Encuentre todas las secuencias binarias de longitud par con la misma suma de la primera y segunda mitad de bits
Dado un número n, encuentre todas las secuencias binarias de longitud 2n tales que la suma de los primeros n bits sea la misma que la suma de los últimos n bits.
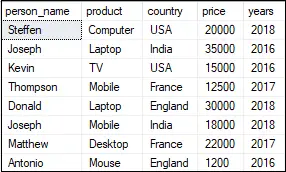
Ejemplos:
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
La idea es arreglar el primer y el último bit y luego repetir los 2*(n-1) bits restantes. Hay cuatro posibilidades cuando arreglamos los primeros y últimos bits:
- El primer y último bit son 1 n restante; 1 bit en ambos lados también debe tener la misma suma.
- El primer y último bit son 0 y los n - 1 bits restantes en ambos lados también deben tener la misma suma.
- El primer bit es 1 y el último bit es 0. La suma de los n - 1 bits restantes en el lado izquierdo debe ser 1 menos que la suma de n - 1 bits en el lado derecho.
- El primer bit es 0 y el último bit es 1. La suma de los n - 1 bits restantes en el lado izquierdo debe ser 1 más que la suma de n - 1 bits en el lado derecho.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior:
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include using namespace std ; // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index void findAllSequences ( int diff char * out int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) cout < < out < < ' ' ; return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program int main () { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char out [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // null terminate output array out [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.* ; import java.util.* ; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences ( int diff char out [] int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if ( Math . abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { System . out . print ( out ); System . out . print ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' ; out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' ; out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program public static void main ( String [] args ) { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char [] out = new char [ 2 * n + 1 ] ; // null terminate output array out [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
Python3 # Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences ( diff out start end ): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) // 2 ): return ; # if all bits are filled if ( start > end ): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ): print ( '' . join ( list ( out )) end = ' ' ); return ; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' ; out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' ; out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); # Driver program # input number n = 2 ; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out = [ '' ] * ( 2 * n ); findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); # This code is contributed by mits
C# // C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System ; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences ( int diff char [] outt int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if ( Math . Abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { Console . Write ( outt ); Console . Write ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt [ start ] = '0' ; outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt [ start ] = '1' ; outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char [] outt = new char [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // null terminate output array outt [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 outt 0 2 * n - 1 ); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
PHP // PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start $end ) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( $diff ) > ( int )(( $end - $start + 1 ) / 2 )) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( $start > $end ) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( $diff == 0 ) print ( implode ( '' $out ) . ' ' ); return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out [ $start ] = '0' ; $out [ $end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( $diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out [ $start ] = $out [ $end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out [ $start ] = $out [ $end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out [ $start ] = '1' ; $out [ $end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( $diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out = array_fill ( 0 2 * $n '' ); findAllSequences ( 0 $out 0 2 * $n - 1 ); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?>
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences ( diff outt start end ) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if ( Math . abs ( diff ) > parseInt (( end - start + 1 ) / 2 10 )) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { document . write ( outt . join ( '' )); document . write ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt [ start ] = '0' ; outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt [ start ] = '1' ; outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); } // input number let n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array ( 2 * n + 1 ); // null terminate output array outt [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 outt 0 2 * n - 1 ); < /script>
Producción
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
Complejidad del tiempo: O((4 ^ N )* N)
4^N debido a 4 llamadas recursivas y N (simplificado de 2N) por el tiempo dedicado a imprimir cadenas de tamaño 2N
Espacio Auxiliar: EN)
Existe otro enfoque mediante el cual generamos todas las cadenas posibles de longitud n y las almacenamos en una lista en un índice que representa su suma. Luego iteramos a través de cada lista y generamos las cadenas de tamaño 2n imprimiendo cada cadena con todas las demás cadenas de la lista sumando el mismo valor.
C++ // C++ program to implement the approach #include using namespace std ; //function that generates the sequence void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n vector < vector < string > >& sumToString vector < string > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if ( n == 0 ) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index string seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . size (); i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence [ i ]; } vector < string > x = sumToString [ sumSoFar ]; x . push_back ( seq ); sumToString [ sumSoFar ] = x ; return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . push_back ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . erase ( sequence . begin ()); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . push_back ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . erase ( sequence . begin ()); } // function to form permutations of the sequences void permuteSequences ( vector < vector < string > > sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . size (); sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. size (); sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. size (); sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . size () - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] . size () - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] . size () - 1 ) { cout < < '1111 ' ; } else { cout < < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] [ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] [ sequence2 ] < < ' ' ; } } } } } // function that finds all the subsequences void findAllSequences ( int n ) { vector < vector < string > > sumToString ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . push_back ( vector < string > ()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString vector < string > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } // Driver Code int main () { // Function Call findAllSequences ( 2 ); return 0 ; } // this code is contributed by phasing17
Java // Java program to implement the approach import java.util.* ; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString = new ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . add ( new ArrayList < String > ()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString new ArrayList < String > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } static void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString ArrayList < String > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if ( n == 0 ) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . size (); i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence . get ( i ); } ArrayList < String > x = sumToString . get ( sumSoFar ); x . add ( seq ); sumToString . set ( sumSoFar x ); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . add ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . remove ( 0 ); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . add ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . remove ( 0 ); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences ( ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . size (); sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ). size (); sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ). size (); sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . size () - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . size () - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . size () - 1 ) { System . out . print ( '1111' ); } else { System . out . println ( sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . get ( sequence1 ) + sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . get ( sequence2 )); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Function Call findAllSequences ( 2 ); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
Python3 def findAllSequences ( n ): sumToString = [[] for x in range ( n + 1 )] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString [] 0 ) permuteSequences ( sumToString ) def generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString sequence sumSoFar ): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0 : sumToString [ sumSoFar ] . append ( '' . join ( sequence )) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence . append ( '0' ) generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ) sequence . pop () #Generate sequence +1 sequence . append ( '1' ) generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ) sequence . pop () def permuteSequences ( sumToString ): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString : # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr : for sequence2 in sumIndexArr : print ( sequence1 + sequence2 ) findAllSequences ( 2 ) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GFG { static void findAllSequences ( int n ) { List < List < string >> sumToString = new List < List < string >> (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . Add ( new List < string > ()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString new List < string > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } static void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n List < List < string >> sumToString List < string > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if ( n == 0 ) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . Count ; i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence [ i ]; } sumToString [ sumSoFar ]. Add ( seq ); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . Add ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . RemoveAt ( 0 ); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . Add ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . RemoveAt ( 0 ); } static void permuteSequences ( List < List < string >> sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . Count ; sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count ; sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count ; sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . Count - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count - 1 ) { Console . Write ( '1111' ); } else { Console . WriteLine ( sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence2 ]); } } } } } static void Main () { findAllSequences ( 2 ); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
JavaScript < script > function findAllSequences ( n ) { let sumToString = []; for ( let i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . push ([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString [] 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } function generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString sequence sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if ( n == 0 ) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString [ sumSoFar ]. push ( sequence . join ( '' )); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . push ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . shift (); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . push ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . shift (); } function permuteSequences ( sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( let sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . length ; sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( let sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length ; sequence1 ++ ) { for ( let sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length ; sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . length - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length - 1 ) { document . write ( '1111' ); } else { document . write ( sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence2 ] + ' ' ); } } } } } findAllSequences ( 2 ); // This code is contributed by decode2207. < /script>
Producción
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Análisis de complejidad del tiempo:
generarSecuenciasConSuma =O((2 norte )*NORTE)
- 2 norte : generamos todas las permutaciones de cadenas binarias de tamaño N
- N: convierte la lista de caracteres en una cadena y la almacena en una matriz. Esto se hace en el caso base.
permutarSecuencias =O((2 norte ) * ¡N!/(N/2)! 2 * norte)
- 2 norte : iteramos a través de toda la cadena generada de tamaño n
- N!/(N/2)! 2 : Este es un poco difícil de explicar.
tomemos N = 2 como ejemplo. Nuestro conjunto de posibles secuencias de tamaño n sería:
| índice de matriz | 1 | 2 | |
| lista de cadenas | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
En la lista de cadenas cuyo índice representa la suma, obtenemos el recuento de cadenas de tamaño 2n usando la fórmula 'n elija k'. En nuestro caso sería nCk *nCk donde k representa el número de unos en cada mitad de la cadena de tamaño 2n:
k = 0 tenemos (2C0)^2 = 1 cadena (0000)
k = 1 tenemos (2C1)^2 cadena = 4 cadenas(0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2 tenemos (2c2)^2 = 1 cadena (1111)
Obtenemos nuestra lista más larga de cadenas cuando k = N/2 por lo tanto norte do n/2 = N!/[(N/2)! * (N - N/2)!] lo que se simplifica a norte do n/2 = N!/(N/2)! 2
Por lo tanto, para cada elemento debemos iterar como máximo norte do n/2 para formar cuerdas de longitud 2N
Sin prueba formal si graficamos 2^N y N!/(N/2)! 2 vemos que 2 norte tiene una tasa de crecimiento más rápida que este último. Por lo tanto O(2 norte * ¡N!/(N/2) 2 ) < O(2 norte *2 norte ) = O(2 2n ) = O(4 norte )
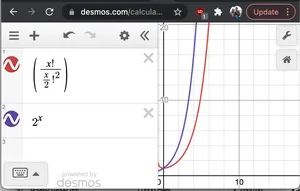
 Gráfica de 2^x y nC(n/2)
Gráfica de 2^x y nC(n/2) - N: debemos imprimir cada cadena de tamaño 2N
Finalmente podemos ignorar la complejidad temporal de generateSequencesWithSum porque permuteSequence es el término principal.
Complejidad del tiempo: o(2 norte *¡N!/(N/2)! 2 * N) (mejor que la primera solución de O((4^N) * N; consulte la explicación anterior para obtener más detalles)
Espacio auxiliar :O(2 norte ) porque almacenamos todas las permutaciones de cadenas binarias de tamaño N
#include using namespace std ; class FirstHalf { public : string data ; int sum ; FirstHalf ( string data int sum ) { this -> data = data ; this -> sum = sum ; } }; // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map < int vector < string >> mp ; // first N-half bits vector < FirstHalf > firstHalf ; // function to find sum of the bits from a String int sumOfString ( string s ) { int sum = 0 ; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( auto c : s ) { sum += ( c - '0' ); } return sum ; } void perm ( string p char * bin int level int n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . push_back ( FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value mp [ sum ]. push_back ( p ); return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { char c = bin [ i ]; perm ( p + c bin level -1 n ); } } void result () { int i = 0 ; for ( auto first : firstHalf ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key vector < string > secondHalf = mp [ sum ]; for ( auto second : secondHalf ) { // append first and second half and print cout < < first . data + second < < ' ' ; // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) cout < < endl ; } } } int main (){ char up [ 2 ] = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; string x = '' ; perm ( x up n n ); result (); return 0 ; } // This code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
Java import java.util.* ; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data ; int sum ; FirstHalf ( String data int sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map < Integer ArrayList < String >> map = new HashMap <> (); //first N-half bits static List < FirstHalf > firstHalf = new ArrayList <> (); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString ( String s ) { int sum = 0 ; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( char c : s . toCharArray ()) { sum += c - '0' ; } return sum ; } public static void perm ( String p char [] bin int level int n ) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . add ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map . putIfAbsent ( sum new ArrayList < String > ()); map . get ( sum ). add ( p ); return ; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( char c : bin ) { perm ( p + c bin level - 1 n ); } } public static void result () { int i = 0 ; for ( FirstHalf first : firstHalf ) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList < String > secondHalf = map . get ( sum ); for ( String second : secondHalf ) { //append first and second half and print System . out . print ( first . data + second + ' ' ); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) System . out . println (); } } } public static void main ( String [] args ) { char [] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; perm ( '' up n n ); result (); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
Python3 # Python code implementation class FirstHalf : def __init__ ( self data sum ): self . data = data self . sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString ( s ): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range ( len ( s )): sum += ord ( s [ i ]) - ord ( '0' ) return sum def perm ( p bin level n ): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0 : # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString ( p ) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . append ( FirstHalf ( p sum )) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map : map [ sum ] = [] map [ sum ] . append ( p ) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range ( len ( bin )): perm ( p + bin [ i ] bin level - 1 n ) def result (): i = 0 for j in range ( len ( firstHalf )): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf [ j ] . sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map [ sum ] for k in range ( len ( secondHalf )): # append first and second half and print print ( firstHalf [ j ] . data + secondHalf [ k ] + ' ' end = '' ) # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if ( i % 6 == 0 ): print ( ' n ' ) up = [ '0' '1' ] n = 2 perm ( '' up n n ) result () # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class FirstHalf { public string data ; public int sum ; public FirstHalf ( string data int sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary < int List < string >> mp = new Dictionary < int List < string >> (); // first N-half bits static List < FirstHalf > firstHalf = new List < FirstHalf > (); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString ( string s ) { int sum = 0 ; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach ( char c in s ) { sum += ( c - '0' ); } return sum ; } static void perm ( string p char [] bin int level int n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . Add ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if ( mp . ContainsKey ( sum )) { mp [ sum ]. Add ( p ); } else { mp . Add ( sum new List < string > { p }); } return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { char c = bin [ i ]; perm ( p + c bin level - 1 n ); } } static void result () { int i = 0 ; foreach ( FirstHalf first in firstHalf ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List < string > secondHalf = mp [ sum ]; foreach ( string second in secondHalf ) { // append first and second half and print Console . Write ( first . data + second + ' ' ); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) Console . WriteLine (); } } } static void Main ( string [] args ) { char [] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; string x = '' ; perm ( x up n n ); result (); } }
JavaScript class FirstHalf { constructor ( data sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map (); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString ( s ) { let sum = 0 ; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( let i = 0 ; i < s . length ; i ++ ) { sum += s . charCodeAt ( i ) - '0' . charCodeAt ( 0 ); } return sum ; } function perm ( p bin level n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . push ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if ( ! map . has ( sum )) map . set ( sum []); map . get ( sum ). push ( p ); return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( let i = 0 ; i < bin . length ; i ++ ) { perm ( p + bin [ i ] bin level - 1 n ); } } function result () { let i = 0 ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < firstHalf . length ; j ++ ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf [ j ]. sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map . get ( sum ); for ( let k = 0 ; k < secondHalf . length ; k ++ ) { // append first and second half and print process . stdout . write ( firstHalf [ j ]. data + secondHalf [ k ] + ' ' ); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) process . stdout . write ( 'n' ); } } } const up = [ '0' '1' ]; const n = 2 ; perm ( '' up n n ); result ();
Producción
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
Algoritmo:
1. Genere todas las permutaciones binarias de tamaño n.
2. Calcule la suma de los bits de cada permutación y recuérdelo para la segunda mitad.
[por ejemplo: para n=2 recuerde que hay dos cadenas con suma = 1, es decir, '01' '10']
3. Iterar todas las permutaciones generadas y para cada una de ellas agregar la segunda mitad según la suma de los bits.
Análisis de complejidad del tiempo:
sumaDeCadena() = O(N): atraviesa cada bit y lo suma a la suma
permanente() =O(2 norte * norte)
2N * N: generamos todas las permutaciones de bits binarios de tamaño N y encontramos la suma de los bits para cada permutación
resultado() =O((2 norte ) * (N!/(N/2)!)2)
2 norte : iteramos a través de todas las permutaciones posibles de tamaño N (primera mitad)
NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)! 2 : (segunda mitad del tamaño máximo): explicación a continuación:
tomemos N = 4 como ejemplo:
//Hash-Map parece
0 -> [0000] ................................(tamaño de lista: 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] ................................(tamaño de lista: 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] ................................(tamaño de lista: 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] ................................(tamaño de lista: 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] ................................(tamaño de lista: 4C4 = 1)
Observamos aquí que cada lista tiene un tamaño de N elija Clave que será máximo en N elija N/2
Ya que estamos iterando los 2 norte permutaciones y añadiendo la segunda mitad del mapa. El mapa tiene la lista de tamaño máximo en la posición N/2.
¡El peor de los casos ocurre en la posición N/2 donde tenemos que atravesar NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)! 2 permutaciones.
Complejidad del tiempo: O(2 norte *¡N!/(N/2)! 2 )
Espacio auxiliar: O(2 norte ) porque almacenamos todas las permutaciones de cadenas binarias de tamaño N