Irányítatlan gráf klónozása

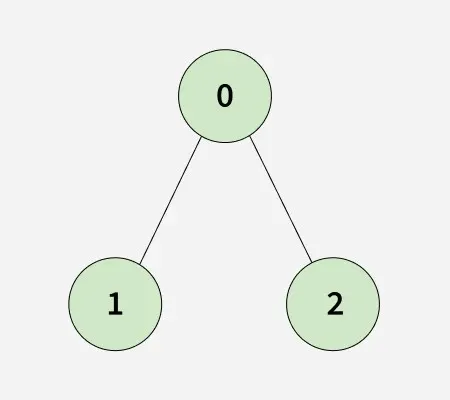
Adott a összekapcsolt irányítatlan gráf szomszédsági lista képviseli adjList[][] -vel n csomópontok és m élek, ahol minden csomópont rendelkezik a külön címke -tól 0-tól n-1-ig és minden adj[i] az i csúcshoz kapcsolódó csúcsok listáját jelenti.
Hozzon létre a klón ahol a gráf minden csomópontja tartalmaz egy egész számot val és egy tömb ( szomszédok ) csomópontok olyan csomópontokat tartalmaz, amelyek szomszédosak az aktuális csomóponttal.
class Node {
val: egész szám
szomszédok: lista[csomópont]
}
Az Ön feladata az adott gráf klónozása és a klónozott gráf hivatkozásának visszaadása.
Jegyzet: Ha az adott gráf helyes másolatát adja vissza, a kimenet igaz lesz; ellenkező esetben, ha a másolat hibás, hamisan nyomtat.
Példák
Bemenet: n = 4 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0 2] [0 1 3] [2]]
Kimenet: igaz
Magyarázat:
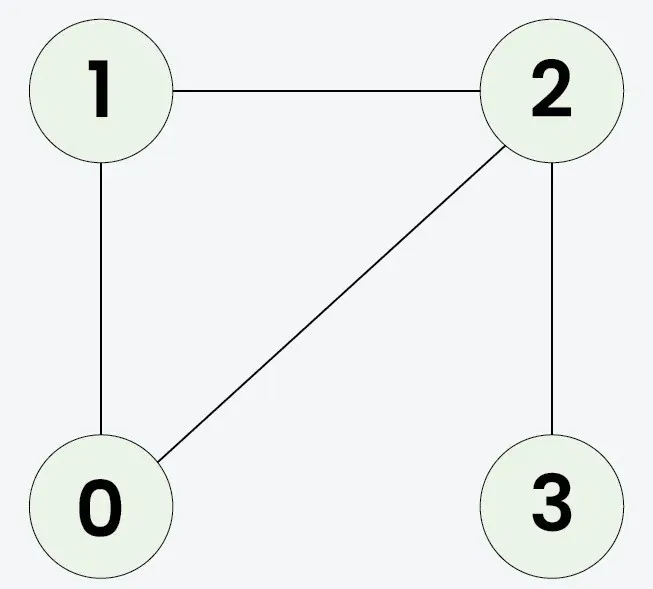
Mivel a klónozott gráf megegyezik az eredetivel, a kimenet igaz lesz.Bemenet: n = 3 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0] [0]]
Kimenet: igaz
Magyarázat:
Mivel a klónozott gráf megegyezik az eredetivel, a kimenet igaz lesz.
Tartalomjegyzék
- Miért kell nyomon követnünk a meglátogatott/klónozott csomópontokat?
- Hogyan lehet nyomon követni a meglátogatott/klónozott csomópontokat?
- Hogyan lehet klón csomópontokat csatlakoztatni?
- Hogyan ellenőrizhető, hogy a klónozott gráf helyes-e?
- [1. megközelítés] BFS bejárás – O(V+E) idő és O(V) tér
- [2. megközelítés] DFS bejárás használata - O(V+E) idő és O(V) tér
Miért kell nyomon követnünk a meglátogatott/klónozott csomópontokat?
Követnünk kell a meglátogatott vagy klónozott csomópontokat, hogy elkerüljük a végtelen rekurziót és a redundáns munkát a gráf klónozása során. Mivel a gráfok tartalmazhatnak ciklusokat (ahol egy csomópont vissza tud mutatni egy korábban meglátogatott csomópontra), anélkül, hogy nyomon követnénk a már klónozott csomópontokat, a klónozási funkció vég nélkül meglátogatja ugyanazokat a csomópontokat, ami veremtúlcsordulást vagy helytelen duplikációt eredményez.
Hogyan lehet nyomon követni a meglátogatott/klónozott csomópontokat?
HashMap/Map szükséges az összes már létrehozott csomópont karbantartásához. Kulcsüzletek : Az eredeti csomópont hivatkozása/címe Értéktárak : A klónozott csomópont hivatkozása/címe A gráf összes csomópontjáról másolat készült.
Hogyan lehet klón csomópontokat csatlakoztatni?
A szomszédos csúcsok meglátogatása közben a csomópont be szerezze be a megfelelő klónozást csomópont mert hívjuk így IN most keresse fel az összes szomszédos csomópontot be és minden szomszédhoz keresse meg a megfelelő klón csomópontot (ha nem található, hozzon létre egyet), majd nyomja be a szomszédos vektorba IN csomópont.
Hogyan ellenőrizhető, hogy a klónozott gráf helyes-e?
Végezzen BFS bejárást az eredeti gráfon a klónozás előtt, majd a klónozás befejezése után ismét a klónozott gráfon. Minden bejárás során nyomtassa ki az egyes csomópontok értékét a címével (vagy hivatkozásával) együtt. A klónozás helyességének ellenőrzéséhez hasonlítsa össze a két bejárás során meglátogatott csomópontok sorrendjét. Ha a csomópontértékek ugyanabban a sorrendben jelennek meg, de a címeik (vagy hivatkozásaik) különböznek, akkor ez megerősíti, hogy a gráf sikeresen és helyesen klónozott.
Fedezze fel, hogyan irányítatlan gráf klónozása, amely több összekapcsolt komponenst tartalmazó gráfokat tartalmaz BFS vagy DFS használatával biztosítva az összes csomópont és él teljes mélymásolatát.
[1. megközelítés] BFS bejárás – O(V+E) idő és O(V) tér
C++A BFS-megközelítésben a gráfot iteratív módon klónozzuk egy sor segítségével. Kezdjük a kezdeti csomópont klónozásával és a sorba helyezésével. Ahogy feldolgozzuk a sor egyes csomópontjait, meglátogatjuk a szomszédokat. Ha egy szomszédot még nem klónoztunk, akkor létrehozunk egy klónt, amelyet egy térképen tárolunk, és sorba helyezzük későbbi feldolgozáshoz. Ezután hozzáadjuk a szomszéd klónját az aktuális csomópont klónjának szomszédok listájához. Ez a folyamat szintről szintre folytatódik, biztosítva, hogy az összes csomópont szélesség-első sorrendben kerüljön látogatásra. A BFS különösen hasznos a mély rekurzió elkerülésére és a nagy vagy széles grafikonok hatékony kezelésére.
#include #include #include #include using namespace std ; // Definition for a Node struct Node { int val ; vector < Node *> neighbors ; }; // Clone the graph Node * cloneGraph ( Node * node ) { if ( ! node ) return nullptr ; map < Node * Node *> mp ; queue < Node *> q ; // Clone the source node Node * clone = new Node (); clone -> val = node -> val ; mp [ node ] = clone ; q . push ( node ); while ( ! q . empty ()) { Node * u = q . front (); q . pop (); for ( auto neighbor : u -> neighbors ) { // Clone neighbor if not already cloned if ( mp . find ( neighbor ) == mp . end ()) { Node * neighborClone = new Node (); neighborClone -> val = neighbor -> val ; mp [ neighbor ] = neighborClone ; q . push ( neighbor ); } // Link clone of neighbor to clone of current node mp [ u ] -> neighbors . push_back ( mp [ neighbor ]); } } return mp [ node ]; } // Build graph Node * buildGraph () { Node * node1 = new Node (); node1 -> val = 0 ; Node * node2 = new Node (); node2 -> val = 1 ; Node * node3 = new Node (); node3 -> val = 2 ; Node * node4 = new Node (); node4 -> val = 3 ; node1 -> neighbors = { node2 node3 }; node2 -> neighbors = { node1 node3 }; node3 -> neighbors = { node1 node2 node4 }; node4 -> neighbors = { node3 }; return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality bool compareGraphs ( Node * node1 Node * node2 map < Node * Node *>& visited ) { if ( ! node1 || ! node2 ) return node1 == node2 ; if ( node1 -> val != node2 -> val || node1 == node2 ) return false ; visited [ node1 ] = node2 ; if ( node1 -> neighbors . size () != node2 -> neighbors . size ()) return false ; for ( size_t i = 0 ; i < node1 -> neighbors . size (); ++ i ) { Node * n1 = node1 -> neighbors [ i ]; Node * n2 = node2 -> neighbors [ i ]; if ( visited . count ( n1 )) { if ( visited [ n1 ] != n2 ) return false ; } else { if ( ! compareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } // Driver Code int main () { Node * original = buildGraph (); Node * cloned = cloneGraph ( original ); map < Node * Node *> visited ; cout < < ( compareGraphs ( original cloned visited ) ? 'true' : 'false' ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.* ; // Definition for a Node class Node { public int val ; public ArrayList < Node > neighbors ; public Node () { neighbors = new ArrayList <> (); } public Node ( int val ) { this . val = val ; neighbors = new ArrayList <> (); } } public class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node cloneGraph ( Node node ) { if ( node == null ) return null ; Map < Node Node > mp = new HashMap <> (); Queue < Node > q = new LinkedList <> (); // Clone the starting node Node clone = new Node ( node . val ); mp . put ( node clone ); q . offer ( node ); while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) { Node current = q . poll (); for ( Node neighbor : current . neighbors ) { // Clone neighbor if it hasn't been cloned yet if ( ! mp . containsKey ( neighbor )) { mp . put ( neighbor new Node ( neighbor . val )); q . offer ( neighbor ); } // Add the clone of the neighbor to the current node's clone mp . get ( current ). neighbors . add ( mp . get ( neighbor )); } } return mp . get ( node ); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph () { Node node1 = new Node ( 0 ); Node node2 = new Node ( 1 ); Node node3 = new Node ( 2 ); Node node4 = new Node ( 3 ); node1 . neighbors . addAll ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( node2 node3 ))); node2 . neighbors . addAll ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( node1 node3 ))); node3 . neighbors . addAll ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( node1 node2 node4 ))); node4 . neighbors . addAll ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( node3 ))); return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static boolean compareGraphs ( Node n1 Node n2 HashMap < Node Node > visited ) { if ( n1 == null || n2 == null ) return n1 == n2 ; if ( n1 . val != n2 . val || n1 == n2 ) return false ; visited . put ( n1 n2 ); if ( n1 . neighbors . size () != n2 . neighbors . size ()) return false ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n1 . neighbors . size (); i ++ ) { Node neighbor1 = n1 . neighbors . get ( i ); Node neighbor2 = n2 . neighbors . get ( i ); if ( visited . containsKey ( neighbor1 )) { if ( visited . get ( neighbor1 ) != neighbor2 ) return false ; } else { if ( ! compareGraphs ( neighbor1 neighbor2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node original = buildGraph (); Node cloned = cloneGraph ( original ); boolean isEqual = compareGraphs ( original cloned new HashMap <> ()); System . out . println ( isEqual ? 'true' : 'false' ); } }
Python from collections import deque # Definition for a Node class Node : def __init__ ( self val = 0 ): self . val = val self . neighbors = [] # Clone the graph def cloneGraph ( node ): if not node : return None # Map to hold original nodes as keys and their clones as values mp = {} # Initialize BFS queue q = deque ([ node ]) # Clone the starting node mp [ node ] = Node ( node . val ) while q : current = q . popleft () for neighbor in current . neighbors : # If neighbor not cloned yet if neighbor not in mp : mp [ neighbor ] = Node ( neighbor . val ) q . append ( neighbor ) # Link clone of neighbor to the clone of the current node mp [ current ] . neighbors . append ( mp [ neighbor ]) return mp [ node ] # Build graph def buildGraph (): node1 = Node ( 0 ) node2 = Node ( 1 ) node3 = Node ( 2 ) node4 = Node ( 3 ) node1 . neighbors = [ node2 node3 ] node2 . neighbors = [ node1 node3 ] node3 . neighbors = [ node1 node2 node4 ] node4 . neighbors = [ node3 ] return node1 # Compare two graphs structurally and by values def compareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited ): if not n1 or not n2 : return n1 == n2 if n1 . val != n2 . val or n1 is n2 : return False visited [ n1 ] = n2 if len ( n1 . neighbors ) != len ( n2 . neighbors ): return False for i in range ( len ( n1 . neighbors )): neighbor1 = n1 . neighbors [ i ] neighbor2 = n2 . neighbors [ i ] if neighbor1 in visited : if visited [ neighbor1 ] != neighbor2 : return False else : if not compareGraphs ( neighbor1 neighbor2 visited ): return False return True # Driver if __name__ == '__main__' : original = buildGraph () cloned = cloneGraph ( original ) result = compareGraphs ( original cloned {}) print ( 'true' if result else 'false' )
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; // Definition for a Node public class Node { public int val ; public List < Node > neighbors ; public Node () { neighbors = new List < Node > (); } public Node ( int val ) { this . val = val ; neighbors = new List < Node > (); } } class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node CloneGraph ( Node node ) { if ( node == null ) return null ; var mp = new Dictionary < Node Node > (); var q = new Queue < Node > (); // Clone the starting node var clone = new Node ( node . val ); mp [ node ] = clone ; q . Enqueue ( node ); while ( q . Count > 0 ) { var current = q . Dequeue (); foreach ( var neighbor in current . neighbors ) { // If neighbor not cloned clone it and enqueue if ( ! mp . ContainsKey ( neighbor )) { mp [ neighbor ] = new Node ( neighbor . val ); q . Enqueue ( neighbor ); } // Add clone of neighbor to clone of current mp [ current ]. neighbors . Add ( mp [ neighbor ]); } } return mp [ node ]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph () { var node1 = new Node ( 0 ); var node2 = new Node ( 1 ); var node3 = new Node ( 2 ); var node4 = new Node ( 3 ); node1 . neighbors . AddRange ( new [] { node2 node3 }); node2 . neighbors . AddRange ( new [] { node1 node3 }); node3 . neighbors . AddRange ( new [] { node1 node2 node4 }); node4 . neighbors . AddRange ( new [] { node3 }); return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static bool CompareGraphs ( Node n1 Node n2 Dictionary < Node Node > visited ) { if ( n1 == null || n2 == null ) return n1 == n2 ; if ( n1 . val != n2 . val || ReferenceEquals ( n1 n2 )) return false ; visited [ n1 ] = n2 ; if ( n1 . neighbors . Count != n2 . neighbors . Count ) return false ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n1 . neighbors . Count ; i ++ ) { var neighbor1 = n1 . neighbors [ i ]; var neighbor2 = n2 . neighbors [ i ]; if ( visited . ContainsKey ( neighbor1 )) { if ( ! ReferenceEquals ( visited [ neighbor1 ] neighbor2 )) return false ; } else { if ( ! CompareGraphs ( neighbor1 neighbor2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } public static void Main () { var original = BuildGraph (); var cloned = CloneGraph ( original ); var visited = new Dictionary < Node Node > (); Console . WriteLine ( CompareGraphs ( original cloned visited ) ? 'true' : 'false' ); } }
JavaScript // Definition for a Node class Node { constructor ( val = 0 ) { this . val = val ; this . neighbors = []; } } // Clone the graph function cloneGraph ( node ) { if ( ! node ) return null ; const mp = new Map (); const q = [ node ]; // Clone the initial node mp . set ( node new Node ( node . val )); while ( q . length > 0 ) { const current = q . shift (); for ( const neighbor of current . neighbors ) { if ( ! mp . has ( neighbor )) { mp . set ( neighbor new Node ( neighbor . val )); q . push ( neighbor ); } // Link clone of neighbor to clone of current mp . get ( current ). neighbors . push ( mp . get ( neighbor )); } } return mp . get ( node ); } // Build graph function buildGraph () { const node1 = new Node ( 0 ); const node2 = new Node ( 1 ); const node3 = new Node ( 2 ); const node4 = new Node ( 3 ); node1 . neighbors = [ node2 node3 ]; node2 . neighbors = [ node1 node3 ]; node3 . neighbors = [ node1 node2 node4 ]; node4 . neighbors = [ node3 ]; return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs structurally and by value function compareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited = new Map ()) { if ( ! n1 || ! n2 ) return n1 === n2 ; if ( n1 . val !== n2 . val || n1 === n2 ) return false ; visited . set ( n1 n2 ); if ( n1 . neighbors . length !== n2 . neighbors . length ) return false ; for ( let i = 0 ; i < n1 . neighbors . length ; i ++ ) { const neighbor1 = n1 . neighbors [ i ]; const neighbor2 = n2 . neighbors [ i ]; if ( visited . has ( neighbor1 )) { if ( visited . get ( neighbor1 ) !== neighbor2 ) return false ; } else { if ( ! compareGraphs ( neighbor1 neighbor2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } // Driver const original = buildGraph (); const cloned = cloneGraph ( original ); const result = compareGraphs ( original cloned ); console . log ( result ? 'true' : 'false' );
Kimenet
true
[2. megközelítés] DFS bejárás használata - O(V+E) idő és O(V) tér
C++A DFS megközelítésben a gráfot rekurzió segítségével klónozzuk. Az adott csomópontból indulunk ki, és a visszalépés előtt minden ág mentén a lehető legmesszebbre járunk. Egy térkép (vagy szótár) a már klónozott csomópontok nyomon követésére szolgál, hogy elkerülje ugyanazon csomópont többszöri feldolgozását és a ciklusok kezelését. Amikor először találkozunk egy csomóponttal, klónt készítünk róla, és eltároljuk a térképen. Ezután az adott csomópont minden szomszédját rekurzívan klónozzuk, és hozzáadjuk a klónozott szomszédot az aktuális csomópont klónjához. Ez biztosítja, hogy az összes csomópontot alaposan meglátogassák a visszatérés előtt, és a gráf szerkezetét hűen másolja.
#include #include #include #include using namespace std ; // Definition for a Node struct Node { int val ; vector < Node *> neighbors ; }; // Map to hold original node to its copy unordered_map < Node * Node *> copies ; // Function to clone the graph Node * cloneGraph ( Node * node ) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if ( ! node ) return NULL ; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if ( copies . find ( node ) == copies . end ()) { Node * clone = new Node (); clone -> val = node -> val ; copies [ node ] = clone ; // Recursively clone neighbors for ( Node * neighbor : node -> neighbors ) { clone -> neighbors . push_back ( cloneGraph ( neighbor )); } } // Return the clone return copies [ node ]; } // Build graph Node * buildGraph () { Node * node1 = new Node (); node1 -> val = 0 ; Node * node2 = new Node (); node2 -> val = 1 ; Node * node3 = new Node (); node3 -> val = 2 ; Node * node4 = new Node (); node4 -> val = 3 ; node1 -> neighbors = { node2 node3 }; node2 -> neighbors = { node1 node3 }; node3 -> neighbors = { node1 node2 node4 }; node4 -> neighbors = { node3 }; return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality bool compareGraphs ( Node * node1 Node * node2 map < Node * Node *>& visited ) { if ( ! node1 || ! node2 ) return node1 == node2 ; if ( node1 -> val != node2 -> val || node1 == node2 ) return false ; visited [ node1 ] = node2 ; if ( node1 -> neighbors . size () != node2 -> neighbors . size ()) return false ; for ( size_t i = 0 ; i < node1 -> neighbors . size (); ++ i ) { Node * n1 = node1 -> neighbors [ i ]; Node * n2 = node2 -> neighbors [ i ]; if ( visited . count ( n1 )) { if ( visited [ n1 ] != n2 ) return false ; } else { if ( ! compareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } // Driver Code int main () { Node * original = buildGraph (); // Clone the graph Node * cloned = cloneGraph ( original ); // Compare original and cloned graph map < Node * Node *> visited ; cout < < ( compareGraphs ( original cloned visited ) ? 'true' : 'false' ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.* ; // Definition for a Node class Node { int val ; ArrayList < Node > neighbors ; Node () { neighbors = new ArrayList <> (); } Node ( int val ) { this . val = val ; neighbors = new ArrayList <> (); } } public class GfG { // Map to hold original node to its copy static HashMap < Node Node > copies = new HashMap <> (); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node cloneGraph ( Node node ) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if ( node == null ) return null ; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if ( ! copies . containsKey ( node )) { Node clone = new Node ( node . val ); copies . put ( node clone ); // Recursively clone neighbors for ( Node neighbor : node . neighbors ) { clone . neighbors . add ( cloneGraph ( neighbor )); } } // Return the clone return copies . get ( node ); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph () { Node node1 = new Node ( 0 ); Node node2 = new Node ( 1 ); Node node3 = new Node ( 2 ); Node node4 = new Node ( 3 ); node1 . neighbors . addAll ( Arrays . asList ( node2 node3 )); node2 . neighbors . addAll ( Arrays . asList ( node1 node3 )); node3 . neighbors . addAll ( Arrays . asList ( node1 node2 node4 )); node4 . neighbors . addAll ( Arrays . asList ( node3 )); return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static boolean compareGraphs ( Node node1 Node node2 HashMap < Node Node > visited ) { if ( node1 == null || node2 == null ) return node1 == node2 ; if ( node1 . val != node2 . val || node1 == node2 ) return false ; visited . put ( node1 node2 ); if ( node1 . neighbors . size () != node2 . neighbors . size ()) return false ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < node1 . neighbors . size (); i ++ ) { Node n1 = node1 . neighbors . get ( i ); Node n2 = node2 . neighbors . get ( i ); if ( visited . containsKey ( n1 )) { if ( visited . get ( n1 ) != n2 ) return false ; } else { if ( ! compareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } // Driver Code public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node original = buildGraph (); // Clone the graph Node cloned = cloneGraph ( original ); // Compare original and cloned graph boolean result = compareGraphs ( original cloned new HashMap <> ()); System . out . println ( result ? 'true' : 'false' ); } }
Python # Definition for a Node class Node : def __init__ ( self val = 0 neighbors = None ): self . val = val self . neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else [] # Map to hold original node to its copy copies = {} # Function to clone the graph def cloneGraph ( node ): # If the node is None return None if not node : return None # If node is not yet cloned clone it if node not in copies : # Create a clone of the node clone = Node ( node . val ) copies [ node ] = clone # Recursively clone neighbors for neighbor in node . neighbors : clone . neighbors . append ( cloneGraph ( neighbor )) # Return the clone return copies [ node ] def buildGraph (): node1 = Node ( 0 ) node2 = Node ( 1 ) node3 = Node ( 2 ) node4 = Node ( 3 ) node1 . neighbors = [ node2 node3 ] node2 . neighbors = [ node1 node3 ] node3 . neighbors = [ node1 node2 node4 ] node4 . neighbors = [ node3 ] return node1 # Compare two graphs for structural and value equality def compareGraphs ( node1 node2 visited ): if not node1 or not node2 : return node1 == node2 if node1 . val != node2 . val or node1 is node2 : return False visited [ node1 ] = node2 if len ( node1 . neighbors ) != len ( node2 . neighbors ): return False for i in range ( len ( node1 . neighbors )): n1 = node1 . neighbors [ i ] n2 = node2 . neighbors [ i ] if n1 in visited : if visited [ n1 ] != n2 : return False else : if not compareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited ): return False return True # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : original = buildGraph () # Clone the graph using DFS cloned = cloneGraph ( original ) # Compare original and cloned graph visited = {} print ( 'true' if compareGraphs ( original cloned visited ) else 'false' )
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; public class Node { public int val ; public List < Node > neighbors ; public Node () { val = 0 ; neighbors = new List < Node > (); } public Node ( int _val ) { val = _val ; neighbors = new List < Node > (); } } class GfG { // Dictionary to hold original node to its copy static Dictionary < Node Node > copies = new Dictionary < Node Node > (); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node CloneGraph ( Node node ) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if ( node == null ) return null ; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if ( ! copies . ContainsKey ( node )) { Node clone = new Node ( node . val ); copies [ node ] = clone ; // Recursively clone neighbors foreach ( Node neighbor in node . neighbors ) { clone . neighbors . Add ( CloneGraph ( neighbor )); } } // Return the clone return copies [ node ]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph () { Node node1 = new Node ( 0 ); Node node2 = new Node ( 1 ); Node node3 = new Node ( 2 ); Node node4 = new Node ( 3 ); node1 . neighbors . Add ( node2 ); node1 . neighbors . Add ( node3 ); node2 . neighbors . Add ( node1 ); node2 . neighbors . Add ( node3 ); node3 . neighbors . Add ( node1 ); node3 . neighbors . Add ( node2 ); node3 . neighbors . Add ( node4 ); node4 . neighbors . Add ( node3 ); return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static bool CompareGraphs ( Node node1 Node node2 Dictionary < Node Node > visited ) { if ( node1 == null || node2 == null ) return node1 == node2 ; if ( node1 . val != node2 . val || node1 == node2 ) return false ; visited [ node1 ] = node2 ; if ( node1 . neighbors . Count != node2 . neighbors . Count ) return false ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < node1 . neighbors . Count ; i ++ ) { Node n1 = node1 . neighbors [ i ]; Node n2 = node2 . neighbors [ i ]; if ( visited . ContainsKey ( n1 )) { if ( visited [ n1 ] != n2 ) return false ; } else { if ( ! CompareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } // Driver Code public static void Main () { Node original = BuildGraph (); // Clone the graph using DFS Node cloned = CloneGraph ( original ); // Compare original and cloned graph bool isEqual = CompareGraphs ( original cloned new Dictionary < Node Node > ()); Console . WriteLine ( isEqual ? 'true' : 'false' ); } }
JavaScript // Definition for a Node class Node { constructor ( val = 0 ) { this . val = val ; this . neighbors = []; } } // Map to hold original node to its copy const copies = new Map (); // Function to clone the graph using DFS function cloneGraph ( node ) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if ( node === null ) return null ; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if ( ! copies . has ( node )) { const clone = new Node ( node . val ); copies . set ( node clone ); // Recursively clone neighbors for ( let neighbor of node . neighbors ) { clone . neighbors . push ( cloneGraph ( neighbor )); } } // Return the clone return copies . get ( node ); } // Build graph function buildGraph () { const node1 = new Node ( 0 ); const node2 = new Node ( 1 ); const node3 = new Node ( 2 ); const node4 = new Node ( 3 ); node1 . neighbors . push ( node2 node3 ); node2 . neighbors . push ( node1 node3 ); node3 . neighbors . push ( node1 node2 node4 ); node4 . neighbors . push ( node3 ); return node1 ; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality function compareGraphs ( node1 node2 visited = new Map ()) { if ( ! node1 || ! node2 ) return node1 === node2 ; if ( node1 . val !== node2 . val || node1 === node2 ) return false ; visited . set ( node1 node2 ); if ( node1 . neighbors . length !== node2 . neighbors . length ) return false ; for ( let i = 0 ; i < node1 . neighbors . length ; i ++ ) { const n1 = node1 . neighbors [ i ]; const n2 = node2 . neighbors [ i ]; if ( visited . has ( n1 )) { if ( visited . get ( n1 ) !== n2 ) return false ; } else { if ( ! compareGraphs ( n1 n2 visited )) return false ; } } return true ; } // Driver Code const original = buildGraph (); // Clone the graph using DFS const cloned = cloneGraph ( original ); // Compare original and cloned graph console . log ( compareGraphs ( original cloned ) ? 'true' : 'false' );
Kimenet
true