Učinkovito dizajnirajte umetnite, izbrišite i srednje upite na setu
S obzirom na prazan set u početku i niz upita na njemu, svaki od sljedećih vrsta:
- Umetnite 'x' se vrši pomoću ažuriranja (1 0 10^6 x 1). Imajte na umu da se korijen stabla prenosi indeks start prolazi kao 0 i krajnji indeks kao 10^6 tako da se svi rasponi koji imaju x ažuriraju.
- Izbrišite 'x' se vrši pomoću ažuriranja (1 0 10^6 X -1). Imajte na umu da se korijen stabla prenosi indeks start prolazi kao 0 i krajnji indeks kao 10^6 tako da se svi rasponi koji imaju x ažuriraju.
Primjer:
Input : Insert 1 Insert 4 Insert 7 Median Output : The first three queries should insert 1 4 and 7 into an empty set. The fourth query should return 4 (median of 1 4 7).
U svrhu izlaganja pretpostavljamo sljedeće, ali ove pretpostavke nisu ograničenja ovdje raspravljene metode:
1. U bilo kojem slučaju svi su elementi različiti, a nijedan se od njih ne događa više od jednom.
2. "Medijan" upit se vrši samo kad u setu ima neparnog broja elemenata. (Morat ćemo unijeti dva upita na stablu našeg segmenta u slučaju čak i brojeva)
3. Elementi u skupu kreću se od 1 do +10^6.
Metoda 1 (naivna)
U naivnoj implementaciji možemo napraviti prva dva upita u O (1), ali posljednji upit u O (max_elem) gdje je max_elem maksimalni element svih vremena (uključujući izbrisane elemente).
Pretpostavimo niz računati[] (veličine 10^6 + 1) Za održavanje broja svakog elementa u podskupini. Slijede jednostavni i samoobjavljeni algoritmi za 3 upita:
Umetnite x upit:
count[x]++; if (x > max_elem) max_elem = x; n++;
Izbriši x upit:
if (count[x] > 0) count[x]--; n--;
Srednji upit:
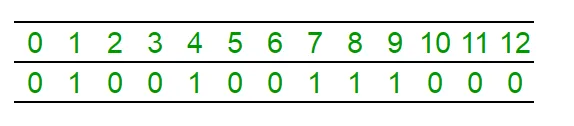
sum = 0; i = 0; while( sum <= n / 2 ) { i++; sum += count[i]; } median = i; return median; Ilustracija broja nizova [] koji predstavlja skup {1 4 7 8 9} Srednji element je '7':

'Medijan' upit namjerava pronaći (n + 1)/2. '1' u nizu u ovom slučaju 3. '1'; Sada isto radimo koristeći segment stabla.
Metoda 2 (koristeći Segment )
Napravimo a segment za pohranu zbroja intervala u kojima interval [a b] predstavlja broj elemenata prisutnih u setu koji je trenutno u rasponu [a b]. Na primjer, ako uzmemo u obzir gornji primjer upita (3 7) vraća 2 upita (4 4) vraća 1 upit (5 5) vraća 0.
Umetci umetnite i izbrišite su jednostavni i oba se mogu implementirati pomoću UPDATE -a funkcije (int x int diff) (dodaje 'diff' u indeksu 'x')
Algoritam
// adds ‘diff’ at index ‘x’ update(node a b x diff) // If leaf node If a == b and a == x segmentTree[node] += diff // If non-leaf node and x lies in its range If x is in [a b] // Update children recursively update(2*node a (a + b)/2 x diff) update(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b x diff) // Update node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[2 * node] + segmentTree[2 * node + 1]
Gore navedena rekurzivna funkcija radi u O (log (max_elem)) (u ovom slučaju max_elem je 10^6) i koristi se za umetanje i brisanje sljedećim pozivima:
Sada je funkcija pronalaska indeksa s KTH '1' gdje će 'k' u ovom slučaju uvijek biti (n + 1) / 2 Ovo će djelovati poput binarnog pretraživanja. Možete ga smatrati rekurzivnom binarnom funkcijom pretraživanja na stablu segmenta.
Uzmimo primjer da shvatimo da naš skup trenutno ima elemente {1 4 7 8 9} i stoga je predstavljen sljedećim stablom segmenta.
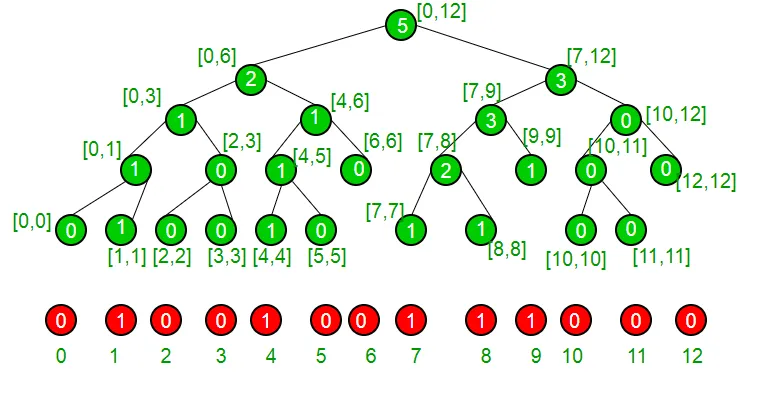
Ako smo na čvoru bez lišća, sigurni smo da ima i oboje djece, vidimo ima li lijevo dijete više ili jednakog broja kao "k" ako smo sigurni da naš indeks leži u lijevom podzemlju, u suprotnom, ako lijevo subtree ima manji broj od 1 od k, sigurni smo da naš indeks leži u desnom podzemlju. To radimo rekurzivno da bismo postigli svoj indeks i odatle ga vraćamo.
Algoritam
1.findKth(node a b k) 2. If a != b 3. If segmentTree[ 2 * node ] >= k 4. return findKth(2*node a (a + b)/2 k) 5. else 6. return findKth(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[ 2 * node ]) 7. else 8. return a
Gore navedena rekurzivna funkcija radi u O (log (max_elem)) .
// A C++ program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree #include #define maxn 3000005 #define max_elem 1000000 using namespace std ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. int segmentTree [ maxn ]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. void update ( int node int a int b int x int diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' is in its // range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree int findKth ( int node int a int b int k ) { // non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 k ); // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]); } // if at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return ( segmentTree [ node ]) ? a : -1 ; } // insert x in the set void insert ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // delete x from the set void delete ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x -1 ); } // returns median element of the set with odd // cardinality only int median () { int k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code int main () { insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); cout < < 'Median for the set {147} = ' < < median () < < endl ; insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); cout < < 'Median for the set {14789} = ' < < median () < < endl ; delete ( 1 ); delete ( 8 ); cout < < 'Median for the set {479} = ' < < median () < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree import java.io.* ; class GFG { public static int maxn = 3000005 ; public static int max_elem = 1000000 ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int [] segmentTree = new int [ maxn ] ; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update ( int node int a int b int x int diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ] ; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth ( int node int a int b int k ) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) { return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 k ); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ] ); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return ( segmentTree [ node ] != 0 ) ? a : - 1 ; } // Insert x in the set public static void insert ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median () { int k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); System . out . println ( 'Median for the set {147} = ' + median ()); insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); System . out . println ( 'Median for the set {14789} = ' + median ()); delete ( 1 ); delete ( 8 ); System . out . println ( 'Median for the set {479} = ' + median ()); } } // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Python3 # A Python3 program to implement insert delete and # median queries using segment tree maxn = 3000005 max_elem = 1000000 # A global array to store segment tree. # Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. segmentTree = [ 0 for i in range ( maxn )] # Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. # Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and # 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored # in current node. # 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. def update ( node a b x diff ): global segmentTree # If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b and a == x ): # add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff return # If current node is non-leaf and 'x' is in its # range if ( x >= a and x <= b ): # update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) // 2 x diff ) update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) // 2 + 1 b x diff ) # Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ] # Returns k'th node in segment tree def findKth ( node a b k ): global segmentTree # non-leaf node will definitely have both # children left and right if ( a != b ): # If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ): return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) // 2 k ) # If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) // 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]) # if at a leaf node return the index it stores # information about return a if ( segmentTree [ node ]) else - 1 # insert x in the set def insert ( x ): update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ) # delete x from the set def delete ( x ): update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ) # returns median element of the set with odd # cardinality only def median (): k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) // 2 return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : insert ( 1 ) insert ( 4 ) insert ( 7 ) print ( 'Median for the set {147} =' median ()) insert ( 8 ) insert ( 9 ) print ( 'Median for the set {14789} =' median ()) delete ( 1 ) delete ( 8 ) print ( 'Median for the set {479} =' median ()) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C# // A C# program to implement insert delete // and median queries using segment tree using System ; class GFG { public static int maxn = 3000005 ; public static int max_elem = 1000000 ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int [] segmentTree = new int [ maxn ]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update ( int node int a int b int x int diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth ( int node int a int b int k ) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) { return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 k ); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it // stores information about if ( segmentTree [ node ] != 0 ) { return a ; } else { return - 1 ; } } // Insert x in the set public static void insert ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median () { int k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code static public void Main () { insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Median for the set {147} = ' + median ()); insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Median for the set {14789} = ' + median ()); delete ( 1 ); delete ( 8 ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Median for the set {479} = ' + median ()); } } // This code is contributed by rag2127
JavaScript < script > // A Javascript program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree let maxn = 3000005 ; let max_elem = 1000000 ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. let segmentTree = new Array ( maxn ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < maxn ; i ++ ) { segmentTree [ i ] = 0 ; } // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. function update ( node a b x diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree function findKth ( node a b k ) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) { return findKth ( node * 2 a Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) k ); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return ( segmentTree [ node ] != 0 ) ? a : - 1 ; } // Insert x in the set function insert ( x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // Delete x from the set function delet ( x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only function median () { let k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); document . write ( 'Median for the set {147} = ' + median () + '
' ); insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); document . write ( 'Median for the set {14789} = ' + median () + '
' ); delet ( 1 ); delet ( 8 ); document . write ( 'Median for the set {479} = ' + median () + '
' ); // This code is contributed by unknown2108 < /script>
Izlaz:
Median for the set {147} = 4 Median for the set {14789} = 7 Median for the set {479} = 7
Zaključak:
Sva tri upita ulaze u O (log (max_elem)) U ovom slučaju max_elem = 10^6 Dakle, log (max_elem) je približno jednak 20.
Stablo segmenta koristi O (max_elem) prostor.
Da je upit za brisanje bilo tamo, problem bi mogao biti i s poznatim algoritmom ovdje .