Java.io.LineNumberInputStream osztály Java nyelven
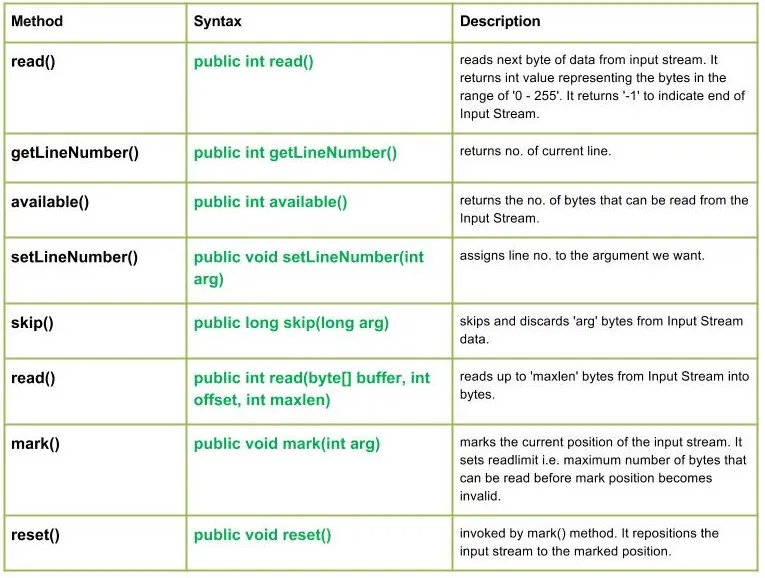
A java.io.LineNumberInputStream osztály egyszerűen a bemeneti adatfolyam kiterjesztése, amely extra lehetőséget biztosít az aktuális sorszám nyilvántartására.
Vonal egy : 'r'-re végződő bájtok sorozata, azaz egy kocsivissza karakter vagy egy újsor karakter: 'n' vagy egy soremelés karakter, amely a kocsivissza karaktert követi.
Nyilatkozat:
public class LineNumberInputStream extends Reader
Konstruktorok:
LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) : Constructs a newline no. stream that reads it's input from the specified Input Stream.
Mód:
Szintaxis:
public int read() Parameters : ------- Return : int value representing the bytes in the range of '0 - 255'. return -1 indicating end of Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Megvalósítás:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Megjegyzés:
A következő Java kód nem fog futni itt, mivel nem tudunk hozzáférni egyetlen fájlhoz sem az online IDE-n.
Tehát másolja a programot a rendszerére, és futtassa ott.
A ABC.txt a programban használt fájl tartalmazza:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Kimenet:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Szintaxis:
public int getLineNumber() Parameters : ------- Return : no. of current line
Megvalósítás:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of getLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of getLineNumber() : to print line no. a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( ' At line : ' + a ); System . out . print ( c ); } a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( ' at line: ' + a ); } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Megjegyzés:
A következő Java kód nem fog futni itt, mivel nem tudunk hozzáférni egyetlen fájlhoz sem az online IDE-n.
Tehát másolja a programot a rendszerére, és futtassa ott.
A ABC.txt a programban használt fájl tartalmazza:
no. of lines
Kimenet:
At line : 0 n At line : 0 o At line : 0 . At line : 0 At line : 0 o At line : 0 f At line : 1 At line : 1 l At line : 1 i At line : 1 n At line : 1 e At line : 1 s at line: 1
Szintaxis:
public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Megvalósítás:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of available() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read a = geekline . available (); System . out . println ( c + ' Bytes available : ' + a ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Megjegyzés:
A következő Java kód nem fog futni itt, mivel nem tudunk hozzáférni egyetlen fájlhoz sem az online IDE-n.
Tehát másolja a programot a rendszerére, és futtassa ott.
A ABC.txt a programban használt fájl tartalmazza:
available
Kimenet:
a Bytes available : 4 v Bytes available : 3 a Bytes available : 3 i Bytes available : 2 l Bytes available : 2 a Bytes available : 1 b Bytes available : 1 l Bytes available : 0 e Bytes available : 0
Szintaxis:
public void setLineNumber(int arg) Parameters : arg : line number to assign Return : void Exception: -----
Megvalósítás:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b = 0 ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // Use of setLineNumber() : to set the line no. geekline . setLineNumber ( 100 + b ); // getLineNumber() : returning the current line no. a = geekline . getLineNumber (); System . out . println ( c + ' Line No. Set : ' + a ); b ++ ; } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Megjegyzés:
A következő Java kód nem fog futni itt, mivel nem tudunk hozzáférni egyetlen fájlhoz sem az online IDE-n.
Tehát másolja a programot a rendszerére, és futtassa ott.
A ABC.txt a programban használt fájl tartalmazza:
LineNumber
Kimenet:
L Line No. Set : 100 i Line No. Set : 101 n Line No. Set : 102 e Line No. Set : 103 N Line No. Set : 104 u Line No. Set : 105 m Line No. Set : 106 b Line No. Set : 107 e Line No. Set : 108 r Line No. Set : 109
Szintaxis:
public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of Input Stream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Megvalósítás:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a b = 0 ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); while (( a = geekline . read ()) != - 1 ) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; // skip() : to skip and discard 'arg' bytes // Here skip() will skip and discard 3 bytes. geekline . skip ( 3 ); System . out . println ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Megjegyzés:
A következő Java kód nem fog futni itt, mivel nem tudunk hozzáférni egyetlen fájlhoz sem az online IDE-n.
Tehát másolja a programot a rendszerére, és futtassa ott.
A ABC.txt a programban használt fájl tartalmazza:
Program Explaining Skip() method
Kimenet: '
P r E a n k ) t
Szintaxis:
public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : buffer whose data to read offset : starting offset of the data maxlen : max. no. of bytes to read Return : total no. of bytes else return -1 if End of Input Stream is identified Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Megvalósítás:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geekinput = null ; try { char c ; int a ; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geekinput ); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while (( a = geekline . read ()) !=- 1 ) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = ( char ) a ; System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( Exception e ) { // In case of error e . printStackTrace (); System . out . println ( 'ERROR Occurs ' ); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if ( geekinput != null ) geekinput . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Megjegyzés:
A következő Java kód nem fog futni itt, mivel nem tudunk hozzáférni egyetlen fájlhoz sem az online IDE-n.
Tehát másolja a programot a rendszerére, és futtassa ott.
A ABC.txt a programban használt fájl tartalmazza:
Read() method
amit a metódus csinál, az offset = r és maxlen = 5... tehát ---azaz. 3 eltolás, majd 5 bájt, azaz Read( majd ismét eltolás tehát --
Kimenet:
The number of char read: 5 ---Read(--
Szintaxis:
public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
Szintaxis:
public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
Java program, amely elmagyarázza a LineNumberInputStream osztály metódusait: reset() és mark()
Java // Java program illustrating the working of LineNumberInputStream method // mark() and reset() import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { LineNumberInputStream geekline = null ; FileInputStream geek = null ; try { geek = new FileInputStream ( 'GEEKS.txt' ); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream ( geek ); // read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); // mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream geekline . mark ( 0 ); // skip() : it results in reading of 'e' in G'e'eeks geekline . skip ( 1 ); System . out . println ( 'skip() method comes to play' ); System . out . println ( 'mark() method comes to play' ); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); boolean check = geekline . markSupported (); if ( geekline . markSupported ()) { // reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions. geekline . reset (); System . out . println ( 'reset() invoked' ); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); System . out . println ( 'Char : ' + ( char ) geekline . read ()); } else { System . out . println ( 'reset() method not supported.' ); } System . out . println ( 'geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : ' + check ); } catch ( Exception except ) { // in case of I/O error except . printStackTrace (); } finally { // releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes if ( geek != null ) geek . close (); if ( geekline != null ) geekline . close (); } } }
Megjegyzés:
Ez a kód nem fut az online IDE-n, mivel itt nincs ilyen fájl.
Futtathatja ezt a kódot a rendszeren a működés ellenőrzéséhez.
ABC.txt a kódban használt fájl rendelkezik
HelloGeeks
Kimenet:
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() method not supported. geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : false
Lehet, Hogy Tetszeni Fog
Top Cikkek
Kategória
Érdekes Cikkek