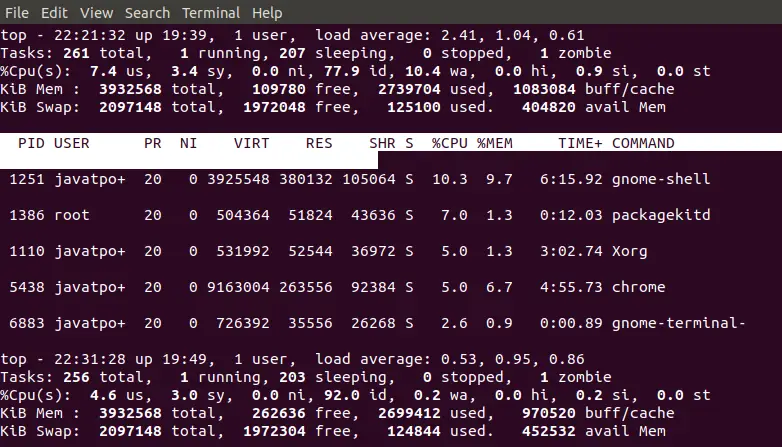
Minimális számú négyzetre vágott papír
Adott egy téglalap alakú papír méretei a x b . A feladat az, hogy az egész papírt a minimális száma négyzet darabok. Bármilyen méretű négyzet alakú darabot választhatunk, de ezeket vágni kell anélkül, hogy átfedne, vagy extra helyet hagyna .
Példák:
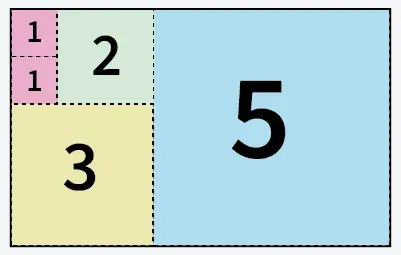
Bemenet: a = 5 b = 8
5 db 5 x 8 méretű papírból kivágott négyzet
Kimenet: 5
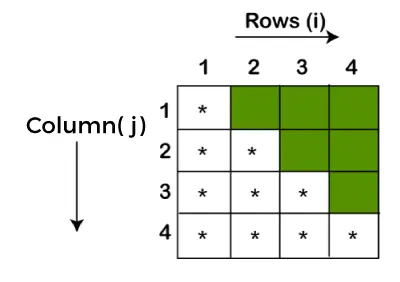
Magyarázat: A papírt 5 négyzetre vághatjuk: 1 négyzet 5x5 1 négyzet 3x3 1 négyzet 2x2 és 2 négyzet 1x1 méretű.Bemenet: a = 13 b = 11
6 négyzet 13x11 méretű papírból vágva
Kimenet: 6
Magyarázat: A papírt 6 négyzetre vághatjuk: 1 négyzet 7x7 1 négyzet 6x6 1 négyzet 5x5 2 négyzet 4x4 és 1 négyzet 1x1 méretű.Bemenet: a = 6 b = 7
5 négyzet 6x7 méretű papírból vágva
Kimenet: 5
Magyarázat: A papírt 5 négyzetre vághatjuk: 1 négyzet 4x4 2 négyzet 3x3 és 2 négyzet 3x3 méretű.
Tartalomjegyzék
- [Helytelen megközelítés 1] Mohó technika használata
- [2. helytelen megközelítés] Dinamikus programozás használata
- [Helyes megközelítés] DFS és dinamikus programozás használata
[Helytelen megközelítés 1] Mohó technika használata
Első pillantásra úgy tűnhet, hogy a probléma könnyen megoldható úgy, hogy először a lehető legnagyobb négyzetet vágjuk ki a papírból, majd a maradék papírból vágjuk ki a legnagyobb négyzetet, és így tovább, amíg az egész papírt le nem vágjuk. De ez a megoldás helytelen.
Miért nem működik a Greedy Approach?
Vegyünk egy méretű papírt 6x7 majd ha mohón próbáljuk vágni a papírt, akkor azt kapjuk 7 négyzetek: 1 négyzet méretű 6x6 és 6 négyzet méretű 1x1 míg a helyes megoldás: 5. Ezért a mohó megközelítés nem fog működni.
[2. helytelen megközelítés] Dinamikus programozás használata
Dinamikus programozás függőleges vagy vízszintes vágásokkal: Egy másik megoldás, amely helyesnek tűnhet, a használata Dinamikus programozás . Fenntarthatunk egy dp[][] táblát úgy, hogy dp[i][j] = a méretű papírból kivágható négyzetek minimális száma i x j . Aztán méretű papírra axb
- Megpróbálhatjuk minden sor mentén levágni: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) ahol k az [1 i - 1] tartományban lehet.
- Megpróbálhatjuk minden oszlop mentén vágni: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) ahol k az [1 j - 1] tartományban lehet.
Végül a minimális vágás lesz a válasz. De ez a megoldás is helytelen.
Miért nem működik a függőleges vagy vízszintes vágás a dinamikus programozási módszerrel?
Ez nem fog működni, mert feltételezzük, hogy a függőleges vagy vízszintes vágás mindig két részre osztja a téglalapot. Vegyünk egy méretű papírt 13x11 akkor ha DP megközelítéssel próbáljuk kivágni a papírt, 8 négyzetet kapunk, de a helyes válasz (a példákban látható) 6. Ezért a dinamikus programozás nem fog működni.
[Helyes megközelítés] DFS és dinamikus programozás használata
C++A ötlet az egész papírt le kell vágni DFS be alulról felfelé módon. Minden lépésben keresse meg a papír bal alsó sarkát, és próbáljon meg abból a sarokból kivágni minden lehetséges méretű négyzetet. Miután újra kivágott egy négyzetet, keresse meg a maradék papír bal alsó sarkát, hogy minden lehetséges méretű négyzetet kivághasson és így tovább. De ha minden lehetséges papírméretet a bal alsó sarokból próbálnánk kivágni, akkor az eléggé hatástalan lenne. Használatával tudjuk optimalizálni Dinamikus programozás hogy minden lehetséges papírmérethez minimális vágást tároljon.
Bármely papírméret egyedi azonosításához fenntarthatunk egy remSq[] tömböt úgy, hogy a remSq[i] a papír i-edik oszlopában tárolja a fennmaradó 1x1 méretű négyzetek számát. Tehát egy 6x7 remSq [] méretű papírra = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Szintén a bal alsó sarok megkereséséhez megtaláljuk az első indexet, amely a maximálisan megmaradt négyzeteket tartalmazza. Így kivonatolhatjuk a remSq[] tömb értékét, hogy egyedi kulcsot találjunk a remSq[] tömb összes lehetséges értékéhez.
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include using namespace std ; // function to get the hash key for remSq array int getKey ( vector < int > & remSq int b ) { int base = 1 ; int key = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * base ); base = base * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array int minCutUtil ( vector < int > & remSq int a int b map < int int > & memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( memo . find ( key ) != memo . end ()) return memo [ key ]; int maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ]; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq == 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; vector < int > newRemSq = remSq ; int ans = INT_MAX ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( int i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } return memo [ key ] = ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b int minCut ( int a int b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a == b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns vector < int > remSq ( b a ); map < int int > memo ; return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } int main () { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb cout < < minCut ( a b ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.* ; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey ( int [] remSq int b ) { int base = 1 ; int key = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * base ); base = base * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil ( int [] remSq int a int b Map < Integer Integer > memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( memo . containsKey ( key )) return memo . get ( key ); int maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ] ; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq == 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; int [] newRemSq = Arrays . copyOf ( remSq b ); int ans = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( int i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math . min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } memo . put ( key ans ); return ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut ( int a int b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a == b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int [] remSq = new int [ b ] ; Arrays . fill ( remSq a ); Map < Integer Integer > memo = new HashMap <> (); return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System . out . println ( minCut ( a b )); } }
Python # Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey ( remSq b ): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range ( b ): key += remSq [ i ] * base base = base * ( b + 1 ) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey ( remSq b ) if key in memo : return memo [ key ] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range ( b ): if remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq : maxRemSq = remSq [ i ] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0 : return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq [:] ans = float ( 'inf' ) # Find the ending point of min height while end < b : # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq or newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 : break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range ( start end + 1 ): newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )) end += 1 memo [ key ] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut ( a b ): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b : return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [ a ] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ) if __name__ == '__main__' : # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print ( minCut ( a b ))
C# // C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey ( int [] remSq int b ) { int baseVal = 1 ; int key = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * baseVal ); baseVal = baseVal * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil ( int [] remSq int a int b Dictionary < int int > memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( memo . ContainsKey ( key )) return memo [ key ]; int maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ]; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq == 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; int [] newRemSq = ( int []) remSq . Clone (); int ans = int . MaxValue ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( int i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math . Min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } memo [ key ] = ans ; return ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut ( int a int b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a == b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int [] remSq = new int [ b ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) remSq [ i ] = a ; Dictionary < int int > memo = new Dictionary < int int > (); return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } static void Main () { int a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console . WriteLine ( minCut ( a b )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey ( remSq b ) { let base = 1 ; let key = 0 ; for ( let i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * base ); base = base * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( key in memo ) return memo [ key ]; let maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( let i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ]; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq === 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; let newRemSq = remSq . slice (); let ans = Infinity ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( let i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math . min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } memo [ key ] = ans ; return ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut ( a b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a === b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array ( b ). fill ( a ); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console . log ( minCut ( a b ));
Kimenet
6
Időbonyolultság: O(a^b) minden b oszlophoz lehet egy négyzet.
Segédtér: O(a^b) az egyes egyedi állapotokat tároló memoizáció miatt.
 5 db 5 x 8 méretű papírból kivágott négyzet
5 db 5 x 8 méretű papírból kivágott négyzet  6 négyzet 13x11 méretű papírból vágva
6 négyzet 13x11 méretű papírból vágva  5 négyzet 6x7 méretű papírból vágva
5 négyzet 6x7 méretű papírból vágva