Csövek
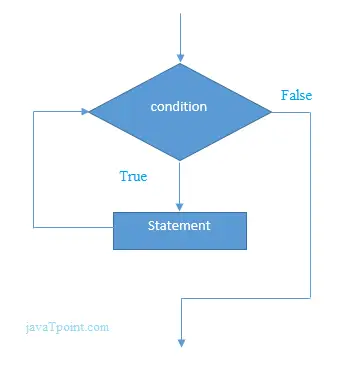
Csövek in IO kapcsolatot biztosít két JVM-ben egyidejűleg futó szál között. Tehát a csöveket forrásként vagy célként is használják.
- A PipedInputStream a PipedOutputStream segítségével is csővezetékes. Tehát az adatok írhatók a PipedOutputStream segítségével, és írhatók a PipedInputStream segítségével. De mindkét szál egyidejű használata holtpontot hoz létre a szálak számára.
- Egy csőről azt mondjuk, hogy megszakadt, ha egy szál, amely adatbájtokat szolgáltatott a csatlakoztatott vezetékes kimeneti adatfolyamnak, már nem él.
Nyilatkozat: public class PipedInputStream extends InputStream
Konstruktor: | PipedInputStream() : | létrehoz egy PipedInputStream-et, amelyhez nincs csatlakoztatva.
| PipedInputStream(int pSize): | létrehoz egy PipedInputStream-et, amely nincs a megadott csőmérettel összekötve.
| PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream outStream) : | létrehoz egy PipedInputStream-et, amely a PipedOutputStream - "outStream" -hez csatlakozik.
| PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream outStream int pSize) : | létrehoz egy vezetékes bemeneti adatfolyamot, amely a megadott csőmérettel csatlakozik a vezetékes kimeneti adatfolyamhoz. Mód: | int read(): | Reads the next byte of data from this piped input stream.The value byte is returned as an int in the range 0 to 255. This method blocks until input data is available the end of the stream is detected or an exception is thrown. Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { PipedInputStream geek_input = new PipedInputStream (); PipedOutputStream geek_output = new PipedOutputStream (); try { // Use of connect() : connecting geek_input with geek_output geek_input . connect ( geek_output ); // Use of read() method : geek_output . write ( 71 ); System . out . println ( 'using read() : ' + ( char ) geek_input . read ()); geek_output . write ( 69 ); System . out . println ( 'using read() : ' + ( char ) geek_input . read ()); geek_output . write ( 75 ); System . out . println ( 'using read() : ' + ( char ) geek_input . read ()); } catch ( IOException except ) { except . printStackTrace (); } } } Kimenet: using read() : G using read() : E using read() : K
| read(byte[] puffer int offset int maxlen): | java.io.PipedInputStream.read(byte[] puffer int offset int maxlen) maximum bájtnyi adatot olvas be a Piped Input Streamből a pufferek tömbjébe. A metódus blokkolja, ha eléri a Stream végét vagy kivételt dob. Szintaxis: public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : the destination buffer into which the data is to be read offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'. maxlen : maximum length of array to be read Return : next 'maxlen' bytes of the data as an integer value return -1 is end of stream is reached Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. -> NullPointerException : if buffer is null. -> IndexOutOfBoundsException : if offset is -ve or maxlen is -ve or maxlen > buffer.length - offset.
| fogadás (int byte): | java.io.PipedInputStream.receive(int byte) bájtot kap az adatokból. Ha nem áll rendelkezésre bemenet, akkor a metódus blokkol. Szintaxis: protected void receive(int byte) Parameters : byte : the bytes of the data received Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs or pipe is broken.
| bezár() : | java.io.PipedInputStream.close() bezárja a vezetékes bemeneti adatfolyamot, és felszabadítja a hozzárendelt erőforrásokat. Szintaxis: public void close() Parameters : -------------- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
| csatlakozás (PipedOutputStream forrás): | java.io.PipedInputStream.connect (PipedOutputStream forrás) összeköti a vezetékes bemeneti adatfolyamot a "forrás" vezetékes kimeneti adatfolyammal, és abban az esetben, ha a "forrás" csövek, más adatfolyam IO kivétellel Szintaxis: public void connect(PipedOutputStream source) Parameters : source : the Piped Output Stream to be connected to Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
| elérhető() : | java.io.PipedInputStream.available() sz. bájtok, amelyek leolvashatók a Bemeneti adatfolyamból anélkül, hogy ténylegesen blokkolnák őket. Szintaxis: public int available() Parameters : ------------- Return : no. of bytes that can be read from Input Stream without actually being blocked. 0 if the stream is already closed but by invoking close() method Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
Java program, amely elmagyarázza a PipedInputStream osztálymetódusok működését: Java // Java program illustrating the working of PipedInputStream // connect() read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) // close() available() import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { PipedInputStream geek_input = new PipedInputStream (); PipedOutputStream geek_output = new PipedOutputStream (); try { // Use of connect() : connecting geek_input with geek_output geek_input . connect ( geek_output ); geek_output . write ( 71 ); geek_output . write ( 69 ); geek_output . write ( 69 ); geek_output . write ( 75 ); geek_output . write ( 83 ); // Use of available() : System . out . println ( 'Use of available() : ' + geek_input . available ()); // Use of read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) : byte [] buffer = new byte [ 5 ] ; // destination 'buffer' geek_input . read ( buffer 0 5 ); String str = new String ( buffer ); System . out . println ( 'Using read(buffer offset maxlen) : ' + str ); // USe of close() method : System . out . println ( 'Closing the stream' ); geek_input . close (); } catch ( IOException except ) { except . printStackTrace (); } } } Kimenet: Use of available() : 5 Using read(buffer offset maxlen) : GEEKS Closing the stream
Next Article: Java.io.PipedOutputStream osztály Java nyelven Kvíz létrehozása

 Csövek in IO kapcsolatot biztosít két JVM-ben egyidejűleg futó szál között. Tehát a csöveket forrásként vagy célként is használják.
Csövek in IO kapcsolatot biztosít két JVM-ben egyidejűleg futó szál között. Tehát a csöveket forrásként vagy célként is használják.