldali gyermekként
A csomópont megfelelő helyére történő beillesztése után a bal és jobb szálakat a sorrend elődjére, illetve utódjára kell mutatnunk. A csomópont, ami volt rend utódja . Tehát az új csomópont bal és jobb szála lesz-
tmp -> left = par ->left; tmp -> right = par;
A beszúrás előtt a szülő bal mutatója egy szál volt, de beillesztés után az új csomópontra mutató hivatkozás lesz.
par -> lthread = false; par -> left = temp;
A következő példa egy csomópontot a szülő bal oldali gyermekeként szúr be.

A 13 beillesztése után

A 14 elődje a 13 elődjévé válik, így a bal szál 13 pontról 10-re.
A 13 utódja a 14, tehát a 13 pontos jobb oldali szál a bal gyermekhez képest, ami 13.
A 14-es bal mutató nem egy szál, hanem a bal oldali gyermekre mutat, amely 13.
3. eset: Amikor az új csomópont a megfelelő gyermekként kerül beillesztésre
A tmp szülője a rendes elődje. Az a csomópont, amely a szülő sorrendi utódja volt, most ennek a tmp csomópontnak a rendes utódja. Tehát az új csomópont bal és jobb szála lesz-
tmp -> left = par; tmp -> right = par -> right;
A beillesztés előtt a szülő jobb oldali mutatója egy szál volt, de beillesztés után az új csomópontra mutató hivatkozás lesz.
par -> rthread = false; par -> right = tmp;
A következő példa azt mutatja be, hogy egy csomópont a szülőjének megfelelő gyermekeként kerül beillesztésre.

15 beillesztés után

A 14 utódja a 15 utódja lesz, tehát a 15 pont jobb szála 16-hoz
A 15 elődje a 14, tehát a bal szál 15 pontból 14-re.
A 14-es jobb oldali mutató nem egy szál, hanem a 15-ös jobb gyermekre mutat.
C++ implementáció új csomópont beszúrásához a Threaded Binary Search Tree-ba:
Mint szabványos BST betét a kulcsértéket keressük a fában. Ha a kulcs már jelen van, akkor visszatérünk, ellenkező esetben az új kulcsot beszúrjuk arra a pontra, ahol a keresés véget ér. A BST-ben a keresés akkor fejeződik be, amikor megtaláljuk a kulcsot, vagy amikor elérjük a NULL bal vagy jobb mutatót. Itt minden bal és jobb NULL mutatót szálak váltanak fel, kivéve az első csomópont bal mutatóját és az utolsó csomópont jobb oldali mutatóját. Tehát itt a keresés sikertelen lesz, ha elérünk egy NULL mutatót vagy egy szálat.
Végrehajtás:
C++ // Insertion in Threaded Binary Search Tree. #include using namespace std ; struct Node { struct Node * left * right ; int info ; // False if left pointer points to predecessor // in Inorder Traversal bool lthread ; // False if right pointer points to successor // in Inorder Traversal bool rthread ; }; // Insert a Node in Binary Threaded Tree struct Node * insert ( struct Node * root int ikey ) { // Searching for a Node with given value Node * ptr = root ; Node * par = NULL ; // Parent of key to be inserted while ( ptr != NULL ) { // If key already exists return if ( ikey == ( ptr -> info )) { printf ( 'Duplicate Key ! n ' ); return root ; } par = ptr ; // Update parent pointer // Moving on left subtree. if ( ikey < ptr -> info ) { if ( ptr -> lthread == false ) ptr = ptr -> left ; else break ; } // Moving on right subtree. else { if ( ptr -> rthread == false ) ptr = ptr -> right ; else break ; } } // Create a new node Node * tmp = new Node ; tmp -> info = ikey ; tmp -> lthread = true ; tmp -> rthread = true ; if ( par == NULL ) { root = tmp ; tmp -> left = NULL ; tmp -> right = NULL ; } else if ( ikey < ( par -> info )) { tmp -> left = par -> left ; tmp -> right = par ; par -> lthread = false ; par -> left = tmp ; } else { tmp -> left = par ; tmp -> right = par -> right ; par -> rthread = false ; par -> right = tmp ; } return root ; } // Returns inorder successor using rthread struct Node * inorderSuccessor ( struct Node * ptr ) { // If rthread is set we can quickly find if ( ptr -> rthread == true ) return ptr -> right ; // Else return leftmost child of right subtree ptr = ptr -> right ; while ( ptr -> lthread == false ) ptr = ptr -> left ; return ptr ; } // Printing the threaded tree void inorder ( struct Node * root ) { if ( root == NULL ) printf ( 'Tree is empty' ); // Reach leftmost node struct Node * ptr = root ; while ( ptr -> lthread == false ) ptr = ptr -> left ; // One by one print successors while ( ptr != NULL ) { printf ( '%d ' ptr -> info ); ptr = inorderSuccessor ( ptr ); } } // Driver Program int main () { struct Node * root = NULL ; root = insert ( root 20 ); root = insert ( root 10 ); root = insert ( root 30 ); root = insert ( root 5 ); root = insert ( root 16 ); root = insert ( root 14 ); root = insert ( root 17 ); root = insert ( root 13 ); inorder ( root ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program Insertion in Threaded Binary Search Tree. import java.util.* ; public class solution { static class Node { Node left right ; int info ; // False if left pointer points to predecessor // in Inorder Traversal boolean lthread ; // False if right pointer points to successor // in Inorder Traversal boolean rthread ; }; // Insert a Node in Binary Threaded Tree static Node insert ( Node root int ikey ) { // Searching for a Node with given value Node ptr = root ; Node par = null ; // Parent of key to be inserted while ( ptr != null ) { // If key already exists return if ( ikey == ( ptr . info )) { System . out . printf ( 'Duplicate Key !n' ); return root ; } par = ptr ; // Update parent pointer // Moving on left subtree. if ( ikey < ptr . info ) { if ( ptr . lthread == false ) ptr = ptr . left ; else break ; } // Moving on right subtree. else { if ( ptr . rthread == false ) ptr = ptr . right ; else break ; } } // Create a new node Node tmp = new Node (); tmp . info = ikey ; tmp . lthread = true ; tmp . rthread = true ; if ( par == null ) { root = tmp ; tmp . left = null ; tmp . right = null ; } else if ( ikey < ( par . info )) { tmp . left = par . left ; tmp . right = par ; par . lthread = false ; par . left = tmp ; } else { tmp . left = par ; tmp . right = par . right ; par . rthread = false ; par . right = tmp ; } return root ; } // Returns inorder successor using rthread static Node inorderSuccessor ( Node ptr ) { // If rthread is set we can quickly find if ( ptr . rthread == true ) return ptr . right ; // Else return leftmost child of right subtree ptr = ptr . right ; while ( ptr . lthread == false ) ptr = ptr . left ; return ptr ; } // Printing the threaded tree static void inorder ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) System . out . printf ( 'Tree is empty' ); // Reach leftmost node Node ptr = root ; while ( ptr . lthread == false ) ptr = ptr . left ; // One by one print successors while ( ptr != null ) { System . out . printf ( '%d ' ptr . info ); ptr = inorderSuccessor ( ptr ); } } // Driver Program public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node root = null ; root = insert ( root 20 ); root = insert ( root 10 ); root = insert ( root 30 ); root = insert ( root 5 ); root = insert ( root 16 ); root = insert ( root 14 ); root = insert ( root 17 ); root = insert ( root 13 ); inorder ( root ); } } //contributed by Arnab Kundu // This code is updated By Susobhan Akhuli
Python3 # Insertion in Threaded Binary Search Tree. class newNode : def __init__ ( self key ): # False if left pointer points to # predecessor in Inorder Traversal self . info = key self . left = None self . right = None self . lthread = True # False if right pointer points to # successor in Inorder Traversal self . rthread = True # Insert a Node in Binary Threaded Tree def insert ( root ikey ): # Searching for a Node with given value ptr = root par = None # Parent of key to be inserted while ptr != None : # If key already exists return if ikey == ( ptr . info ): print ( 'Duplicate Key !' ) return root par = ptr # Update parent pointer # Moving on left subtree. if ikey < ptr . info : if ptr . lthread == False : ptr = ptr . left else : break # Moving on right subtree. else : if ptr . rthread == False : ptr = ptr . right else : break # Create a new node tmp = newNode ( ikey ) if par == None : root = tmp tmp . left = None tmp . right = None elif ikey < ( par . info ): tmp . left = par . left tmp . right = par par . lthread = False par . left = tmp else : tmp . left = par tmp . right = par . right par . rthread = False par . right = tmp return root # Returns inorder successor using rthread def inorderSuccessor ( ptr ): # If rthread is set we can quickly find if ptr . rthread == True : return ptr . right # Else return leftmost child of # right subtree ptr = ptr . right while ptr . lthread == False : ptr = ptr . left return ptr # Printing the threaded tree def inorder ( root ): if root == None : print ( 'Tree is empty' ) # Reach leftmost node ptr = root while ptr . lthread == False : ptr = ptr . left # One by one print successors while ptr != None : print ( ptr . info end = ' ' ) ptr = inorderSuccessor ( ptr ) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : root = None root = insert ( root 20 ) root = insert ( root 10 ) root = insert ( root 30 ) root = insert ( root 5 ) root = insert ( root 16 ) root = insert ( root 14 ) root = insert ( root 17 ) root = insert ( root 13 ) inorder ( root ) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
C# using System ; // C# program Insertion in Threaded Binary Search Tree. public class solution { public class Node { public Node left right ; public int info ; // False if left pointer points to predecessor // in Inorder Traversal public bool lthread ; // False if right pointer points to successor // in Inorder Traversal public bool rthread ; } // Insert a Node in Binary Threaded Tree public static Node insert ( Node root int ikey ) { // Searching for a Node with given value Node ptr = root ; Node par = null ; // Parent of key to be inserted while ( ptr != null ) { // If key already exists return if ( ikey == ( ptr . info )) { Console . Write ( 'Duplicate Key !n' ); return root ; } par = ptr ; // Update parent pointer // Moving on left subtree. if ( ikey < ptr . info ) { if ( ptr . lthread == false ) { ptr = ptr . left ; } else { break ; } } // Moving on right subtree. else { if ( ptr . rthread == false ) { ptr = ptr . right ; } else { break ; } } } // Create a new node Node tmp = new Node (); tmp . info = ikey ; tmp . lthread = true ; tmp . rthread = true ; if ( par == null ) { root = tmp ; tmp . left = null ; tmp . right = null ; } else if ( ikey < ( par . info )) { tmp . left = par . left ; tmp . right = par ; par . lthread = false ; par . left = tmp ; } else { tmp . left = par ; tmp . right = par . right ; par . rthread = false ; par . right = tmp ; } return root ; } // Returns inorder successor using rthread public static Node inorderSuccessor ( Node ptr ) { // If rthread is set we can quickly find if ( ptr . rthread == true ) { return ptr . right ; } // Else return leftmost child of right subtree ptr = ptr . right ; while ( ptr . lthread == false ) { ptr = ptr . left ; } return ptr ; } // Printing the threaded tree public static void inorder ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) { Console . Write ( 'Tree is empty' ); } // Reach leftmost node Node ptr = root ; while ( ptr . lthread == false ) { ptr = ptr . left ; } // One by one print successors while ( ptr != null ) { Console . Write ( '{0:D} ' ptr . info ); ptr = inorderSuccessor ( ptr ); } } // Driver Program public static void Main ( string [] args ) { Node root = null ; root = insert ( root 20 ); root = insert ( root 10 ); root = insert ( root 30 ); root = insert ( root 5 ); root = insert ( root 16 ); root = insert ( root 14 ); root = insert ( root 17 ); root = insert ( root 13 ); inorder ( root ); } } // This code is contributed by Shrikant13
JavaScript < script > // javascript program Insertion in Threaded Binary Search Tree. class Node { constructor (){ this . left = null this . right = null ; this . info = 0 ; // False if left pointer points to predecessor // in Inorder Traversal this . lthread = false ; // False if right pointer points to successor // in Inorder Traversal this . rthread = false ; } } // Insert a Node in Binary Threaded Tree function insert ( root ikey ) { // Searching for a Node with given value var ptr = root ; var par = null ; // Parent of key to be inserted while ( ptr != null ) { // If key already exists return if ( ikey == ( ptr . info )) { document . write ( 'Duplicate Key !n' ); return root ; } par = ptr ; // Update parent pointer // Moving on left subtree. if ( ikey < ptr . info ) { if ( ptr . lthread == false ) ptr = ptr . left ; else break ; } // Moving on right subtree. else { if ( ptr . rthread == false ) ptr = ptr . right ; else break ; } } // Create a new node var tmp = new Node (); tmp . info = ikey ; tmp . lthread = true ; tmp . rthread = true ; if ( par == null ) { root = tmp ; tmp . left = null ; tmp . right = null ; } else if ( ikey < ( par . info )) { tmp . left = par . left ; tmp . right = par ; par . lthread = false ; par . left = tmp ; } else { tmp . left = par ; tmp . right = par . right ; par . rthread = false ; par . right = tmp ; } return root ; } // Returns inorder successor using rthread function inorderSuccessor ( ptr ) { // If rthread is set we can quickly find if ( ptr . rthread == true ) return ptr . right ; // Else return leftmost child of right subtree ptr = ptr . right ; while ( ptr . lthread == false ) ptr = ptr . left ; return ptr ; } // Printing the threaded tree function inorder ( root ) { if ( root == null ) document . write ( 'Tree is empty' ); // Reach leftmost node var ptr = root ; while ( ptr . lthread == false ) ptr = ptr . left ; // One by one print successors while ( ptr != null ) { document . write ( ptr . info + ' ' ); ptr = inorderSuccessor ( ptr ); } } // Driver Program var root = null ; root = insert ( root 20 ); root = insert ( root 10 ); root = insert ( root 30 ); root = insert ( root 5 ); root = insert ( root 16 ); root = insert ( root 14 ); root = insert ( root 17 ); root = insert ( root 13 ); inorder ( root ); // This code contributed by aashish1995 < /script>
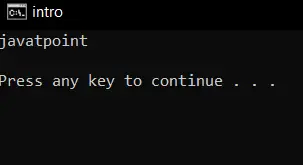
Kimenet
5 10 13 14 16 17 20 30
Időbonyolultság: O(log N)
A tér összetettsége: O(1) mivel nem használnak több helyet.
Kvíz létrehozása