Drucken aller Lösungen im N-Queen-Problem
Gegeben eine ganze Zahl N Die Aufgabe besteht darin, alle zu finden unterschiedliche Lösungen zum N-Damen-Problem Wo N Königinnen werden auf eine gelegt n * n Schachbrett so, dass sich keine zwei Damen gegenseitig angreifen können.
Notiz: Jede Lösung ist eine einzigartige Konfiguration von N Königinnen dargestellt als Permutation von [123....n] . Die Nummer am ich Th Position gibt die Reihe der Königin in der an ich Th Spalte. Zum Beispiel [3142] zeigt ein solches Layout.
Beispiel:
Eingang: n = 4
Ausgabe: [2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]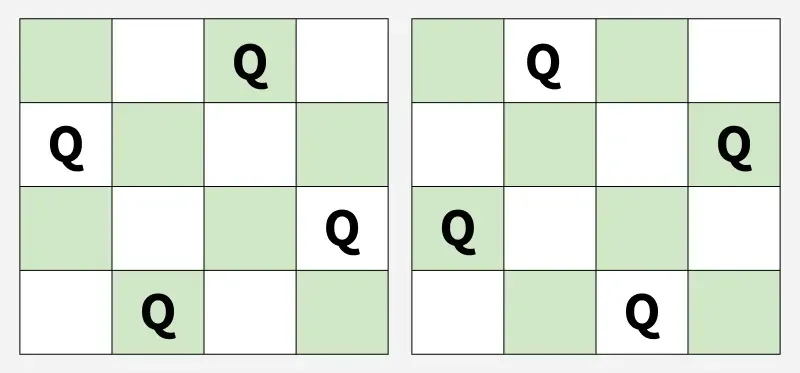
Erläuterung : Dies sind die 2 möglichen Lösungen.Eingang: n = 2
Ausgabe: []
Erläuterung: Keine Lösung, da Königinnen sich in allen möglichen Konfigurationen gegenseitig angreifen können.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- [Naiver Ansatz] Durch Generieren aller Permutationen mithilfe der Rekursion
- [Erwarteter Ansatz] Verwendung von Backtracking mit Pruning
- [Alternativer Ansatz] Backtracking mithilfe der Bitmaskierung
[Naiver Ansatz] – Rekursion verwenden – O(n! * n) Zeit und O(n) Raum
Eine einfache Idee, das zu lösen N-Queens-Problem besteht darin, alle möglichen Permutationen von zu generieren [1 2 3 ... n] und prüfen Sie dann, ob es sich um eine gültige N-Queens-Konfiguration handelt. Da sich jede Königin in einer anderen Zeile und Spalte befinden muss Permutationen automatisch verwenden kümmert sich um diese Regeln. Aber wir müssen noch überprüfen, ob sich keine zwei Königinnen auf dem Feld befinden gleiche Diagonale.
Unten ist angegeben Durchführung:
C++ //C++ program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion #include #include #include using namespace std ; // Function to check if the current placement is safe bool isSafe ( vector < int >& board int currRow int currCol ) { // Check all previously placed queens for ( int i = 0 ; i < board . size (); ++ i ) { int placedRow = board [ i ]; // Columns are 1-based int placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check if the queen is on the same diagonal if ( abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } // Safe to place the queen return true ; } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations void nQueenUtil ( int col int n vector < int >& board vector < vector < int >>& res vector < bool >& visited ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . push_back ( board ); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if the row is already used if ( ! visited [ row ]) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark the row as used visited [ row ] = true ; // Place the queen board . push_back ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop_back (); // Unmark row visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle vector < vector < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { vector < vector < int >> res ; // Current board configuration vector < int > board ; // Track used rows vector < bool > visited ( n + 1 false ); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } int main () { int n = 4 ; vector < vector < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < res . size (); i ++ ) { cout < < '[' ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { cout < < res [ i ][ j ]; if ( j != n - 1 ) cout < < ' ' ; } cout < < '] n ' ; } return 0 ; }
Java //Java program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion import java.util.ArrayList ; class GfG { // Check if placement is safe static boolean isSafe ( ArrayList < Integer > board int currRow int currCol ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < board . size (); i ++ ) { int placedRow = board . get ( i ); int placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check diagonals if ( Math . abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == Math . abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } return true ; // Safe to place } // Recursive utility to solve static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n ArrayList < Integer > board ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res boolean [] visited ) { // If all queens placed add to res if ( col > n ) { res . add ( new ArrayList <> ( board )); return ; } // Try each row in column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; row ++ ) { // If row not used if ( ! visited [ row ] ) { // Check safety if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark row visited [ row ] = true ; // Place queen board . add ( row ); // Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack board . remove ( board . size () - 1 ); visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Function to solve N-Queen static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nQueen ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = new ArrayList <> (); ArrayList < Integer > board = new ArrayList <> (); boolean [] visited = new boolean [ n + 1 ] ; nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 4 ; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > row : res ) { System . out . print ( '[' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < row . size (); i ++ ) { System . out . print ( row . get ( i )); if ( i != row . size () - 1 ) System . out . print ( ' ' ); } System . out . println ( ']' ); } } }
Python #Python program to find all solution of N queen problem #using recursion # Function to check if placement is safe def isSafe ( board currRow currCol ): for i in range ( len ( board )): placedRow = board [ i ] placedCol = i + 1 # Check diagonals if abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == abs ( placedCol - currCol ): return False # Not safe return True # Safe to place # Recursive utility to solve N-Queens def nQueenUtil ( col n board res visited ): # If all queens placed add to res if col > n : res . append ( board . copy ()) return # Try each row in column for row in range ( 1 n + 1 ): # If row not used if not visited [ row ]: # Check safety if isSafe ( board row col ): # Mark row visited [ row ] = True # Place queen board . append ( row ) # Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ) # Backtrack board . pop () visited [ row ] = False # Main N-Queen solver def nQueen ( n ): res = [] board = [] visited = [ False ] * ( n + 1 ) nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ) return res if __name__ == '__main__' : n = 4 res = nQueen ( n ) for row in res : print ( row )
C# //C# program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Check if placement is safe static bool isSafe ( List < int > board int currRow int currCol ){ for ( int i = 0 ; i < board . Count ; i ++ ) { int placedRow = board [ i ]; int placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check diagonals if ( Math . Abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == Math . Abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } return true ; // Safe to place } // Recursive utility to solve static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n List < int > board List < List < int > > res bool [] visited ){ // If all queens placed add to res if ( col > n ) { res . Add ( new List < int > ( board )); return ; } // Try each row in column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; row ++ ) { // If row not used if ( ! visited [ row ]) { // Check safety if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark row visited [ row ] = true ; // Place queen board . Add ( row ); // Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack board . RemoveAt ( board . Count - 1 ); visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Main N-Queen solver static List < List < int >> nQueen ( int n ){ List < List < int > > res = new List < List < int > > (); List < int > board = new List < int > (); bool [] visited = new bool [ n + 1 ]; nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int n = 4 ; List < List < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); foreach ( var temp in res ) { Console . WriteLine ( '[' + String . Join ( ' ' temp ) + ']' ); } } }
JavaScript //JavaScript program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion // Function to check if placement is safe function isSafe ( board currRow currCol ){ for ( let i = 0 ; i < board . length ; i ++ ) { let placedRow = board [ i ]; let placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check diagonals if ( Math . abs ( placedRow - currRow ) === Math . abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } return true ; // Safe to place } // Recursive utility to solve N-Queens function nQueenUtil ( col n board res visited ){ // If all queens placed add to res if ( col > n ) { res . push ([... board ]); return ; } // Try each row in column for ( let row = 1 ; row <= n ; row ++ ) { // If row not used if ( ! visited [ row ]) { // Check safety if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark row visited [ row ] = true ; // Place queen board . push ( row ); // Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack board . pop (); visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Main N-Queen solver function nQueen ( n ){ let res = []; let board = []; let visited = Array ( n + 1 ). fill ( false ); nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } // Driver code let n = 4 ; let res = nQueen ( n ); res . forEach ( row => console . log ( row ));
Ausgabe
[2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]
Zeitkomplexität: O(n!*n) n! um alles zu erzeugen Permutationen und O(n) zur Validierung jeder Permutation.
Hilfsraum: An)
[Erwarteter Ansatz] – Verwendung von Backtracking mit Pruning – O(n!) Zeit und O(n) Raum
Zur Optimierung können wir den oben genannten Ansatz verwenden Zurückkehren mit Beschneiden . Anstatt alle möglichen Permutationen zu generieren, bauen wir die Lösung inkrementell auf und können dabei bei jedem Schritt sicherstellen, dass die Teillösung gültig bleibt. Wenn ein Konflikt auftritt, werden wir sofort einen Rückzieher machen, das hilft vermeiden unnötig Berechnungen .
Schrittweise Umsetzung :
- Beginnen Sie mit der ersten Spalte und versuchen Sie, in jede Reihe eine Königin zu platzieren.
- Behalten Sie Arrays, um zu verfolgen, welche Reihen sind bereits besetzt. Ähnliches gilt für die Nachverfolgung wesentlich Und kleine Diagonalen sind bereits besetzt.
- Wenn eine Königin Platzierung Konflikte mit bestehenden Königinnen überspringen Das Reihe Und zurückgehen die Königin, um das nächste zu versuchen möglich Zeile (Beschneiden und Zurückverfolgen während eines Konflikts).
// C++ program to find all solution of N queen problem by // using backtracking and pruning #include #include #include using namespace std ; // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. void nQueenUtil ( int j int n vector < int > & board vector < bool > & rows vector < bool > & diag1 vector < bool > & diag2 vector < vector < int >> & res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . push_back ( board ); return ; } for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ]) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . push_back ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . pop_back (); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. vector < vector < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { vector < vector < int >> res ; vector < int > board ; // Rows occupied vector < bool > rows ( n + 1 false ); // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) vector < bool > diag1 ( 2 * n + 1 false ); vector < bool > diag2 ( 2 * n + 1 false ); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } int main () { int n = 4 ; vector < vector < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < res . size (); i ++ ) { cout < < '[' ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { cout < < res [ i ][ j ]; if ( j != n - 1 ) cout < < ' ' ; } cout < < '] n ' ; } return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem // using backtracking and pruning import java.util.ArrayList ; import java.util.List ; class GfG { // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. static void nQueenUtil ( int j int n ArrayList < Integer > board boolean [] rows boolean [] diag1 boolean [] diag2 ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . add ( new ArrayList <> ( board )); return ; } for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ] ) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . add ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . remove ( board . size () - 1 ); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nQueen ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = new ArrayList <> (); ArrayList < Integer > board = new ArrayList <> (); // Rows occupied boolean [] rows = new boolean [ n + 1 ] ; // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) boolean [] diag1 = new boolean [ 2 * n + 1 ] ; boolean [] diag2 = new boolean [ 2 * n + 1 ] ; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 4 ; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > solution : res ) { System . out . print ( '[' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < solution . size (); i ++ ) { System . out . print ( solution . get ( i )); if ( i != solution . size () - 1 ) { System . out . print ( ' ' ); } } System . out . println ( ']' ); } } }
Python # Python program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem # using backtracking and pruning def nQueenUtil ( j n board rows diag1 diag2 res ): if j > n : # A solution is found res . append ( board [:]) return for i in range ( 1 n + 1 ): if not rows [ i ] and not diag1 [ i + j ] and not diag2 [ i - j + n ]: # Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = True board . append ( i ) # Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ) # Remove queen (backtrack) board . pop () rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = False def nQueen ( n ): res = [] board = [] # Rows occupied rows = [ False ] * ( n + 1 ) # Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) diag1 = [ False ] * ( 2 * n + 1 ) diag2 = [ False ] * ( 2 * n + 1 ) # Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ) return res if __name__ == '__main__' : n = 4 res = nQueen ( n ) for temp in res : print ( temp )
C# // C# program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem // using backtracking and pruning using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. static void nQueenUtil ( int j int n List < int > board bool [] rows bool [] diag1 bool [] diag2 List < List < int >> res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . Add ( new List < int > ( board )); return ; } for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ]) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . Add ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . RemoveAt ( board . Count - 1 ); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. static List < List < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { List < List < int >> res = new List < List < int >> (); List < int > board = new List < int > (); // Rows occupied bool [] rows = new bool [ n + 1 ]; // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) bool [] diag1 = new bool [ 2 * n + 1 ]; bool [] diag2 = new bool [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int n = 4 ; List < List < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); foreach ( var temp in res ) { Console . WriteLine ( '[' + String . Join ( ' ' temp ) + ']' ); } } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem // using backtracking and pruning // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. function nQueenUtil ( j n board rows diag1 diag2 res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . push ([... board ]); return ; } for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ]) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . push ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . pop (); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. function nQueen ( n ) { const res = []; const board = []; // Rows occupied const rows = Array ( n + 1 ). fill ( false ); // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) const diag1 = Array ( 2 * n + 1 ). fill ( false ); const diag2 = Array ( 2 * n + 1 ). fill ( false ); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } // Driver Code const n = 4 ; const res = nQueen ( n ); res . forEach ( temp => console . log ( temp ));
Ausgabe
[2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]
Zeitkomplexität: O(n!) Zum Generieren aller Permutationen .
Hilfsraum: An)
[Alternativer Ansatz] – Backtracking mithilfe der Bitmaskierung
Um die weiter zu optimieren Zurückverfolgen Ansatz insbesondere für größere Werte von N wir können verwenden Bitmaskierung effizient zu verfolgen besetzt Reihen und Diagonalen. Bitmaskierung können wir ganze Zahlen verwenden ( Reihen ld rd ), um schnell zu verfolgen, welche Reihen und Diagonalen belegt sind bitweise Operationen für schneller Berechnungen. Der Ansatz bleibt derselbe wie oben.
Unten ist angegeben Durchführung:
C++ //C++ program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion #include #include using namespace std ; // Function to check if the current placement is safe bool isSafe ( int row int col int rows int ld int rd int n ) { return ! (( rows >> row ) & 1 ) && ! (( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) && ! (( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations void nQueenUtil ( int col int n vector < int >& board vector < vector < int >>& res int rows int ld int rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . push_back ( board ); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . push_back ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop_back (); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle vector < vector < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { vector < vector < int >> res ; // Current board configuration vector < int > board ; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } int main () { int n = 4 ; vector < vector < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < res . size (); i ++ ) { cout < < '[' ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { cout < < res [ i ][ j ]; if ( j != n - 1 ) cout < < ' ' ; } cout < < '] n ' ; } return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find all solution of N queen problem // using recursion import java.util.* ; class GfG { // Function to check if the current placement is safe static boolean isSafe ( int row int col int rows int ld int rd int n ) { return ! ((( rows >> row ) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ) == 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n ArrayList < Integer > board ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res int rows int ld int rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . add ( new ArrayList <> ( board )); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . add ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . remove ( board . size () - 1 ); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nQueen ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = new ArrayList <> (); // Current board configuration ArrayList < Integer > board = new ArrayList <> (); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 4 ; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > solution : res ) { System . out . print ( '[' ); for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { System . out . print ( solution . get ( j )); if ( j != n - 1 ) System . out . print ( ' ' ); } System . out . println ( ']' ); } } }
Python # Python program to find all solution of N queen problem # using recursion # Function to check if the current placement is safe def isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n ): return not (( rows >> row ) & 1 ) and not (( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) and not (( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ) # Recursive function to generate all possible permutations def nQueenUtil ( col n board res rows ld rd ): # If all queens are placed add into res if col > n : res . append ( board [:]) return # Try placing a queen in each row # of the current column for row in range ( 1 n + 1 ): # Check if it's safe to place the queen if isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n ): # Place the queen board . append ( row ) # Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))) # Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop () # Main function to find all distinct # res to the n-queens puzzle def nQueen ( n ): res = [] # Current board configuration board = [] # Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ) return res if __name__ == '__main__' : n = 4 res = nQueen ( n ) for solution in res : print ( '[' end = '' ) for j in range ( n ): print ( solution [ j ] end = '' ) if j != n - 1 : print ( ' ' end = '' ) print ( ']' )
C# // C# program to find all solution of N queen problem // using recursion using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Function to check if the current placement is safe static bool isSafe ( int row int col int rows int ld int rd int n ) { return ! ((( rows >> row ) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ) == 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n List < int > board List < List < int >> res int rows int ld int rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . Add ( new List < int > ( board )); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . Add ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . RemoveAt ( board . Count - 1 ); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle static List < List < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { List < List < int >> res = new List < List < int >> (); // Current board configuration List < int > board = new List < int > (); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } static void Main () { int n = 4 ; List < List < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); foreach ( var solution in res ) { Console . Write ( '[' ); for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { Console . Write ( solution [ j ]); if ( j != n - 1 ) Console . Write ( ' ' ); } Console . WriteLine ( ']' ); } } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find all solution of N queen problem // using recursion // Function to check if the current placement is safe function isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n ) { return ! (( rows >> row ) & 1 ) && ! (( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) && ! (( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations function nQueenUtil ( col n board res rows ld rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . push ([... board ]); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( let row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . push ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop (); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle function nQueen ( n ) { let res = []; // Current board configuration let board = []; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } // Driver Code let n = 4 ; let res = nQueen ( n ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < res . length ; i ++ ) { process . stdout . write ( '[' ); for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { process . stdout . write ( res [ i ][ j ]. toString ()); if ( j !== n - 1 ) process . stdout . write ( ' ' ); } console . log ( ']' ); }
Ausgabe
[2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]
Zeitkomplexität: O(n!) zur Generierung aller Permutationen.
Raumkomplexität: An)