Odmotan povezani popis | Set 1 (Uvod)
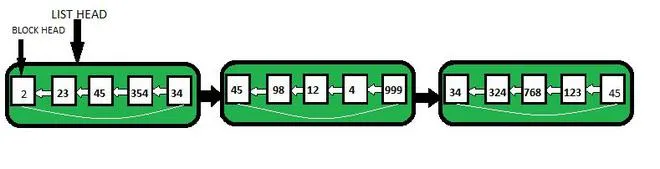
Poput polja i povezanog popisa, razmotani povezani popis također je linearna struktura podataka i varijanta je povezanog popisa.
Zašto nam treba razmotana povezana lista?
Jedna od najvećih prednosti povezanih popisa u odnosu na nizove jest ta da je za umetanje elementa na bilo koje mjesto potrebno samo O(1). Međutim, caka je u tome što je za pretraživanje elementa u povezanom popisu potrebno O(n). Dakle, da bi se riješio problem pretraživanja, tj. smanjilo vrijeme za pretraživanje elementa, predstavljen je koncept nerazmotanih povezanih lista. Neodmotani povezani popis pokriva prednosti niza i povezanog popisa jer smanjuje opterećenje memorije u usporedbi s jednostavnim povezanim popisima pohranjivanjem više elemenata na svakom čvoru, a također ima prednost brzog umetanja i brisanja kao kod povezanog popisa.


Prednosti:
- Zbog Cache ponašanja linearno pretraživanje puno je brže u odmotanim povezanim popisima.
- U usporedbi s običnim povezanim popisom zahtijeva manje prostora za pohranu za pokazivače/reference.
- Izvodi operacije poput umetanja, brisanja i obilaženja brže od običnih povezanih popisa (jer je pretraživanje brže).
Nedostaci:
- Troškovi po čvoru su relativno visoki od jednostruko povezanih popisa. Pogledajte primjer čvora u donjem kodu
Primjer: Recimo da imamo 8 elemenata pa je sqrt(8)=2,82 što zaokružuje na 3. Dakle, svaki blok će pohraniti 3 elementa. Dakle, za pohranu 8 elemenata stvorit će se 3 bloka od kojih će prva dva bloka pohraniti 3 elementa, a zadnji blok pohraniti 2 elementa.
Kako pretraživanje postaje bolje u odmotanim povezanim popisima?
Dakle, uzimajući gornji primjer, ako želimo tražiti 7. element na popisu, prelazimo popis blokova do onog koji sadrži 7. element. Potrebno je samo O(sqrt(n)) budući da smo ga pronašli kroz ne više od sqrt(n) blokova.
Jednostavna implementacija:
Donji program stvara jednostavnu odmotanu povezanu listu s 3 čvora koji sadrže varijabilni broj elemenata u svakom. Također prelazi kreirani popis.
C++ // C++ program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include using namespace std ; #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public : int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) cout < < n -> array [ i ] < < ' ' ; // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { Node * head = NULL ; Node * second = NULL ; Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; } // This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C // C program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include #include #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node struct Node { int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; struct Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( struct Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' n -> array [ i ]); // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { struct Node * head = NULL ; struct Node * second = NULL ; struct Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); second = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); third = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static final int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node static class Node { int numElements ; int [] array = new int [ maxElements ] ; Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) System . out . print ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Python3 # Python3 program to implement unrolled # linked list and traversing it. maxElements = 4 # Unrolled Linked List Node class Node : def __init__ ( self ): self . numElements = 0 self . array = [ 0 for i in range ( maxElements )] self . next = None # Function to traverse an unrolled linked list # and print all the elements def printUnrolledList ( n ): while ( n != None ): # Print elements in current node for i in range ( n . numElements ): print ( n . array [ i ] end = ' ' ) # Move to next node n = n . next # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : head = None second = None third = None # Allocate 3 Nodes head = Node () second = Node () third = Node () # Let us put some values in second # node (Number of values must be # less than or equal to # maxElement) head . numElements = 3 head . array [ 0 ] = 1 head . array [ 1 ] = 2 head . array [ 2 ] = 3 # Link first Node with the second Node head . next = second # Let us put some values in second node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) second . numElements = 3 second . array [ 0 ] = 4 second . array [ 1 ] = 5 second . array [ 2 ] = 6 # Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third # Let us put some values in third node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 third . array [ 0 ] = 7 third . array [ 1 ] = 8 third . array [ 2 ] = 9 third . next = None printUnrolledList ( head ) # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# // C# program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. using System ; class GFG { static readonly int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public int numElements ; public int [] array = new int [ maxElements ]; public Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) Console . Write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void Main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. const maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { constructor () { this . numElements = 0 ; this . array = new Array ( maxElements ); this . next = null ; } } // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements function printUnrolledList ( n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( var i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) document . write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes var head = null ; var second = null ; var third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); < /script>
Izlaz
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Analiza složenosti:
U ovom smo članku predstavili razmotani popis i njegove prednosti. Također smo pokazali kako preći kroz listu. U sljedećem članku ćemo detaljno raspravljati o brisanju umetanja i vrijednostima maxElements/numElements.
Umetanje u Unrolled Linked List
Napravi kviz