Análisis asintótico y comparación de algoritmos de clasificación.
Es un hecho bien establecido que la ordenación por fusión se ejecuta más rápido que la ordenación por inserción. Usando análisis asintótico . podemos demostrar que la ordenación por fusión se ejecuta en tiempo O (nlogn) y la ordenación por inserción toma O (n^2). Es obvio porque la ordenación por fusión utiliza un enfoque de divide y vencerás al resolver los problemas de forma recursiva, mientras que la ordenación por inserción sigue un enfoque incremental. Si analizamos aún más el análisis de la complejidad del tiempo, sabremos que el tipo de inserción no es tan malo. Sorprendentemente, la ordenación por inserción supera a la ordenación por combinación en un tamaño de entrada más pequeño. Esto se debe a que hay pocas constantes que ignoramos al deducir la complejidad del tiempo. En tamaños de entrada más grandes del orden 10^4 esto no influye en el comportamiento de nuestra función. Pero cuando los tamaños de entrada caen por debajo de, digamos, menos de 40, entonces las constantes de la ecuación dominan el tamaño de entrada 'n'. Hasta ahora, todo bien. Pero no estaba satisfecho con ese análisis matemático. Como estudiantes de informática debemos creer en escribir código. Escribí un programa en C para tener una idea de cómo los algoritmos compiten entre sí por varios tamaños de entrada. Y también por qué se realiza un análisis matemático tan riguroso para establecer las complejidades del tiempo de ejecución de estos algoritmos de clasificación.
Implementación:
CPP #include #include #include #include #define MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY 1000000001 int cmpfunc ( const void * a const void * b ) { // Compare function used by qsort return ( * ( int * ) a - * ( int * ) b ); } int * generate_random_array ( int n ) { srand ( time ( NULL )); int * a = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = rand () % MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ; return a ; } int * copy_array ( int a [] int n ) { int * arr = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * n ); int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) arr [ i ] = a [ i ]; return arr ; } // Code for Insertion Sort void insertion_sort_asc ( int a [] int start int end ) { int i ; for ( i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; ++ i ) { int key = a [ i ]; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; -- j ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Code for Merge Sort void merge ( int a [] int start int end int mid ) { int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; int * aux = malloc ( sizeof ( int ) * ( end - start + 1 )); while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; else aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; } while ( i <= mid ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ i ++ ]; while ( j <= end ) aux [ k ++ ] = a [ j ++ ]; j = 0 ; for ( i = start ; i <= end ; ++ i ) a [ i ] = aux [ j ++ ]; free ( aux ); } void _merge_sort ( int a [] int start int end ) { if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; _merge_sort ( a start mid ); _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void merge_sort ( int a [] int n ) { return _merge_sort ( a 0 n - 1 ); } void insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( int a [] int start int end int k ) { // Performs insertion sort if size of array is less than or equal to k // Otherwise uses mergesort if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { return insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ); } int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } void test_sorting_runtimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Measuring the runtime of the sorting algorithms int number_of_times = num_of_times ; int t = number_of_times ; int n = size ; double insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 ; double merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 ; while ( t -- ) { clock_t start end ; int * a = generate_random_array ( n ); int * b = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 n - 1 ); end = clock (); insertion_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( b ); int * c = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); merge_sort ( c n ); end = clock (); merge_sort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( c ); int * d = copy_array ( a n ); start = clock (); insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 n - 1 40 ); end = clock (); merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( d ); start = clock (); qsort ( a n sizeof ( int ) cmpfunc ); end = clock (); qsort_time += (( double )( end - start )) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC ; free ( a ); } insertion_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_time /= number_of_times ; merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= number_of_times ; qsort_time /= number_of_times ; printf ( ' n Time taken to sort: n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f n ' '%-35s %f nn ' '(i)Insertion sort: ' insertion_sort_time '(ii)Merge sort: ' merge_sort_time '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time '(iv)Qsort library function: ' qsort_time ); } int main ( int argc char const * argv []) { int t ; scanf ( '%d' & t ); while ( t -- ) { int size num_of_times ; scanf ( '%d %d' & size & num_of_times ); test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ); } return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Scanner ; import java.util.Arrays ; import java.util.Random ; public class SortingAlgorithms { // Maximum element in array static final int MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; public static void main ( String [] args ) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( System . in ); int t = scanner . nextInt (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < t ; i ++ ) { int size = scanner . nextInt (); int num_of_times = scanner . nextInt (); testSortingRuntimes ( size num_of_times ); } scanner . close (); } static int [] generateRandomArray ( int n ) { // Generate an array of n random integers. int [] arr = new int [ n ] ; Random random = new Random (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { arr [ i ] = random . nextInt ( MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ); } return arr ; } static void insertionSortAsc ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for ( int i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { int key = a [ i ] ; int j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] ; j -- ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } static void merge ( int [] a int start int end int mid ) { // Merge two sorted sublists of a. // The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. int [] aux = new int [ end - start + 1 ] ; int i = start j = mid + 1 k = 0 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ] ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } else { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ; } System . arraycopy ( aux 0 a start aux . length ); } static void mergeSort ( int [] a ) { // Perform an in-place merge sort on a. mergeSortHelper ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } static void mergeSortHelper ( int [] a int start int end ) { // Recursive merge sort function. if ( start < end ) { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; mergeSortHelper ( a start mid ); mergeSortHelper ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } static void insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( int [] a int start int end int k ) { /* Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. */ if ( start < end ) { int size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { int mid = start + ( end - start ) / 2 ; insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } static void testSortingRuntimes ( int size int num_of_times ) { // Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. double insertionSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortTime = 0 ; double mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; double qsortTime = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < num_of_times ; i ++ ) { int [] a = generateRandomArray ( size ); int [] b = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); long start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); long end = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; int [] c = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSort ( c ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; int [] d = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; int [] e = Arrays . copyOf ( a a . length ); start = System . currentTimeMillis (); Arrays . sort ( e ); end = System . currentTimeMillis (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortTime /= num_of_times ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= num_of_times ; qsortTime /= num_of_times ; System . out . println ( 'nTime taken to sort:n' + '(i) Insertion sort: ' + insertionSortTime + 'n' + '(ii) Merge sort: ' + mergeSortTime + 'n' + '(iii) Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ' + mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime + 'n' + '(iv) Qsort library function: ' + qsortTime + 'n' ); } }
Python3 import time import random import copy from typing import List # Maximum element in array MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 def generate_random_array ( n : int ) -> List [ int ]: #Generate a list of n random integers. return [ random . randint ( 0 MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY ) for _ in range ( n )] def insertion_sort_asc ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end. for i in range ( start + 1 end + 1 ): key = a [ i ] j = i - 1 while j >= start and a [ j ] > key : a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ] j -= 1 a [ j + 1 ] = key def merge ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int mid : int ) -> None : #Merge two sorted sublists of a. #The first sublist is a[start:mid+1] and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1]. aux = [] i = start j = mid + 1 while i <= mid and j <= end : if a [ i ] <= a [ j ]: aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 else : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 while i <= mid : aux . append ( a [ i ]) i += 1 while j <= end : aux . append ( a [ j ]) j += 1 a [ start : end + 1 ] = aux def _merge_sort ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int ) -> None : #Recursive merge sort function. if start < end : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 _merge_sort ( a start mid ) _merge_sort ( a mid + 1 end ) merge ( a start end mid ) def merge_sort ( a : List [ int ]) -> None : #Perform an in-place merge sort on a. _merge_sort ( a 0 len ( a ) - 1 ) def insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a : List [ int ] start : int end : int k : int ) -> None : ''' Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end. If the size of the list is less than or equal to k use insertion sort. Otherwise use merge sort. ''' if start < end : size = end - start + 1 if size <= k : insertion_sort_asc ( a start end ) else : mid = start + ( end - start ) // 2 insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a start mid k ) insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( a mid + 1 end k ) merge ( a start end mid ) def test_sorting_runtimes ( size : int num_of_times : int ) -> None : #Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms. insertion_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_time = 0 merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0 qsort_time = 0 for _ in range ( num_of_times ): a = generate_random_array ( size ) b = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_sort_asc ( b 0 len ( b ) - 1 ) end = time . time () insertion_sort_time += end - start c = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () merge_sort ( c ) end = time . time () merge_sort_time += end - start d = copy . deepcopy ( a ) start = time . time () insertion_and_merge_sort_combine ( d 0 len ( d ) - 1 40 ) end = time . time () merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += end - start start = time . time () a . sort () end = time . time () qsort_time += end - start insertion_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_time /= num_of_times merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= num_of_times qsort_time /= num_of_times print ( f ' n Time taken to sort: n ' f '(i)Insertion sort: { insertion_sort_time } n ' f '(ii)Merge sort: { merge_sort_time } n ' f '(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: { merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time } n ' f '(iv)Qsort library function: { qsort_time } n ' ) def main () -> None : t = int ( input ()) for _ in range ( t ): size num_of_times = map ( int input () . split ()) test_sorting_runtimes ( size num_of_times ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript // Importing required modules const { performance } = require ( 'perf_hooks' ); // Maximum element in array const MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001 ; // Function to generate a list of n random integers function generateRandomArray ( n ) { return Array . from ({ length : n } () => Math . floor ( Math . random () * MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY )); } // Function to perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end function insertionSortAsc ( a start end ) { for ( let i = start + 1 ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { let key = a [ i ]; let j = i - 1 ; while ( j >= start && a [ j ] > key ) { a [ j + 1 ] = a [ j ]; j -= 1 ; } a [ j + 1 ] = key ; } } // Function to merge two sorted sublists of a function merge ( a start end mid ) { let aux = []; let i = start ; let j = mid + 1 ; while ( i <= mid && j <= end ) { if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ]) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } else { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } } while ( i <= mid ) { aux . push ( a [ i ]); i += 1 ; } while ( j <= end ) { aux . push ( a [ j ]); j += 1 ; } for ( let i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) { a [ i ] = aux [ i - start ]; } } // Recursive merge sort function function _mergeSort ( a start end ) { if ( start < end ) { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); _mergeSort ( a start mid ); _mergeSort ( a mid + 1 end ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } // Function to perform an in-place merge sort on a function mergeSort ( a ) { _mergeSort ( a 0 a . length - 1 ); } // Function to perform an in-place sort on a from start to end function insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start end k ) { if ( start < end ) { let size = end - start + 1 ; if ( size <= k ) { insertionSortAsc ( a start end ); } else { let mid = start + Math . floor (( end - start ) / 2 ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a start mid k ); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( a mid + 1 end k ); merge ( a start end mid ); } } } // Function to test the runtime of the sorting algorithms function testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ) { let insertionSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortTime = 0 ; let mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0 ; let qsortTime = 0 ; for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < numOfTimes ; _ ++ ) { let a = generateRandomArray ( size ); let b = [... a ]; let start = performance . now (); insertionSortAsc ( b 0 b . length - 1 ); let end = performance . now (); insertionSortTime += end - start ; let c = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); mergeSort ( c ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortTime += end - start ; let d = [... a ]; start = performance . now (); insertionAndMergeSortCombine ( d 0 d . length - 1 40 ); end = performance . now (); mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start ; start = performance . now (); a . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); end = performance . now (); qsortTime += end - start ; } insertionSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortTime /= numOfTimes ; mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= numOfTimes ; qsortTime /= numOfTimes ; console . log ( `nTime taken to sort:n(i)Insertion sort: ${ insertionSortTime } n(ii)Merge sort: ${ mergeSortTime } n(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ${ mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime } n(iv)Qsort library function: ${ qsortTime } n` ); } // Main function function main () { let t = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of test cases: ' )); for ( let _ = 0 ; _ < t ; _ ++ ) { let size = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the size of the array: ' )); let numOfTimes = parseInt ( prompt ( 'Enter the number of times to run the test: ' )); testSortingRuntimes ( size numOfTimes ); } } // Call the main function main ();
He comparado los tiempos de ejecución de los siguientes algoritmos:
- Orden de inserción : El algoritmo tradicional sin modificaciones/optimización. Funciona muy bien para tamaños de entrada más pequeños. Y sí, supera la ordenación por combinación
- va el destino : Sigue el enfoque de divide y vencerás. Para tamaños de entrada del orden de 10^5, este algoritmo es la elección correcta. Hace que la ordenación por inserción no sea práctica para tamaños de entrada tan grandes.
- Versión combinada de ordenación por inserción y ordenación por combinación: He modificado un poco la lógica de ordenación por combinación para lograr un tiempo de ejecución considerablemente mejor para tamaños de entrada más pequeños. Como sabemos, merge sort divide su entrada en dos mitades hasta que sea lo suficientemente trivial como para ordenar los elementos. Pero aquí, cuando el tamaño de entrada cae por debajo de un umbral como 'n' < 40 then this hybrid algorithm makes a call to traditional insertion sort procedure. From the fact that insertion sort runs faster on smaller inputs and merge sort runs faster on larger inputs this algorithm makes best use both the worlds.
- Clasificación rápida: No he implementado este procedimiento. Esta es la función de biblioteca qsort() que está disponible en formato . He considerado este algoritmo para conocer el significado de la implementación. Se requiere una gran experiencia en programación para minimizar la cantidad de pasos y aprovechar al máximo las primitivas del lenguaje subyacente para implementar un algoritmo de la mejor manera posible. Esta es la razón principal por la que se recomienda utilizar funciones de biblioteca. Están escritos para manejar cualquier cosa. Se optimizan al máximo posible. ¡Y antes de que me olvide de mi análisis, qsort() se ejecuta increíblemente rápido en prácticamente cualquier tamaño de entrada!
El análisis:
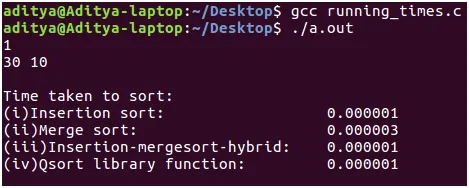
- Aporte: El usuario debe proporcionar la cantidad de veces que desea probar el algoritmo correspondiente a la cantidad de casos de prueba. Para cada caso de prueba, el usuario debe ingresar dos números enteros separados por espacios que indican el tamaño de entrada 'n' y el 'num_of_times' que indica la cantidad de veces que desea ejecutar el análisis y tomar el promedio. (Aclaración: si 'num_of_times' es 10, entonces cada uno de los algoritmos especificados anteriormente se ejecuta 10 veces y se toma el promedio. Esto se hace porque la matriz de entrada se genera aleatoriamente correspondiente al tamaño de entrada que usted especifica. La matriz de entrada podría estar toda ordenada. Nuestro podría corresponder al peor de los casos, es decir, orden descendente. Para evitar tiempos de ejecución de dichas matrices de entrada. El algoritmo se ejecuta 'num_of_times' y se toma el promedio). Rutina clock() y la macro CLOCKS_PER_SEC se utiliza para medir el tiempo necesario. Compilación: he escrito el código anterior en un entorno Linux (Ubuntu 16.04 LTS). Copie el fragmento de código de arriba. Compílelo usando la clave gcc en las entradas como se especifica y admire el poder de los algoritmos de clasificación.
- Resultados: Como puede ver, para tamaños de entrada pequeños, la inserción ordena los tiempos, la combinación se ordena por 2 * 10 ^ -6 seg. Pero esta diferencia de tiempo no es tan significativa. Por otro lado, el algoritmo híbrido y la función de biblioteca qsort() funcionan tan bien como la ordenación por inserción.
 El tamaño de entrada ahora aumenta aproximadamente 100 veces hasta n = 1000 desde n = 30. La diferencia ahora es tangible. La ordenación por combinación se ejecuta 10 veces más rápido que la ordenación por inserción. Nuevamente existe un vínculo entre el desempeño del algoritmo híbrido y la rutina qsort(). Esto sugiere que qsort() se implementa de una manera que es más o menos similar a nuestro algoritmo híbrido, es decir, cambiando entre diferentes algoritmos para aprovecharlos al máximo.
El tamaño de entrada ahora aumenta aproximadamente 100 veces hasta n = 1000 desde n = 30. La diferencia ahora es tangible. La ordenación por combinación se ejecuta 10 veces más rápido que la ordenación por inserción. Nuevamente existe un vínculo entre el desempeño del algoritmo híbrido y la rutina qsort(). Esto sugiere que qsort() se implementa de una manera que es más o menos similar a nuestro algoritmo híbrido, es decir, cambiando entre diferentes algoritmos para aprovecharlos al máximo.  Finalmente, el tamaño de entrada se incrementa a 10^5 (¡1 Lakh!), que probablemente sea el tamaño ideal utilizado en escenarios prácticos. En comparación con la entrada anterior n = 1000, donde la ordenación por combinación venció a la ordenación por inserción al ejecutarse 10 veces más rápido, aquí la diferencia es aún más significativa. ¡La clasificación por combinación supera la clasificación por inserción 100 veces! De hecho, el algoritmo híbrido que hemos escrito supera la clasificación por fusión tradicional al ejecutarse 0,01 segundos más rápido. Y, por último, qsort() la función de biblioteca finalmente nos demuestra que la implementación también juega un papel crucial al medir meticulosamente los tiempos de ejecución al ejecutar 3 milisegundos más rápido. :D
Finalmente, el tamaño de entrada se incrementa a 10^5 (¡1 Lakh!), que probablemente sea el tamaño ideal utilizado en escenarios prácticos. En comparación con la entrada anterior n = 1000, donde la ordenación por combinación venció a la ordenación por inserción al ejecutarse 10 veces más rápido, aquí la diferencia es aún más significativa. ¡La clasificación por combinación supera la clasificación por inserción 100 veces! De hecho, el algoritmo híbrido que hemos escrito supera la clasificación por fusión tradicional al ejecutarse 0,01 segundos más rápido. Y, por último, qsort() la función de biblioteca finalmente nos demuestra que la implementación también juega un papel crucial al medir meticulosamente los tiempos de ejecución al ejecutar 3 milisegundos más rápido. :D

Nota: No ejecute el programa anterior con n >= 10^6 ya que requerirá mucha potencia informática. ¡Gracias y feliz codificación! :)
Crear cuestionario