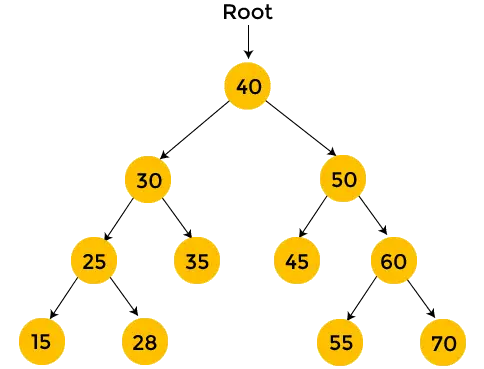
Voltear árbol binario
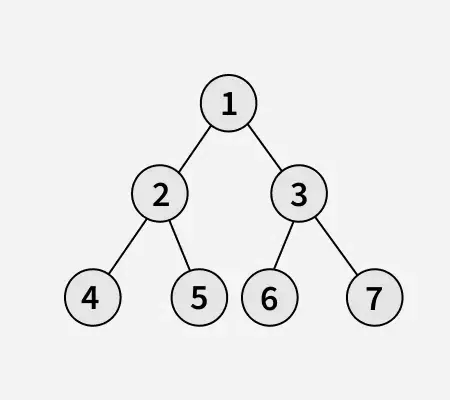
dado un árbol binario la tarea es voltear el árbol binario hacia el dirección correcta n eso es dextrorso.
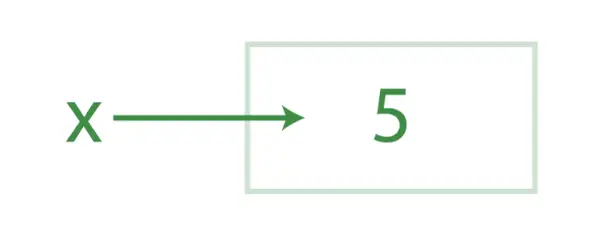
Aporte:

Producción:
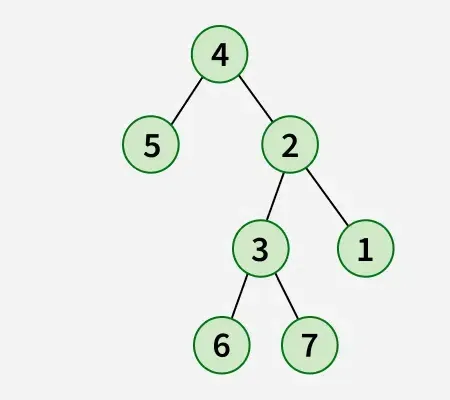
Explicación: En la operación de inversión, el nodo más a la izquierda se convierte en la raíz del árbol invertido y su padre se convierte en su hijo derecho y el hermano derecho se convierte en su hijo izquierdo y se debe hacer lo mismo con todos los nodos más a la izquierda de forma recursiva.
Tabla de contenido
- [Enfoque esperado - 1] Uso de la recursión - O(n) Tiempo y O(n) Espacio
- [Enfoque esperado - 2] Enfoque iterativo - O(n) Tiempo y O(1) Espacio
[Enfoque esperado - 1] Uso de la recursión - O(n) Tiempo y O(n) Espacio
La idea es recursivamente voltear el árbol binario intercambiando el izquierda y bien subárboles de cada nodo. Después de voltear la estructura del árbol se invertirá y la nueva raíz del árbol volteado será el nodo de hoja original más a la izquierda.
A continuación se muestra el principal código de rotación de un subárbol:
- raíz->izquierda->izquierda = raíz->derecha
- raíz->izquierda->derecha = raíz
- raíz->izquierda = NULL
- raíz->derecha = NULL
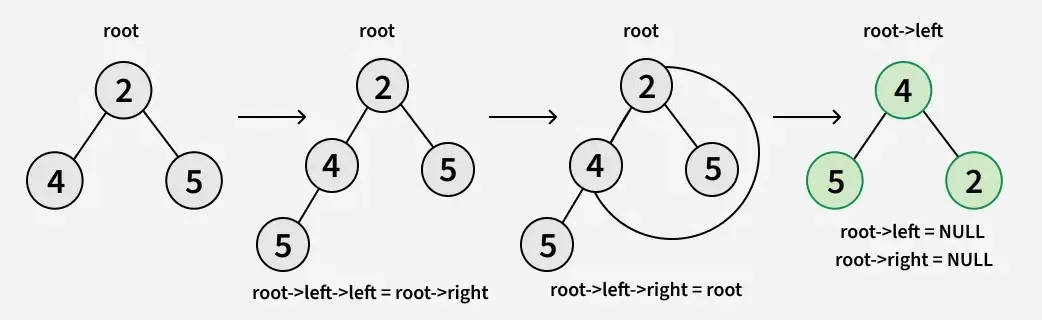
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++ // C++ program to flip a binary tree // using recursion #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * left * right ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = right = nullptr ; } }; // method to flip the binary tree iteratively Node * flipBinaryTree ( Node * root ) { // Base cases if ( root == nullptr ) return root ; if ( root -> left == nullptr && root -> right == nullptr ) return root ; // Recursively call the same method Node * flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree ( root -> left ); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root -> left -> left = root -> right ; root -> left -> right = root ; root -> left = root -> right = nullptr ; return flippedRoot ; } // Iterative method to do level order traversal // line by line void printLevelOrder ( Node * root ) { // Base Case if ( root == nullptr ) return ; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal queue < Node *> q ; // Enqueue Root and initialize height q . push ( root ); while ( 1 ) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates number // of nodes at current level. int nodeCount = q . size (); if ( nodeCount == 0 ) break ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level and // Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { Node * node = q . front (); cout < < node -> data < < ' ' ; q . pop (); if ( node -> left != nullptr ) q . push ( node -> left ); if ( node -> right != nullptr ) q . push ( node -> right ); nodeCount -- ; } cout < < endl ; } } int main () { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node * root = new Node ( 1 ); root -> left = new Node ( 2 ); root -> right = new Node ( 3 ); root -> right -> left = new Node ( 4 ); root -> right -> right = new Node ( 5 ); root = flipBinaryTree ( root ); printLevelOrder ( root ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to flip a binary tree // using recursion class Node { int data ; Node left right ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = right = null ; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree ( Node root ) { // Base cases if ( root == null ) return root ; if ( root . left == null && root . right == null ) return root ; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree ( root . left ); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root . left . left = root . right ; root . left . right = root ; root . left = root . right = null ; return flippedRoot ; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder ( Node root ) { // Base Case if ( root == null ) return ; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java . util . Queue < Node > q = new java . util . LinkedList <> (); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q . add ( root ); while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q . size (); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { Node node = q . poll (); System . out . print ( node . data + ' ' ); if ( node . left != null ) q . add ( node . left ); if ( node . right != null ) q . add ( node . right ); nodeCount -- ; } System . out . println (); } } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 5 ); root = flipBinaryTree ( root ); printLevelOrder ( root ); } }
Python # Python program to flip a binary # tree using recursion class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . left = None self . right = None def flipBinaryTree ( root ): # Base cases if root is None : return root if root . left is None and root . right is None : return root # Recursively call the same method flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree ( root . left ) # Rearranging main root Node after returning # from recursive call root . left . left = root . right root . left . right = root root . left = root . right = None return flippedRoot # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder ( root ): # Base Case if root is None : return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue . append ( root ) while queue : nodeCount = len ( queue ) while nodeCount > 0 : node = queue . pop ( 0 ) print ( node . data end = ' ' ) if node . left is not None : queue . append ( node . left ) if node . right is not None : queue . append ( node . right ) nodeCount -= 1 print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node ( 1 ) root . left = Node ( 2 ) root . right = Node ( 3 ) root . right . left = Node ( 4 ) root . right . right = Node ( 5 ) root = flipBinaryTree ( root ) printLevelOrder ( root )
C# // C# program to flip a binary tree // using recursion using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class Node { public int data ; public Node left right ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = right = null ; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) return root ; if ( root . left == null && root . right == null ) return root ; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = FlipBinaryTree ( root . left ); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root . left . left = root . right ; root . left . right = root ; root . left = root . right = null ; return flippedRoot ; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) return ; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal Queue < Node > q = new Queue < Node > (); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q . Enqueue ( root ); while ( q . Count > 0 ) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q . Count ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { Node node = q . Dequeue (); Console . Write ( node . data + ' ' ); if ( node . left != null ) q . Enqueue ( node . left ); if ( node . right != null ) q . Enqueue ( node . right ); nodeCount -- ; } Console . WriteLine (); } } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 5 ); root = FlipBinaryTree ( root ); PrintLevelOrder ( root ); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using recursion class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . left = null ; this . right = null ; } } // Method to flip the binary tree function flipBinaryTree ( root ) { if ( root === null ) return root ; if ( root . left === null && root . right === null ) return root ; // Recursively call the same method const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree ( root . left ); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root . left . left = root . right ; root . left . right = root ; root . left = root . right = null ; return flippedRoot ; } // Iterative method to do level order traversal // line by line function printLevelOrder ( root ) { if ( root === null ) return ; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal const queue = [ root ]; while ( queue . length > 0 ) { let nodeCount = queue . length ; while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { const node = queue . shift (); console . log ( node . data + ' ' ); if ( node . left !== null ) queue . push ( node . left ); if ( node . right !== null ) queue . push ( node . right ); nodeCount -- ; } console . log (); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 5 ); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree ( root ); printLevelOrder ( flippedRoot );
Producción
2 3 1 4 5
[Enfoque esperado - 2] Enfoque iterativo - O(n) Tiempo y O(n) Espacio
El solución iterativa sigue el mismo enfoque que el recursivo Lo único a lo que debemos prestar atención es ahorro la información del nodo que será sobrescrito .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++ // C++ program to flip a binary tree using // iterative approach #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * left * right ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = right = nullptr ; } }; // Method to flip the binary tree iteratively Node * flipBinaryTree ( Node * root ) { // intiliazing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states Node * curr = root * next = nullptr * prev = nullptr * ptr = nullptr ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { // pointing the next pointer to the // current next of left next = curr -> left ; // making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr -> left = ptr ; // storign the right child of // curr in temp ptr = curr -> right ; curr -> right = prev ; prev = curr ; curr = next ; } return prev ; } // Iterative method to do level order traversal // line by line void printLevelOrder ( Node * root ) { // Base Case if ( root == nullptr ) return ; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal queue < Node *> q ; // Enqueue Root and // initialize height q . push ( root ); while ( 1 ) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates number // of nodes at current level. int nodeCount = q . size (); if ( nodeCount == 0 ) break ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level and // Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { Node * node = q . front (); cout < < node -> data < < ' ' ; q . pop (); if ( node -> left != nullptr ) q . push ( node -> left ); if ( node -> right != nullptr ) q . push ( node -> right ); nodeCount -- ; } cout < < endl ; } } int main () { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node * root = new Node ( 1 ); root -> left = new Node ( 2 ); root -> right = new Node ( 3 ); root -> right -> left = new Node ( 4 ); root -> right -> right = new Node ( 5 ); root = flipBinaryTree ( root ); printLevelOrder ( root ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach class Node { int data ; Node left right ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = right = null ; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree ( Node root ) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states Node curr = root ; Node next = null ; Node prev = null ; Node ptr = null ; while ( curr != null ) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr . left ; // Making the right child of // prev as curr left child curr . left = ptr ; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr . right ; curr . right = prev ; prev = curr ; curr = next ; } return prev ; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) return ; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java . util . Queue < Node > q = new java . util . LinkedList <> (); // Enqueue Root and initialize // height q . add ( root ); while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q . size (); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { Node node = q . poll (); System . out . print ( node . data + ' ' ); if ( node . left != null ) q . add ( node . left ); if ( node . right != null ) q . add ( node . right ); nodeCount -- ; } System . out . println (); } } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 5 ); root = flipBinaryTree ( root ); printLevelOrder ( root ); } }
Python # Python program to flip a binary tree # using iterative approach class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . left = None self . right = None # Method to flip the binary tree # iteratively def flip_binary_tree ( root ): # Initializing the pointers to do # the swapping and storing states curr = root next = None prev = None ptr = None while curr is not None : # Pointing the next pointer to the # current next of left next = curr . left # Making the right child of prev # as curr left child curr . left = ptr # Storing the right child of # curr in ptr ptr = curr . right curr . right = prev prev = curr curr = next return prev # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder ( root ): if root is None : return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue . append ( root ) while queue : nodeCount = len ( queue ) while nodeCount > 0 : node = queue . pop ( 0 ) print ( node . data end = ' ' ) if node . left is not None : queue . append ( node . left ) if node . right is not None : queue . append ( node . right ) nodeCount -= 1 print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node ( 1 ) root . left = Node ( 2 ) root . right = Node ( 3 ) root . right . left = Node ( 4 ) root . right . right = Node ( 5 ) root = flip_binary_tree ( root ) printLevelOrder ( root )
C# // C# program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class Node { public int data ; public Node left right ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; left = right = null ; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree ( Node root ) { // Initializing the pointers to // do the swapping and storing states Node curr = root ; Node next = null ; Node prev = null ; Node ptr = null ; while ( curr != null ) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr . left ; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr . left = ptr ; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr . right ; curr . right = prev ; prev = curr ; curr = next ; } return prev ; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder ( Node root ) { if ( root == null ) return ; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal Queue < Node > q = new Queue < Node > (); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q . Enqueue ( root ); while ( q . Count > 0 ) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q . Count ; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { Node node = q . Dequeue (); Console . Write ( node . data + ' ' ); if ( node . left != null ) q . Enqueue ( node . left ); if ( node . right != null ) q . Enqueue ( node . right ); nodeCount -- ; } Console . WriteLine (); } } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 5 ); root = FlipBinaryTree ( root ); PrintLevelOrder ( root ); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using iterative approach class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . left = null ; this . right = null ; } } function flipBinaryTree ( root ) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states let curr = root ; let next = null ; let prev = null ; let ptr = null ; while ( curr !== null ) { // Pointing the next pointer to the // current next of left next = curr . left ; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr . left = ptr ; // Storing the right child of // curr in ptr ptr = curr . right ; curr . right = prev ; prev = curr ; curr = next ; } return prev ; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line function printLevelOrder ( root ) { if ( root === null ) return ; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal const queue = [ root ]; while ( queue . length > 0 ) { let nodeCount = queue . length ; while ( nodeCount > 0 ) { const node = queue . shift (); console . log ( node . data + ' ' ); if ( node . left !== null ) queue . push ( node . left ); if ( node . right !== null ) queue . push ( node . right ); nodeCount -- ; } console . log (); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node ( 1 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 4 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 5 ); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree ( root ); printLevelOrder ( flippedRoot );
Producción
2 3 1 4 5







![Perro encadenado al frente de una casa en Texas con inundaciones hasta la cabeza [VIDEO DE RESCATE]](https://techcodeview.com/img/trending/65/dog-chained-to-front-of-house-in-texas-flood-waters-up-to-her-head-rescue-video.webp)